Zewen Wang
Multi-Energy Guided Image Translation with Stochastic Differential Equations for Near-Infrared Facial Expression Recognition
Dec 10, 2023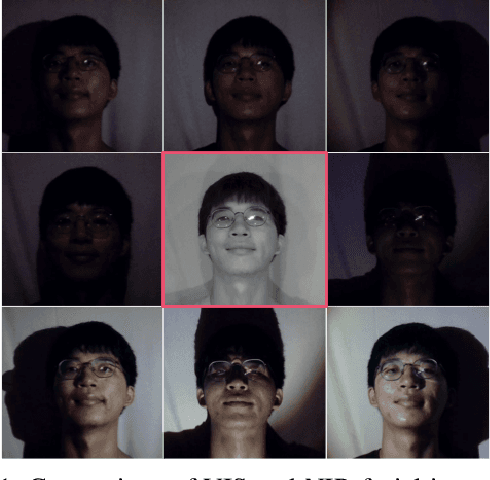
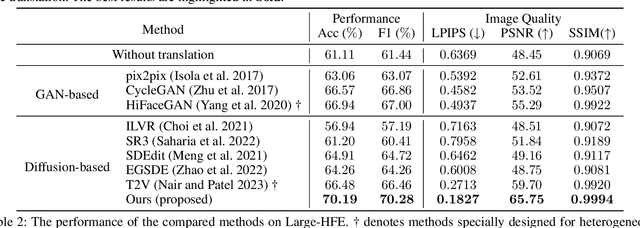
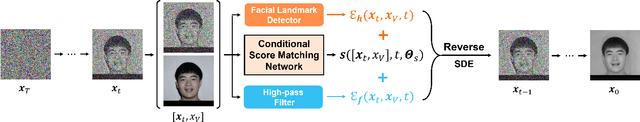
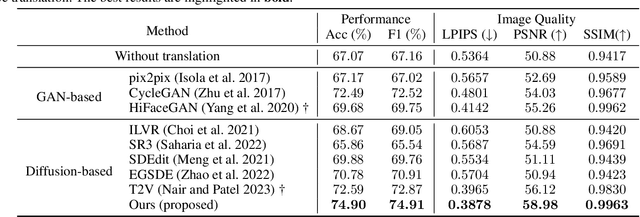
Abstract:Illumination variation has been a long-term challenge in real-world facial expression recognition(FER). Under uncontrolled or non-visible light conditions, Near-infrared (NIR) can provide a simple and alternative solution to obtain high-quality images and supplement the geometric and texture details that are missing in the visible domain. Due to the lack of existing large-scale NIR facial expression datasets, directly extending VIS FER methods to the NIR spectrum may be ineffective. Additionally, previous heterogeneous image synthesis methods are restricted by low controllability without prior task knowledge. To tackle these issues, we present the first approach, called for NIR-FER Stochastic Differential Equations (NFER-SDE), that transforms face expression appearance between heterogeneous modalities to the overfitting problem on small-scale NIR data. NFER-SDE is able to take the whole VIS source image as input and, together with domain-specific knowledge, guide the preservation of modality-invariant information in the high-frequency content of the image. Extensive experiments and ablation studies show that NFER-SDE significantly improves the performance of NIR FER and achieves state-of-the-art results on the only two available NIR FER datasets, Oulu-CASIA and Large-HFE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge