A Benchmark for Low-Switching-Cost Reinforcement Learning
Paper and Code
Dec 13, 2021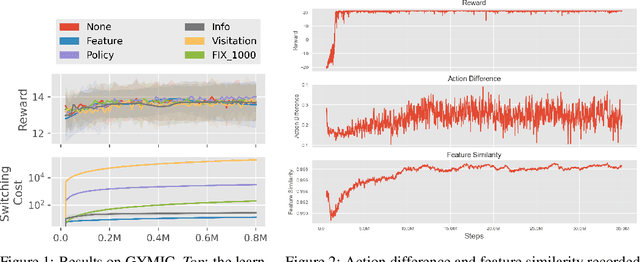
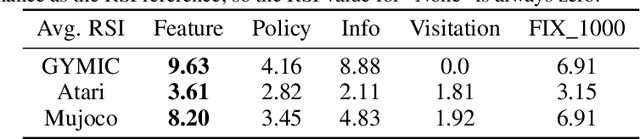
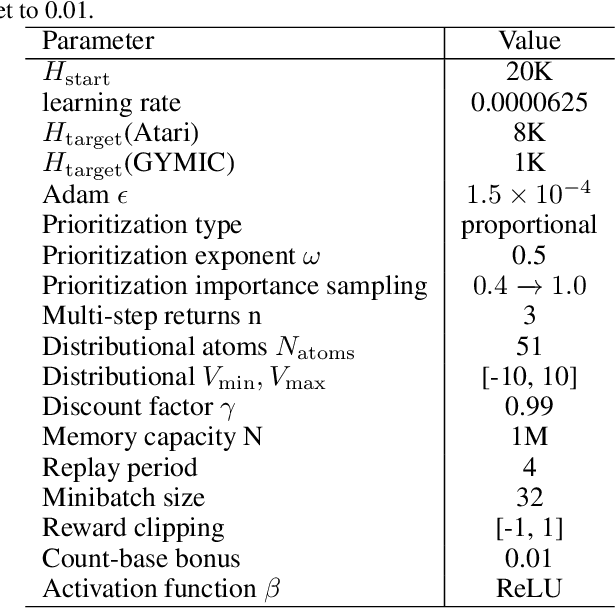
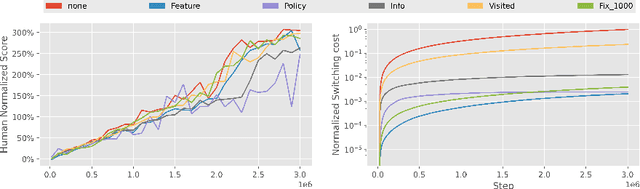
A ubiquitous requirement in many practical reinforcement learning (RL) applications, including medical treatment, recommendation system, education and robotics, is that the deployed policy that actually interacts with the environment cannot change frequently. Such an RL setting is called low-switching-cost RL, i.e., achieving the highest reward while reducing the number of policy switches during training. Despite the recent trend of theoretical studies aiming to design provably efficient RL algorithms with low switching costs, none of the existing approaches have been thoroughly evaluated in popular RL testbeds. In this paper, we systematically studied a wide collection of policy-switching approaches, including theoretically guided criteria, policy-difference-based methods, and non-adaptive baselines. Through extensive experiments on a medical treatment environment, the Atari games, and robotic control tasks, we present the first empirical benchmark for low-switching-cost RL and report novel findings on how to decrease the switching cost while maintain a similar sample efficiency to the case without the low-switching-cost constraint. We hope this benchmark could serve as a starting point for developing more practically effective low-switching-cost RL algorithms. We release our code and complete results in https://sites.google.com/view/low-switching-cost-rl.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge