Yancheng Liang
Chasing Moving Targets with Online Self-Play Reinforcement Learning for Safer Language Models
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Conventional language model (LM) safety alignment relies on a reactive, disjoint procedure: attackers exploit a static model, followed by defensive fine-tuning to patch exposed vulnerabilities. This sequential approach creates a mismatch -- attackers overfit to obsolete defenses, while defenders perpetually lag behind emerging threats. To address this, we propose Self-RedTeam, an online self-play reinforcement learning algorithm where an attacker and defender agent co-evolve through continuous interaction. We cast safety alignment as a two-player zero-sum game, where a single model alternates between attacker and defender roles -- generating adversarial prompts and safeguarding against them -- while a reward LM adjudicates outcomes. This enables dynamic co-adaptation. Grounded in the game-theoretic framework of zero-sum games, we establish a theoretical safety guarantee which motivates the design of our method: if self-play converges to a Nash Equilibrium, the defender will reliably produce safe responses to any adversarial input. Empirically, Self-RedTeam uncovers more diverse attacks (+21.8% SBERT) compared to attackers trained against static defenders and achieves higher robustness on safety benchmarks (e.g., +65.5% on WildJailBreak) than defenders trained against static attackers. We further propose hidden Chain-of-Thought, allowing agents to plan privately, which boosts adversarial diversity and reduces over-refusals. Our results motivate a shift from reactive patching to proactive co-evolution in LM safety training, enabling scalable, autonomous, and robust self-improvement of LMs via multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL).
Improving Human-AI Coordination through Adversarial Training and Generative Models
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:Being able to cooperate with new people is an important component of many economically valuable AI tasks, from household robotics to autonomous driving. However, generalizing to novel humans requires training on data that captures the diversity of human behaviors. Adversarial training is one avenue for searching for such data and ensuring that agents are robust. However, it is difficult to apply in the cooperative setting because adversarial policies intentionally learn to sabotage the task instead of simulating valid cooperation partners. To address this challenge, we propose a novel strategy for overcoming self-sabotage that combines a pre-trained generative model to simulate valid cooperative agent policies with adversarial training to maximize regret. We call our method GOAT: Generative Online Adversarial Training. In this framework, the GOAT dynamically searches for and generates coordination strategies where the learning policy -- the Cooperator agent -- underperforms. GOAT enables better generalization by exposing the Cooperator to various challenging interaction scenarios. We maintain realistic coordination strategies by updating only the generative model's embedding while keeping its parameters frozen, thus avoiding adversarial exploitation. We evaluate GOAT with real human partners, and the results demonstrate state-of-the-art performance on the Overcooked benchmark, highlighting its effectiveness in generalizing to diverse human behaviors.
Cross-environment Cooperation Enables Zero-shot Multi-agent Coordination
Apr 20, 2025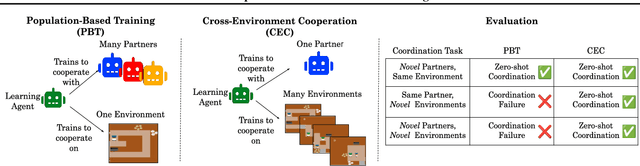
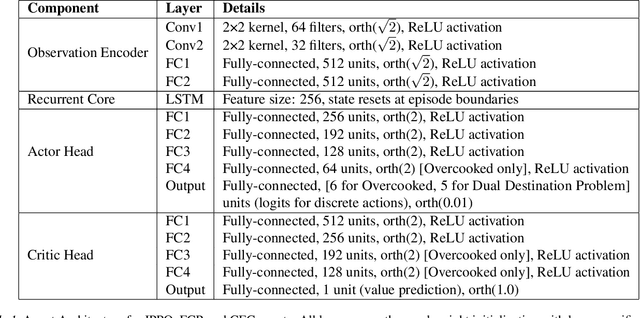
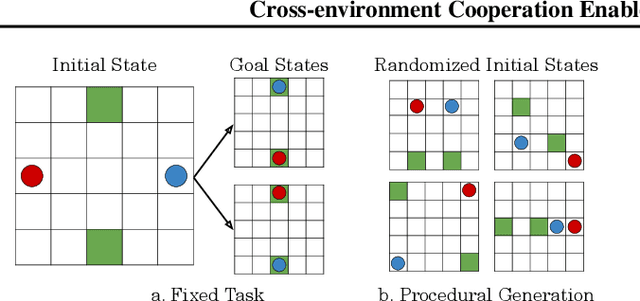
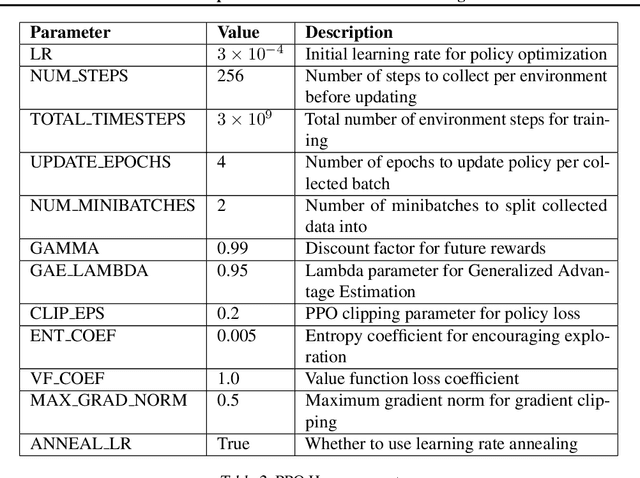
Abstract:Zero-shot coordination (ZSC), the ability to adapt to a new partner in a cooperative task, is a critical component of human-compatible AI. While prior work has focused on training agents to cooperate on a single task, these specialized models do not generalize to new tasks, even if they are highly similar. Here, we study how reinforcement learning on a distribution of environments with a single partner enables learning general cooperative skills that support ZSC with many new partners on many new problems. We introduce two Jax-based, procedural generators that create billions of solvable coordination challenges. We develop a new paradigm called Cross-Environment Cooperation (CEC), and show that it outperforms competitive baselines quantitatively and qualitatively when collaborating with real people. Our findings suggest that learning to collaborate across many unique scenarios encourages agents to develop general norms, which prove effective for collaboration with different partners. Together, our results suggest a new route toward designing generalist cooperative agents capable of interacting with humans without requiring human data.
Learning to Cooperate with Humans using Generative Agents
Nov 21, 2024Abstract:Training agents that can coordinate zero-shot with humans is a key mission in multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL). Current algorithms focus on training simulated human partner policies which are then used to train a Cooperator agent. The simulated human is produced either through behavior cloning over a dataset of human cooperation behavior, or by using MARL to create a population of simulated agents. However, these approaches often struggle to produce a Cooperator that can coordinate well with real humans, since the simulated humans fail to cover the diverse strategies and styles employed by people in the real world. We show \emph{learning a generative model of human partners} can effectively address this issue. Our model learns a latent variable representation of the human that can be regarded as encoding the human's unique strategy, intention, experience, or style. This generative model can be flexibly trained from any (human or neural policy) agent interaction data. By sampling from the latent space, we can use the generative model to produce different partners to train Cooperator agents. We evaluate our method -- \textbf{G}enerative \textbf{A}gent \textbf{M}odeling for \textbf{M}ulti-agent \textbf{A}daptation (GAMMA) -- on Overcooked, a challenging cooperative cooking game that has become a standard benchmark for zero-shot coordination. We conduct an evaluation with real human teammates, and the results show that GAMMA consistently improves performance, whether the generative model is trained on simulated populations or human datasets. Further, we propose a method for posterior sampling from the generative model that is biased towards the human data, enabling us to efficiently improve performance with only a small amount of expensive human interaction data.
MESA: Cooperative Meta-Exploration in Multi-Agent Learning through Exploiting State-Action Space Structure
May 01, 2024



Abstract:Multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) algorithms often struggle to find strategies close to Pareto optimal Nash Equilibrium, owing largely to the lack of efficient exploration. The problem is exacerbated in sparse-reward settings, caused by the larger variance exhibited in policy learning. This paper introduces MESA, a novel meta-exploration method for cooperative multi-agent learning. It learns to explore by first identifying the agents' high-rewarding joint state-action subspace from training tasks and then learning a set of diverse exploration policies to "cover" the subspace. These trained exploration policies can be integrated with any off-policy MARL algorithm for test-time tasks. We first showcase MESA's advantage in a multi-step matrix game. Furthermore, experiments show that with learned exploration policies, MESA achieves significantly better performance in sparse-reward tasks in several multi-agent particle environments and multi-agent MuJoCo environments, and exhibits the ability to generalize to more challenging tasks at test time.
Fictitious Cross-Play: Learning Global Nash Equilibrium in Mixed Cooperative-Competitive Games
Oct 05, 2023Abstract:Self-play (SP) is a popular multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) framework for solving competitive games, where each agent optimizes policy by treating others as part of the environment. Despite the empirical successes, the theoretical properties of SP-based methods are limited to two-player zero-sum games. However, for mixed cooperative-competitive games where agents on the same team need to cooperate with each other, we can show a simple counter-example where SP-based methods cannot converge to a global Nash equilibrium (NE) with high probability. Alternatively, Policy-Space Response Oracles (PSRO) is an iterative framework for learning NE, where the best responses w.r.t. previous policies are learned in each iteration. PSRO can be directly extended to mixed cooperative-competitive settings by jointly learning team best responses with all convergence properties unchanged. However, PSRO requires repeatedly training joint policies from scratch till convergence, which makes it hard to scale to complex games. In this work, we develop a novel algorithm, Fictitious Cross-Play (FXP), which inherits the benefits from both frameworks. FXP simultaneously trains an SP-based main policy and a counter population of best response policies. The main policy is trained by fictitious self-play and cross-play against the counter population, while the counter policies are trained as the best responses to the main policy's past versions. We validate our method in matrix games and show that FXP converges to global NEs while SP methods fail. We also conduct experiments in a gridworld domain, where FXP achieves higher Elo ratings and lower exploitabilities than baselines, and a more challenging football game, where FXP defeats SOTA models with over 94% win rate.
DeRisk: An Effective Deep Learning Framework for Credit Risk Prediction over Real-World Financial Data
Aug 07, 2023


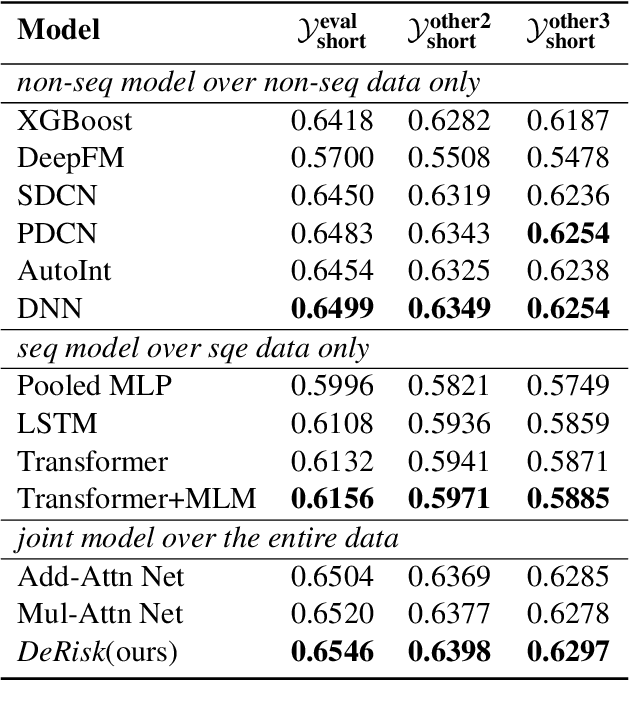
Abstract:Despite the tremendous advances achieved over the past years by deep learning techniques, the latest risk prediction models for industrial applications still rely on highly handtuned stage-wised statistical learning tools, such as gradient boosting and random forest methods. Different from images or languages, real-world financial data are high-dimensional, sparse, noisy and extremely imbalanced, which makes deep neural network models particularly challenging to train and fragile in practice. In this work, we propose DeRisk, an effective deep learning risk prediction framework for credit risk prediction on real-world financial data. DeRisk is the first deep risk prediction model that outperforms statistical learning approaches deployed in our company's production system. We also perform extensive ablation studies on our method to present the most critical factors for the empirical success of DeRisk.
A Benchmark for Low-Switching-Cost Reinforcement Learning
Dec 13, 2021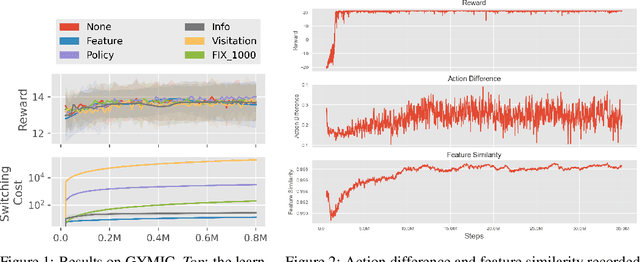
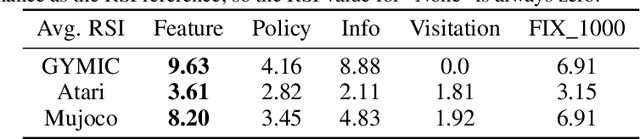
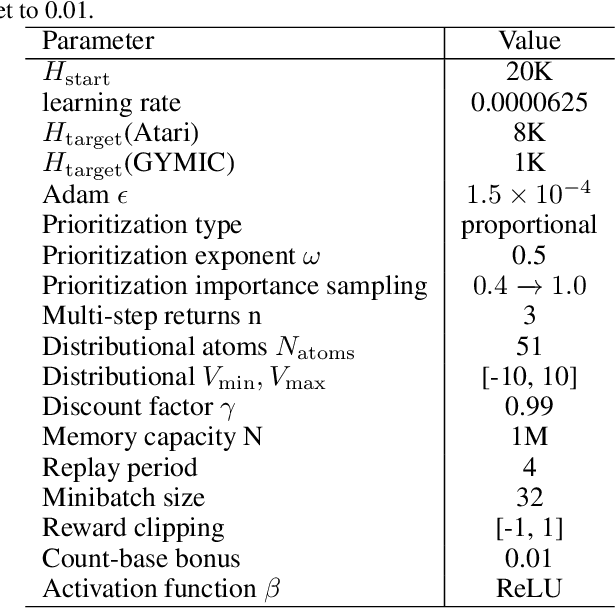
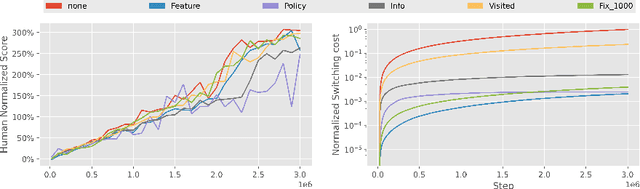
Abstract:A ubiquitous requirement in many practical reinforcement learning (RL) applications, including medical treatment, recommendation system, education and robotics, is that the deployed policy that actually interacts with the environment cannot change frequently. Such an RL setting is called low-switching-cost RL, i.e., achieving the highest reward while reducing the number of policy switches during training. Despite the recent trend of theoretical studies aiming to design provably efficient RL algorithms with low switching costs, none of the existing approaches have been thoroughly evaluated in popular RL testbeds. In this paper, we systematically studied a wide collection of policy-switching approaches, including theoretically guided criteria, policy-difference-based methods, and non-adaptive baselines. Through extensive experiments on a medical treatment environment, the Atari games, and robotic control tasks, we present the first empirical benchmark for low-switching-cost RL and report novel findings on how to decrease the switching cost while maintain a similar sample efficiency to the case without the low-switching-cost constraint. We hope this benchmark could serve as a starting point for developing more practically effective low-switching-cost RL algorithms. We release our code and complete results in https://sites.google.com/view/low-switching-cost-rl.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge