Xiu Yan
ONRW: Optimizing inversion noise for high-quality and robust watermark
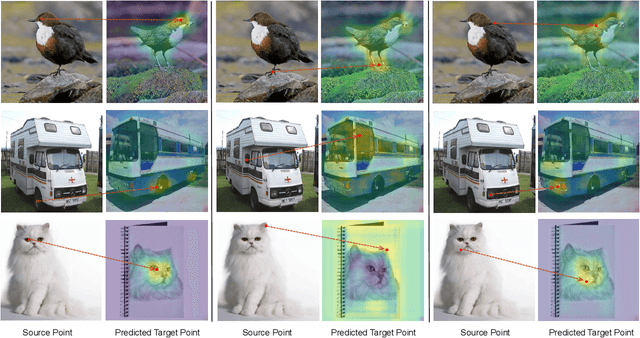
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Watermarking methods have always been effective means of protecting intellectual property, yet they face significant challenges. Although existing deep learning-based watermarking systems can hide watermarks in images with minimal impact on image quality, they often lack robustness when encountering image corruptions during transmission, which undermines their practical application value. To this end, we propose a high-quality and robust watermark framework based on the diffusion model. Our method first converts the clean image into inversion noise through a null-text optimization process, and after optimizing the inversion noise in the latent space, it produces a high-quality watermarked image through an iterative denoising process of the diffusion model. The iterative denoising process serves as a powerful purification mechanism, ensuring both the visual quality of the watermarked image and enhancing the robustness of the watermark against various corruptions. To prevent the optimizing of inversion noise from distorting the original semantics of the image, we specifically introduced self-attention constraints and pseudo-mask strategies. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the superior performance of our method against various image corruptions. In particular, our method outperforms the stable signature method by an average of 10\% across 12 different image transformations on COCO datasets. Our codes are available at https://github.com/920927/ONRW.
Enhancing Few-shot CLIP with Semantic-Aware Fine-Tuning
Nov 09, 2023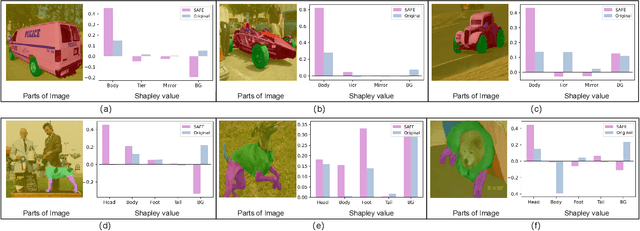
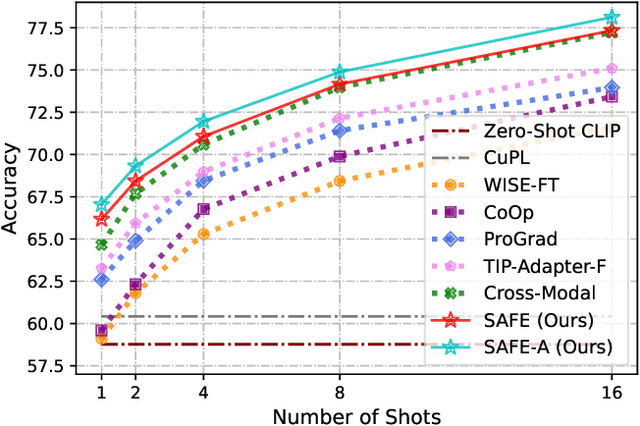
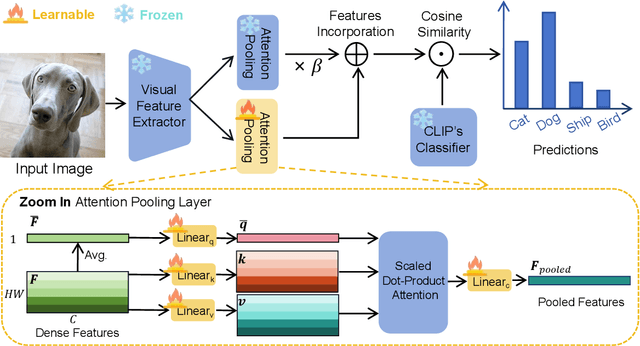
Abstract:Learning generalized representations from limited training samples is crucial for applying deep neural networks in low-resource scenarios. Recently, methods based on Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) have exhibited promising performance in few-shot adaptation tasks. To avoid catastrophic forgetting and overfitting caused by few-shot fine-tuning, existing works usually freeze the parameters of CLIP pre-trained on large-scale datasets, overlooking the possibility that some parameters might not be suitable for downstream tasks. To this end, we revisit CLIP's visual encoder with a specific focus on its distinctive attention pooling layer, which performs a spatial weighted-sum of the dense feature maps. Given that dense feature maps contain meaningful semantic information, and different semantics hold varying importance for diverse downstream tasks (such as prioritizing semantics like ears and eyes in pet classification tasks rather than side mirrors), using the same weighted-sum operation for dense features across different few-shot tasks might not be appropriate. Hence, we propose fine-tuning the parameters of the attention pooling layer during the training process to encourage the model to focus on task-specific semantics. In the inference process, we perform residual blending between the features pooled by the fine-tuned and the original attention pooling layers to incorporate both the few-shot knowledge and the pre-trained CLIP's prior knowledge. We term this method as Semantic-Aware FinE-tuning (SAFE). SAFE is effective in enhancing the conventional few-shot CLIP and is compatible with the existing adapter approach (termed SAFE-A).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge