Xibin Zhao
Adversarial Contrastive Learning for LLM Quantization Attacks
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Model quantization is critical for deploying large language models (LLMs) on resource-constrained hardware, yet recent work has revealed severe security risks that benign LLMs in full precision may exhibit malicious behaviors after quantization. In this paper, we propose Adversarial Contrastive Learning (ACL), a novel gradient-based quantization attack that achieves superior attack effectiveness by explicitly maximizing the gap between benign and harmful responses probabilities. ACL formulates the attack objective as a triplet-based contrastive loss, and integrates it with a projected gradient descent two-stage distributed fine-tuning strategy to ensure stable and efficient optimization. Extensive experiments demonstrate ACL's remarkable effectiveness, achieving attack success rates of 86.00% for over-refusal, 97.69% for jailbreak, and 92.40% for advertisement injection, substantially outperforming state-of-the-art methods by up to 44.67%, 18.84%, and 50.80%, respectively.
Advanced Global Wildfire Activity Modeling with Hierarchical Graph ODE
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Wildfires, as an integral component of the Earth system, are governed by a complex interplay of atmospheric, oceanic, and terrestrial processes spanning a vast range of spatiotemporal scales. Modeling their global activity on large timescales is therefore a critical yet challenging task. While deep learning has recently achieved significant breakthroughs in global weather forecasting, its potential for global wildfire behavior prediction remains underexplored. In this work, we reframe this problem and introduce the Hierarchical Graph ODE (HiGO), a novel framework designed to learn the multi-scale, continuous-time dynamics of wildfires. Specifically, we represent the Earth system as a multi-level graph hierarchy and propose an adaptive filtering message passing mechanism for both intra- and inter-level information flow, enabling more effective feature extraction and fusion. Furthermore, we incorporate GNN-parameterized Neural ODE modules at multiple levels to explicitly learn the continuous dynamics inherent to each scale. Through extensive experiments on the SeasFire Cube dataset, we demonstrate that HiGO significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines on long-range wildfire forecasting. Moreover, its continuous-time predictions exhibit strong observational consistency, highlighting its potential for real-world applications.
Graph-Based Cross-Domain Knowledge Distillation for Cross-Dataset Text-to-Image Person Retrieval
Jan 25, 2025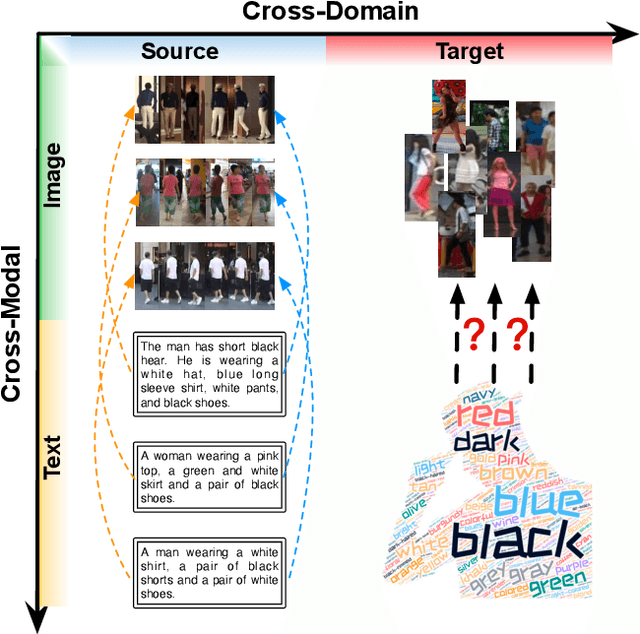
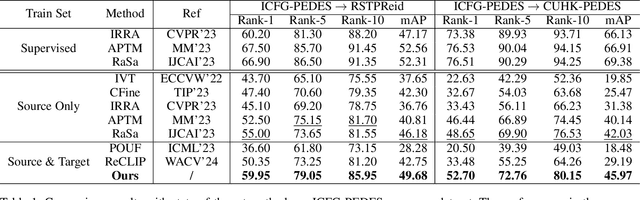
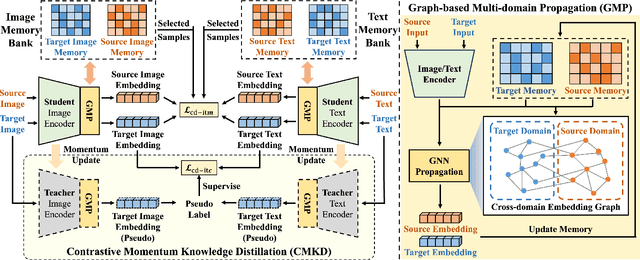
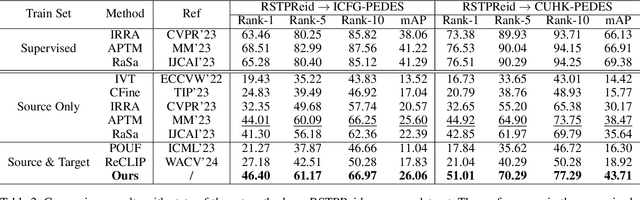
Abstract:Video surveillance systems are crucial components for ensuring public safety and management in smart city. As a fundamental task in video surveillance, text-to-image person retrieval aims to retrieve the target person from an image gallery that best matches the given text description. Most existing text-to-image person retrieval methods are trained in a supervised manner that requires sufficient labeled data in the target domain. However, it is common in practice that only unlabeled data is available in the target domain due to the difficulty and cost of data annotation, which limits the generalization of existing methods in practical application scenarios. To address this issue, we propose a novel unsupervised domain adaptation method, termed Graph-Based Cross-Domain Knowledge Distillation (GCKD), to learn the cross-modal feature representation for text-to-image person retrieval in a cross-dataset scenario. The proposed GCKD method consists of two main components. Firstly, a graph-based multi-modal propagation module is designed to bridge the cross-domain correlation among the visual and textual samples. Secondly, a contrastive momentum knowledge distillation module is proposed to learn the cross-modal feature representation using the online knowledge distillation strategy. By jointly optimizing the two modules, the proposed method is able to achieve efficient performance for cross-dataset text-to-image person retrieval. acExtensive experiments on three publicly available text-to-image person retrieval datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed GCKD method, which consistently outperforms the state-of-the-art baselines.
GLADformer: A Mixed Perspective for Graph-level Anomaly Detection
Jun 02, 2024Abstract:Graph-Level Anomaly Detection (GLAD) aims to distinguish anomalous graphs within a graph dataset. However, current methods are constrained by their receptive fields, struggling to learn global features within the graphs. Moreover, most contemporary methods are based on spatial domain and lack exploration of spectral characteristics. In this paper, we propose a multi-perspective hybrid graph-level anomaly detector namely GLADformer, consisting of two key modules. Specifically, we first design a Graph Transformer module with global spectrum enhancement, which ensures balanced and resilient parameter distributions by fusing global features and spectral distribution characteristics. Furthermore, to uncover local anomalous attributes, we customize a band-pass spectral GNN message passing module that further enhances the model's generalization capability. Through comprehensive experiments on ten real-world datasets from multiple domains, we validate the effectiveness and robustness of GLADformer. This demonstrates that GLADformer outperforms current state-of-the-art models in graph-level anomaly detection, particularly in effectively capturing global anomaly representations and spectral characteristics.
Revisiting Graph-based Fraud Detection in Sight of Heterophily and Spectrum
Dec 11, 2023



Abstract:Graph-based fraud detection (GFD) can be regarded as a challenging semi-supervised node binary classification task. In recent years, Graph Neural Networks(GNN) have been widely applied to GFD, characterizing the anomalous possibility of a node by aggregating neighbor information. However, fraud graphs are inherently heterophilic, thus most of GNNs perform poorly due to their assumption of homophily. In addition, due to the existence of heterophily and class imbalance problem, the existing models do not fully utilize the precious node label information. To address the above issues, this paper proposes a semi-supervised GNN-based fraud detector SEC-GFD. This detector includes a hybrid filtering module and a local environmental constraint module, the two modules are utilized to solve heterophily and label utilization problem respectively. The first module starts from the perspective of the spectral domain, and solves the heterophily problem to a certain extent. Specifically, it divides the spectrum into multiple mixed frequency bands according to the correlation between spectrum energy distribution and heterophily. Then in order to make full use of the node label information, a local environmental constraint module is adaptively designed. The comprehensive experimental results on four real-world fraud detection datasets show that SEC-GFD outperforms other competitive graph-based fraud detectors.
Hypergraph-Guided Disentangled Spectrum Transformer Networks for Near-Infrared Facial Expression Recognition
Dec 10, 2023



Abstract:With the strong robusticity on illumination variations, near-infrared (NIR) can be an effective and essential complement to visible (VIS) facial expression recognition in low lighting or complete darkness conditions. However, facial expression recognition (FER) from NIR images presents more challenging problem than traditional FER due to the limitations imposed by the data scale and the difficulty of extracting discriminative features from incomplete visible lighting contents. In this paper, we give the first attempt to deep NIR facial expression recognition and proposed a novel method called near-infrared facial expression transformer (NFER-Former). Specifically, to make full use of the abundant label information in the field of VIS, we introduce a Self-Attention Orthogonal Decomposition mechanism that disentangles the expression information and spectrum information from the input image, so that the expression features can be extracted without the interference of spectrum variation. We also propose a Hypergraph-Guided Feature Embedding method that models some key facial behaviors and learns the structure of the complex correlations between them, thereby alleviating the interference of inter-class similarity. Additionally, we have constructed a large NIR-VIS Facial Expression dataset that includes 360 subjects to better validate the efficiency of NFER-Former. Extensive experiments and ablation studies show that NFER-Former significantly improves the performance of NIR FER and achieves state-of-the-art results on the only two available NIR FER datasets, Oulu-CASIA and Large-HFE.
Multi-Energy Guided Image Translation with Stochastic Differential Equations for Near-Infrared Facial Expression Recognition
Dec 10, 2023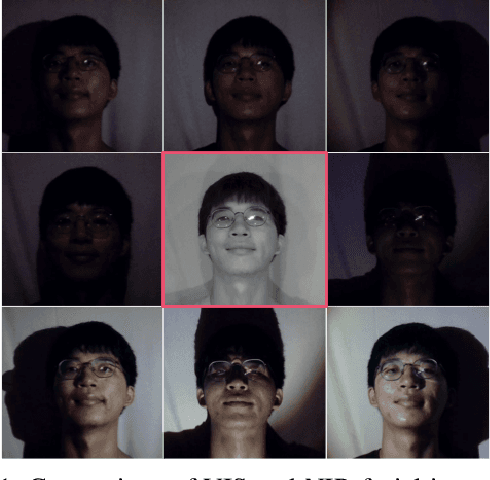
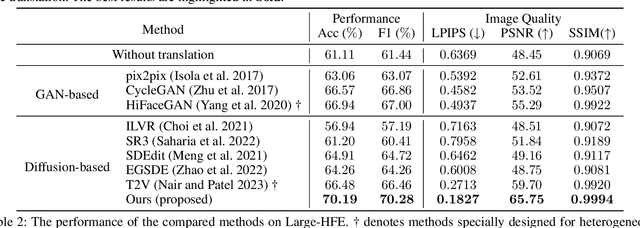
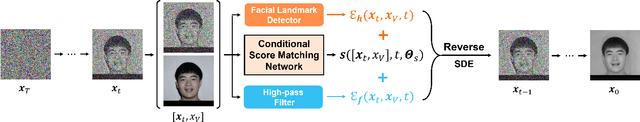
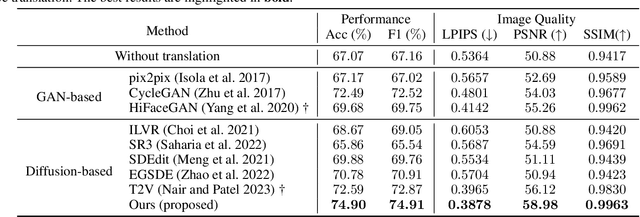
Abstract:Illumination variation has been a long-term challenge in real-world facial expression recognition(FER). Under uncontrolled or non-visible light conditions, Near-infrared (NIR) can provide a simple and alternative solution to obtain high-quality images and supplement the geometric and texture details that are missing in the visible domain. Due to the lack of existing large-scale NIR facial expression datasets, directly extending VIS FER methods to the NIR spectrum may be ineffective. Additionally, previous heterogeneous image synthesis methods are restricted by low controllability without prior task knowledge. To tackle these issues, we present the first approach, called for NIR-FER Stochastic Differential Equations (NFER-SDE), that transforms face expression appearance between heterogeneous modalities to the overfitting problem on small-scale NIR data. NFER-SDE is able to take the whole VIS source image as input and, together with domain-specific knowledge, guide the preservation of modality-invariant information in the high-frequency content of the image. Extensive experiments and ablation studies show that NFER-SDE significantly improves the performance of NIR FER and achieves state-of-the-art results on the only two available NIR FER datasets, Oulu-CASIA and Large-HFE.
Few-shot Message-Enhanced Contrastive Learning for Graph Anomaly Detection
Nov 17, 2023



Abstract:Graph anomaly detection plays a crucial role in identifying exceptional instances in graph data that deviate significantly from the majority. It has gained substantial attention in various domains of information security, including network intrusion, financial fraud, and malicious comments, et al. Existing methods are primarily developed in an unsupervised manner due to the challenge in obtaining labeled data. For lack of guidance from prior knowledge in unsupervised manner, the identified anomalies may prove to be data noise or individual data instances. In real-world scenarios, a limited batch of labeled anomalies can be captured, making it crucial to investigate the few-shot problem in graph anomaly detection. Taking advantage of this potential, we propose a novel few-shot Graph Anomaly Detection model called FMGAD (Few-shot Message-Enhanced Contrastive-based Graph Anomaly Detector). FMGAD leverages a self-supervised contrastive learning strategy within and across views to capture intrinsic and transferable structural representations. Furthermore, we propose the Deep-GNN message-enhanced reconstruction module, which extensively exploits the few-shot label information and enables long-range propagation to disseminate supervision signals to deeper unlabeled nodes. This module in turn assists in the training of self-supervised contrastive learning. Comprehensive experimental results on six real-world datasets demonstrate that FMGAD can achieve better performance than other state-of-the-art methods, regardless of artificially injected anomalies or domain-organic anomalies.
Exploring Global and Local Information for Anomaly Detection with Normal Samples
Jun 03, 2023



Abstract:Anomaly detection aims to detect data that do not conform to regular patterns, and such data is also called outliers. The anomalies to be detected are often tiny in proportion, containing crucial information, and are suitable for application scenes like intrusion detection, fraud detection, fault diagnosis, e-commerce platforms, et al. However, in many realistic scenarios, only the samples following normal behavior are observed, while we can hardly obtain any anomaly information. To address such problem, we propose an anomaly detection method GALDetector which is combined of global and local information based on observed normal samples. The proposed method can be divided into a three-stage method. Firstly, the global similar normal scores and the local sparsity scores of unlabeled samples are computed separately. Secondly, potential anomaly samples are separated from the unlabeled samples corresponding to these two scores and corresponding weights are assigned to the selected samples. Finally, a weighted anomaly detector is trained by loads of samples, then the detector is utilized to identify else anomalies. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed method, we conducted experiments on three categories of real-world datasets from diverse domains, and experimental results show that our method achieves better performance when compared with other state-of-the-art methods.
TBDetector:Transformer-Based Detector for Advanced Persistent Threats with Provenance Graph
Apr 06, 2023



Abstract:APT detection is difficult to detect due to the long-term latency, covert and slow multistage attack patterns of Advanced Persistent Threat (APT). To tackle these issues, we propose TBDetector, a transformer-based advanced persistent threat detection method for APT attack detection. Considering that provenance graphs provide rich historical information and have the powerful attacks historic correlation ability to identify anomalous activities, TBDetector employs provenance analysis for APT detection, which summarizes long-running system execution with space efficiency and utilizes transformer with self-attention based encoder-decoder to extract long-term contextual features of system states to detect slow-acting attacks. Furthermore, we further introduce anomaly scores to investigate the anomaly of different system states, where each state is calculated with an anomaly score corresponding to its similarity score and isolation score. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed method, we have conducted experiments on five public datasets, i.e., streamspot, cadets, shellshock, clearscope, and wget_baseline. Experimental results and comparisons with state-of-the-art methods have exhibited better performance of our proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge