Xuecheng Wu
Dolphin-v2: Universal Document Parsing via Scalable Anchor Prompting
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Document parsing has garnered widespread attention as vision-language models (VLMs) advance OCR capabilities. However, the field remains fragmented across dozens of specialized models with varying strengths, forcing users to navigate complex model selection and limiting system scalability. Moreover, existing two-stage approaches depend on axis-aligned bounding boxes for layout detection, failing to handle distorted or photographed documents effectively. To this end, we present Dolphin-v2, a two-stage document image parsing model that substantially improves upon the original Dolphin. In the first stage, Dolphin-v2 jointly performs document type classification (digital-born versus photographed) alongside layout analysis. For digital-born documents, it conducts finer-grained element detection with reading order prediction. In the second stage, we employ a hybrid parsing strategy: photographed documents are parsed holistically as complete pages to handle geometric distortions, while digital-born documents undergo element-wise parallel parsing guided by the detected layout anchors, enabling efficient content extraction. Compared with the original Dolphin, Dolphin-v2 introduces several crucial enhancements: (1) robust parsing of photographed documents via holistic page-level understanding, (2) finer-grained element detection (21 categories) with semantic attribute extraction such as author information and document metadata, and (3) code block recognition with indentation preservation, which existing systems typically lack. Comprehensive evaluations are conducted on DocPTBench, OmniDocBench, and our self-constructed RealDoc-160 benchmark. The results demonstrate substantial improvements: +14.78 points overall on the challenging OmniDocBench and 91% error reduction on photographed documents, while maintaining efficient inference through parallel processing.
RePose: A Real-Time 3D Human Pose Estimation and Biomechanical Analysis Framework for Rehabilitation
Jan 02, 2026Abstract:We propose a real-time 3D human pose estimation and motion analysis method termed RePose for rehabilitation training. It is capable of real-time monitoring and evaluation of patients'motion during rehabilitation, providing immediate feedback and guidance to assist patients in executing rehabilitation exercises correctly. Firstly, we introduce a unified pipeline for end-to-end real-time human pose estimation and motion analysis using RGB video input from multiple cameras which can be applied to the field of rehabilitation training. The pipeline can help to monitor and correct patients'actions, thus aiding them in regaining muscle strength and motor functions. Secondly, we propose a fast tracking method for medical rehabilitation scenarios with multiple-person interference, which requires less than 1ms for tracking for a single frame. Additionally, we modify SmoothNet for real-time posture estimation, effectively reducing pose estimation errors and restoring the patient's true motion state, making it visually smoother. Finally, we use Unity platform for real-time monitoring and evaluation of patients' motion during rehabilitation, and to display the muscle stress conditions to assist patients with their rehabilitation training.
Disentangling Hardness from Noise: An Uncertainty-Driven Model-Agnostic Framework for Long-Tailed Remote Sensing Classification
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:Long-Tailed distributions are pervasive in remote sensing due to the inherently imbalanced occurrence of grounded objects. However, a critical challenge remains largely overlooked, i.e., disentangling hard tail data samples from noisy ambiguous ones. Conventional methods often indiscriminately emphasize all low-confidence samples, leading to overfitting on noisy data. To bridge this gap, building upon Evidential Deep Learning, we propose a model-agnostic uncertainty-aware framework termed DUAL, which dynamically disentangles prediction uncertainty into Epistemic Uncertainty (EU) and Aleatoric Uncertainty (AU). Specifically, we introduce EU as an indicator of sample scarcity to guide a reweighting strategy for hard-to-learn tail samples, while leveraging AU to quantify data ambiguity, employing an adaptive label smoothing mechanism to suppress the impact of noise. Extensive experiments on multiple datasets across various backbones demonstrate the effectiveness and generalization of our framework, surpassing strong baselines such as TGN and SADE. Ablation studies provide further insights into the crucial choices of our design.
Beyond Pixel Simulation: Pathology Image Generation via Diagnostic Semantic Tokens and Prototype Control
Dec 24, 2025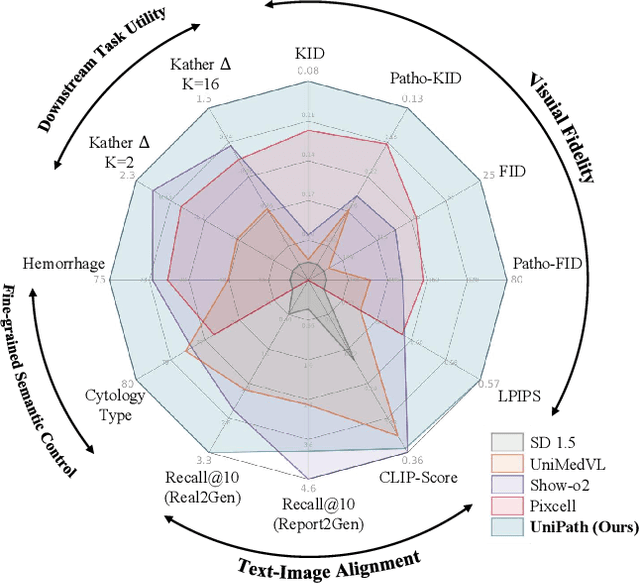
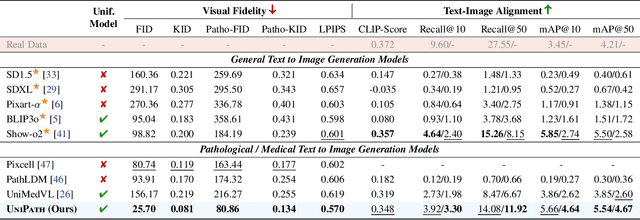
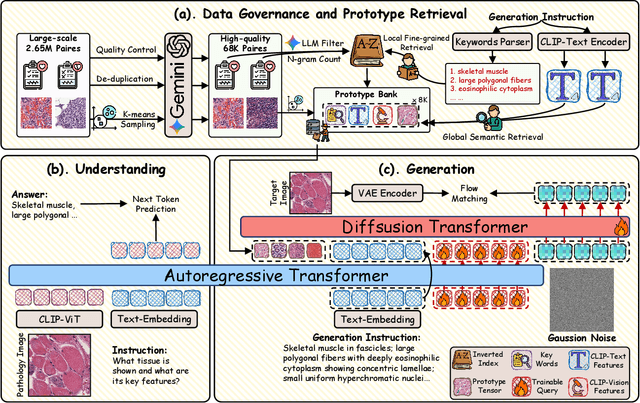
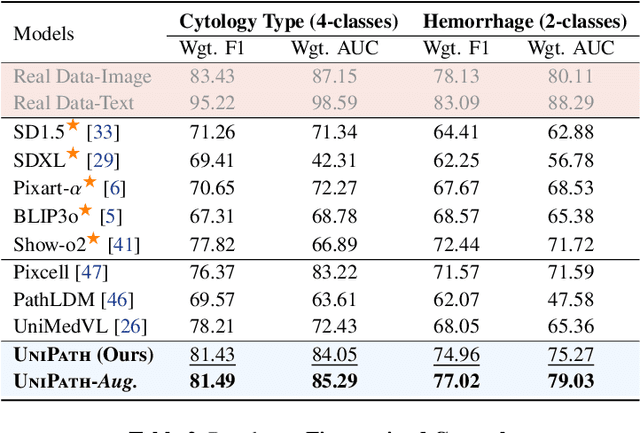
Abstract:In computational pathology, understanding and generation have evolved along disparate paths: advanced understanding models already exhibit diagnostic-level competence, whereas generative models largely simulate pixels. Progress remains hindered by three coupled factors: the scarcity of large, high-quality image-text corpora; the lack of precise, fine-grained semantic control, which forces reliance on non-semantic cues; and terminological heterogeneity, where diverse phrasings for the same diagnostic concept impede reliable text conditioning. We introduce UniPath, a semantics-driven pathology image generation framework that leverages mature diagnostic understanding to enable controllable generation. UniPath implements Multi-Stream Control: a Raw-Text stream; a High-Level Semantics stream that uses learnable queries to a frozen pathology MLLM to distill paraphrase-robust Diagnostic Semantic Tokens and to expand prompts into diagnosis-aware attribute bundles; and a Prototype stream that affords component-level morphological control via a prototype bank. On the data front, we curate a 2.65M image-text corpus and a finely annotated, high-quality 68K subset to alleviate data scarcity. For a comprehensive assessment, we establish a four-tier evaluation hierarchy tailored to pathology. Extensive experiments demonstrate UniPath's SOTA performance, including a Patho-FID of 80.9 (51% better than the second-best) and fine-grained semantic control achieving 98.7% of the real-image. The meticulously curated datasets, complete source code, and pre-trained model weights developed in this study will be made openly accessible to the public.
DARTs: A Dual-Path Robust Framework for Anomaly Detection in High-Dimensional Multivariate Time Series
Dec 14, 2025Abstract:Multivariate time series anomaly detection (MTSAD) aims to accurately identify and localize complex abnormal patterns in the large-scale industrial control systems. While existing approaches excel in recognizing the distinct patterns under the low-dimensional scenarios, they often fail to robustly capture long-range spatiotemporal dependencies when learning representations from the high-dimensional noisy time series. To address these limitations, we propose DARTs, a robust long short-term dual-path framework with window-aware spatiotemporal soft fusion mechanism, which can be primarily decomposed into three complementary components. Specifically, in the short-term path, we introduce a Multi-View Sparse Graph Learner and a Diffusion Multi-Relation Graph Unit that collaborate to adaptively capture hierarchical discriminative short-term spatiotemporal patterns in the high-noise time series. While in the long-term path, we design a Multi-Scale Spatiotemporal Graph Constructor to model salient long-term dynamics within the high-dimensional representation space. Finally, a window-aware spatiotemporal soft-fusion mechanism is introduced to filter the residual noise while seamlessly integrating anomalous patterns. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experimental results across mainstream datasets demonstrate the superiority and robustness of our proposed DARTs. A series of ablation studies are also conducted to explore the crucial design factors of our proposed components. Our code and model will be made publicly open soon.
Improving Multimodal Sentiment Analysis via Modality Optimization and Dynamic Primary Modality Selection
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Sentiment Analysis (MSA) aims to predict sentiment from language, acoustic, and visual data in videos. However, imbalanced unimodal performance often leads to suboptimal fused representations. Existing approaches typically adopt fixed primary modality strategies to maximize dominant modality advantages, yet fail to adapt to dynamic variations in modality importance across different samples. Moreover, non-language modalities suffer from sequential redundancy and noise, degrading model performance when they serve as primary inputs. To address these issues, this paper proposes a modality optimization and dynamic primary modality selection framework (MODS). First, a Graph-based Dynamic Sequence Compressor (GDC) is constructed, which employs capsule networks and graph convolution to reduce sequential redundancy in acoustic/visual modalities. Then, we develop a sample-adaptive Primary Modality Selector (MSelector) for dynamic dominance determination. Finally, a Primary-modality-Centric Cross-Attention (PCCA) module is designed to enhance dominant modalities while facilitating cross-modal interaction. Extensive experiments on four benchmark datasets demonstrate that MODS outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving superior performance by effectively balancing modality contributions and eliminating redundant noise.
MUSE: MCTS-Driven Red Teaming Framework for Enhanced Multi-Turn Dialogue Safety in Large Language Models
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:As large language models~(LLMs) become widely adopted, ensuring their alignment with human values is crucial to prevent jailbreaks where adversaries manipulate models to produce harmful content. While most defenses target single-turn attacks, real-world usage often involves multi-turn dialogues, exposing models to attacks that exploit conversational context to bypass safety measures. We introduce MUSE, a comprehensive framework tackling multi-turn jailbreaks from both attack and defense angles. For attacks, we propose MUSE-A, a method that uses frame semantics and heuristic tree search to explore diverse semantic trajectories. For defense, we present MUSE-D, a fine-grained safety alignment approach that intervenes early in dialogues to reduce vulnerabilities. Extensive experiments on various models show that MUSE effectively identifies and mitigates multi-turn vulnerabilities. Code is available at \href{https://github.com/yansiyu02/MUSE}{https://github.com/yansiyu02/MUSE}.
End4: End-to-end Denoising Diffusion for Diffusion-Based Inpainting Detection
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:The powerful generative capabilities of diffusion models have significantly advanced the field of image synthesis, enhancing both full image generation and inpainting-based image editing. Despite their remarkable advancements, diffusion models also raise concerns about potential misuse for malicious purposes. However, existing approaches struggle to identify images generated by diffusion-based inpainting models, even when similar inpainted images are included in their training data. To address this challenge, we propose a novel detection method based on End-to-end denoising diffusion (End4). Specifically, End4 designs a denoising reconstruction model to improve the alignment degree between the latent spaces of the reconstruction and detection processes, thus reconstructing features that are more conducive to detection. Meanwhile, it leverages a Scale-aware Pyramid-like Fusion Module (SPFM) that refines local image features under the guidance of attention pyramid layers at different scales, enhancing feature discriminability. Additionally, to evaluate detection performance on inpainted images, we establish a comprehensive benchmark comprising images generated from five distinct masked regions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our End4 effectively generalizes to unseen masking patterns and remains robust under various perturbations. Our code and dataset will be released soon.
TiKMiX: Take Data Influence into Dynamic Mixture for Language Model Pre-training
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:The data mixture used in the pre-training of a language model is a cornerstone of its final performance. However, a static mixing strategy is suboptimal, as the model's learning preferences for various data domains shift dynamically throughout training. Crucially, observing these evolving preferences in a computationally efficient manner remains a significant challenge. To address this, we propose TiKMiX, a method that dynamically adjusts the data mixture according to the model's evolving preferences. TiKMiX introduces Group Influence, an efficient metric for evaluating the impact of data domains on the model. This metric enables the formulation of the data mixing problem as a search for an optimal, influence-maximizing distribution. We solve this via two approaches: TiKMiX-D for direct optimization, and TiKMiX-M, which uses a regression model to predict a superior mixture. We trained models with different numbers of parameters, on up to 1 trillion tokens. TiKMiX-D exceeds the performance of state-of-the-art methods like REGMIX while using just 20% of the computational resources. TiKMiX-M leads to an average performance gain of 2% across 9 downstream benchmarks. Our experiments reveal that a model's data preferences evolve with training progress and scale, and we demonstrate that dynamically adjusting the data mixture based on Group Influence, a direct measure of these preferences, significantly improves performance by mitigating the underdigestion of data seen with static ratios.
A Trustworthy Method for Multimodal Emotion Recognition
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Existing emotion recognition methods mainly focus on enhancing performance by employing complex deep models, typically resulting in significantly higher model complexity. Although effective, it is also crucial to ensure the reliability of the final decision, especially for noisy, corrupted and out-of-distribution data. To this end, we propose a novel emotion recognition method called trusted emotion recognition (TER), which utilizes uncertainty estimation to calculate the confidence value of predictions. TER combines the results from multiple modalities based on their confidence values to output the trusted predictions. We also provide a new evaluation criterion to assess the reliability of predictions. Specifically, we incorporate trusted precision and trusted recall to determine the trusted threshold and formulate the trusted Acc. and trusted F1 score to evaluate the model's trusted performance. The proposed framework combines the confidence module that accordingly endows the model with reliability and robustness against possible noise or corruption. The extensive experimental results validate the effectiveness of our proposed model. The TER achieves state-of-the-art performance on the Music-video, achieving 82.40% Acc. In terms of trusted performance, TER outperforms other methods on the IEMOCAP and Music-video, achieving trusted F1 scores of 0.7511 and 0.9035, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge