Xuan Ding
ONRW: Optimizing inversion noise for high-quality and robust watermark
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Watermarking methods have always been effective means of protecting intellectual property, yet they face significant challenges. Although existing deep learning-based watermarking systems can hide watermarks in images with minimal impact on image quality, they often lack robustness when encountering image corruptions during transmission, which undermines their practical application value. To this end, we propose a high-quality and robust watermark framework based on the diffusion model. Our method first converts the clean image into inversion noise through a null-text optimization process, and after optimizing the inversion noise in the latent space, it produces a high-quality watermarked image through an iterative denoising process of the diffusion model. The iterative denoising process serves as a powerful purification mechanism, ensuring both the visual quality of the watermarked image and enhancing the robustness of the watermark against various corruptions. To prevent the optimizing of inversion noise from distorting the original semantics of the image, we specifically introduced self-attention constraints and pseudo-mask strategies. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the superior performance of our method against various image corruptions. In particular, our method outperforms the stable signature method by an average of 10\% across 12 different image transformations on COCO datasets. Our codes are available at https://github.com/920927/ONRW.
AgentsEval: Clinically Faithful Evaluation of Medical Imaging Reports via Multi-Agent Reasoning
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Evaluating the clinical correctness and reasoning fidelity of automatically generated medical imaging reports remains a critical yet unresolved challenge. Existing evaluation methods often fail to capture the structured diagnostic logic that underlies radiological interpretation, resulting in unreliable judgments and limited clinical relevance. We introduce AgentsEval, a multi-agent stream reasoning framework that emulates the collaborative diagnostic workflow of radiologists. By dividing the evaluation process into interpretable steps including criteria definition, evidence extraction, alignment, and consistency scoring, AgentsEval provides explicit reasoning traces and structured clinical feedback. We also construct a multi-domain perturbation-based benchmark covering five medical report datasets with diverse imaging modalities and controlled semantic variations. Experimental results demonstrate that AgentsEval delivers clinically aligned, semantically faithful, and interpretable evaluations that remain robust under paraphrastic, semantic, and stylistic perturbations. This framework represents a step toward transparent and clinically grounded assessment of medical report generation systems, fostering trustworthy integration of large language models into clinical practice.
SpotVLM: Cloud-edge Collaborative Real-time VLM based on Context Transfer
Aug 18, 2025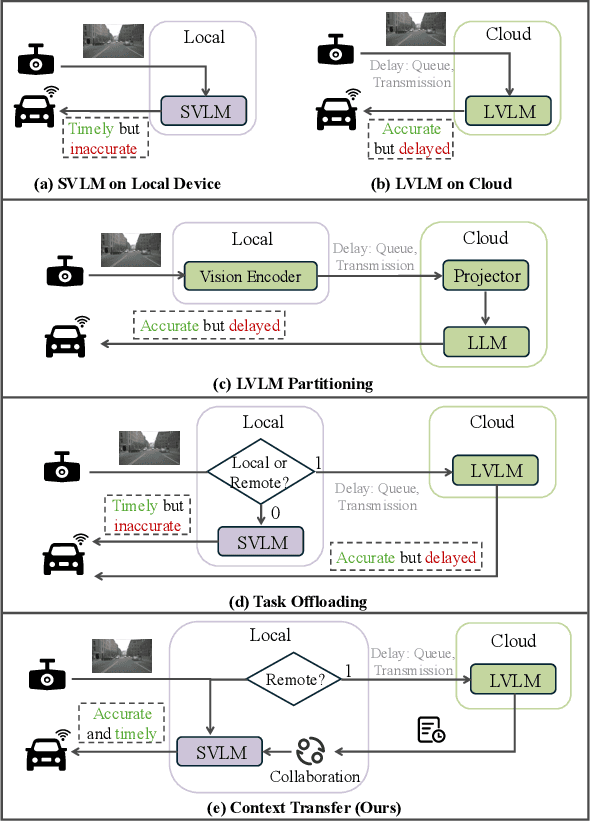
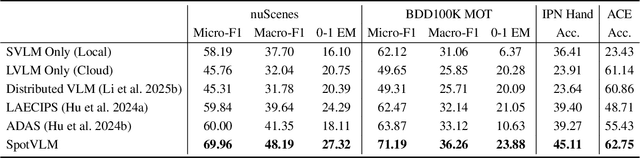
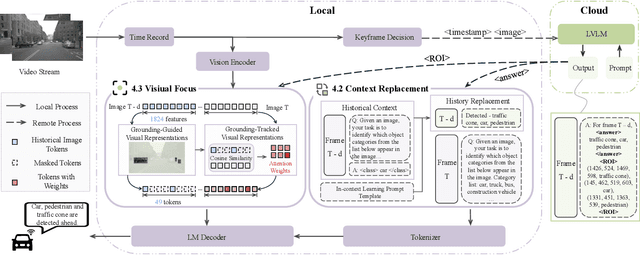
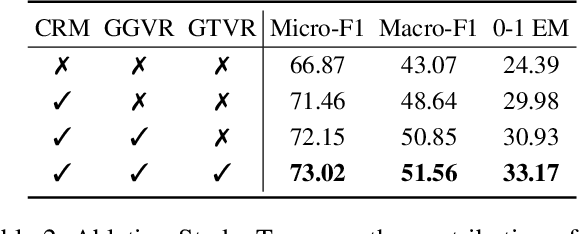
Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) are increasingly deployed in real-time applications such as autonomous driving and human-computer interaction, which demand fast and reliable responses based on accurate perception. To meet these requirements, existing systems commonly employ cloud-edge collaborative architectures, such as partitioned Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) or task offloading strategies between Large and Small Vision-Language Models (SVLMs). However, these methods fail to accommodate cloud latency fluctuations and overlook the full potential of delayed but accurate LVLM responses. In this work, we propose a novel cloud-edge collaborative paradigm for VLMs, termed Context Transfer, which treats the delayed outputs of LVLMs as historical context to provide real-time guidance for SVLMs inference. Based on this paradigm, we design SpotVLM, which incorporates both context replacement and visual focus modules to refine historical textual input and enhance visual grounding consistency. Extensive experiments on three real-time vision tasks across four datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework. The new paradigm lays the groundwork for more effective and latency-aware collaboration strategies in future VLM systems.
SpecOffload: Unlocking Latent GPU Capacity for LLM Inference on Resource-Constrained Devices
May 15, 2025Abstract:Efficient LLM inference on resource-constrained devices presents significant challenges in compute and memory utilization. Due to limited GPU memory, existing systems offload model weights to CPU memory, incurring substantial I/O overhead between the CPU and GPU. This leads to two major inefficiencies: (1) GPU cores are underutilized, often remaining idle while waiting for data to be loaded; and (2) GPU memory has low impact on performance, as reducing its capacity has minimal effect on overall throughput.In this paper, we propose SpecOffload, a high-throughput inference engine that embeds speculative decoding into offloading. Our key idea is to unlock latent GPU resources for storing and executing a draft model used for speculative decoding, thus accelerating inference at near-zero additional cost. To support this, we carefully orchestrate the interleaved execution of target and draft models in speculative decoding within the offloading pipeline, and propose a planner to manage tensor placement and select optimal parameters. Compared to the best baseline, SpecOffload improves GPU core utilization by 4.49x and boosts inference throughput by 2.54x. Our code is available at https://github.com/MobiSense/SpecOffload .
A Sliding Layer Merging Method for Efficient Depth-Wise Pruning in LLMs
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Compared to width-wise pruning, depth-wise pruning can significantly accelerate inference in resource-constrained scenarios. Howerver, treating the entire Transformer layer as the minimum pruning unit may degrade model performance by indiscriminately discarding the entire information of the layer. This paper reveals the "Patch-like" feature relationship between layers in large language models by analyzing the correlation of the outputs of different layers in the reproducing kernel Hilbert space. Building on this observation, we proposes a sliding layer merging method that dynamically selects and fuses consecutive layers from top to bottom according to a pre-defined similarity threshold, thereby simplifying the model structure while maintaining its performance. Extensive experiments on LLMs with various architectures and different parameter scales show that our method outperforms existing pruning techniques in both zero-shot inference performance and retraining recovery quality after pruning. In particular, in the experiment with 35\% pruning on the Vicuna-7B model, our method achieved a 1.654\% improvement in average performance on zero-shot tasks compared to the existing method. Moreover, we further reveal the potential of combining depth pruning with width pruning to enhance the pruning effect. Our codes are available at https://github.com/920927/SLM-a-sliding-layer-merging-method.
An Improved Artificial Fish Swarm Algorithm for Solving the Problem of Investigation Path Planning
Oct 20, 2023



Abstract:Informationization is a prevailing trend in today's world. The increasing demand for information in decision-making processes poses significant challenges for investigation activities, particularly in terms of effectively allocating limited resources to plan investigation programs. This paper addresses the investigation path planning problem by formulating it as a multi-traveling salesman problem (MTSP). Our objective is to minimize costs, and to achieve this, we propose a chaotic artificial fish swarm algorithm based on multiple population differential evolution (DE-CAFSA). To overcome the limitations of the artificial fish swarm algorithm, such as low optimization accuracy and the inability to consider global and local information, we incorporate adaptive field of view and step size adjustments, replace random behavior with the 2-opt operation, and introduce chaos theory and sub-optimal solutions to enhance optimization accuracy and search performance. Additionally, we integrate the differential evolution algorithm to create a hybrid algorithm that leverages the complementary advantages of both approaches. Experimental results demonstrate that DE-CAFSA outperforms other algorithms on various public datasets of different sizes, as well as showcasing excellent performance on the examples proposed in this study.
AIM 2019 Challenge on Image Demoireing: Methods and Results
Nov 08, 2019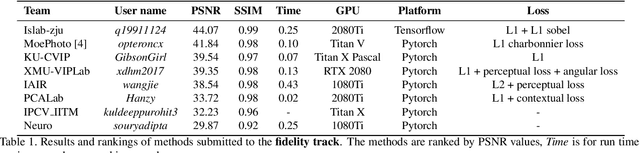
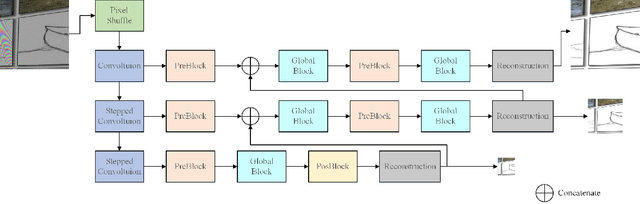
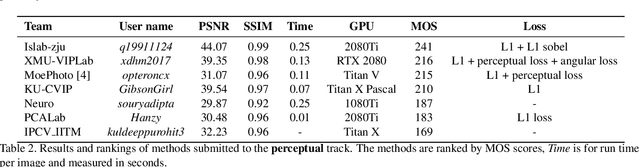
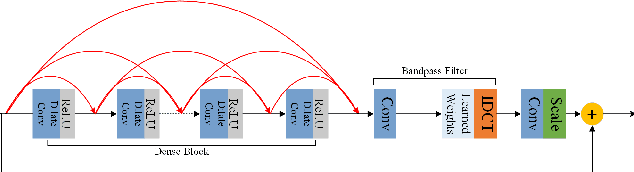
Abstract:This paper reviews the first-ever image demoireing challenge that was part of the Advances in Image Manipulation (AIM) workshop, held in conjunction with ICCV 2019. This paper describes the challenge, and focuses on the proposed solutions and their results. Demoireing is a difficult task of removing moire patterns from an image to reveal an underlying clean image. A new dataset, called LCDMoire was created for this challenge, and consists of 10,200 synthetically generated image pairs (moire and clean ground truth). The challenge was divided into 2 tracks. Track 1 targeted fidelity, measuring the ability of demoire methods to obtain a moire-free image compared with the ground truth, while Track 2 examined the perceptual quality of demoire methods. The tracks had 60 and 39 registered participants, respectively. A total of eight teams competed in the final testing phase. The entries span the current the state-of-the-art in the image demoireing problem.
Automated Detecting and Placing Road Objects from Street-level Images
Sep 17, 2019



Abstract:Navigation services utilized by autonomous vehicles or ordinary users require the availability of detailed information about road-related objects and their geolocations, especially at road intersections. However, these road intersections are mainly represented as point elements without detailed information, or are even not available in current versions of crowdsourced mapping databases including OpenStreetMap(OSM). This study develops an approach to automatically detect road objects and place them to right location from street-level images. Our processing pipeline relies on two convolutional neural networks: the first segments the images, while the second detects and classifies the specific objects. Moreover, to locate the detected objects, we establish an attributed topological binary tree(ATBT) based on urban grammar for each image to depict the coherent relations of topologies, attributes and semantics of the road objects. Then the ATBT is further matched with map features on OSM to determine the right placed location. The proposed method has been applied to a case study in Berlin, Germany. We validate the effectiveness of our method on two object classes: traffic signs and traffic lights. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approach provides near-precise localization results in terms of completeness and positional accuracy. Among many potential applications, the output may be combined with other sources of data to guide autonomous vehicles
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge