Xiaowen Liu
Strategic priorities for transformative progress in advancing biology with proteomics and artificial intelligence
Feb 21, 2025

Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming scientific research, including proteomics. Advances in mass spectrometry (MS)-based proteomics data quality, diversity, and scale, combined with groundbreaking AI techniques, are unlocking new challenges and opportunities in biological discovery. Here, we highlight key areas where AI is driving innovation, from data analysis to new biological insights. These include developing an AI-friendly ecosystem for proteomics data generation, sharing, and analysis; improving peptide and protein identification and quantification; characterizing protein-protein interactions and protein complexes; advancing spatial and perturbation proteomics; integrating multi-omics data; and ultimately enabling AI-empowered virtual cells.
A Privacy-Preserving Domain Adversarial Federated learning for multi-site brain functional connectivity analysis
Feb 03, 2025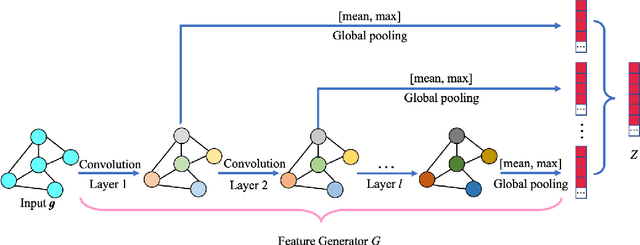
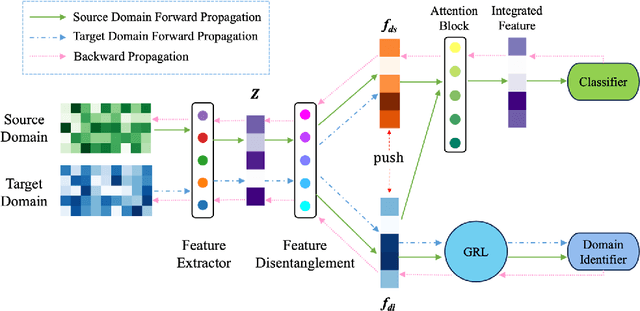
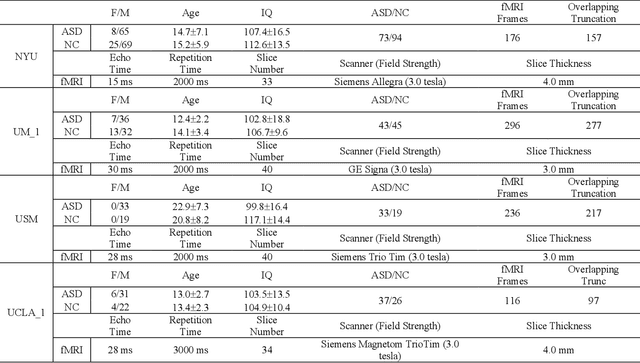
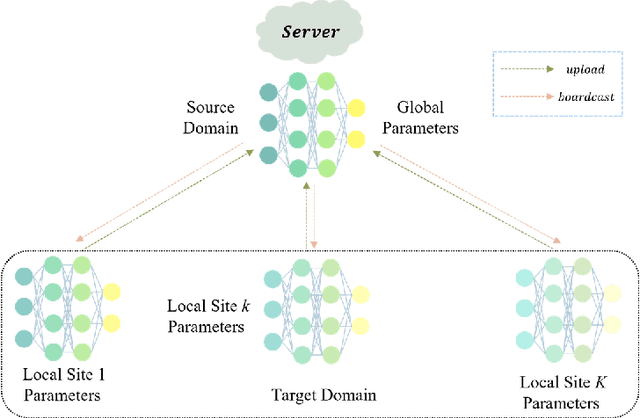
Abstract:Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rs-fMRI) and its derived functional connectivity networks (FCNs) have become critical for understanding neurological disorders. However, collaborative analyses and the generalizability of models still face significant challenges due to privacy regulations and the non-IID (non-independent and identically distributed) property of multiple data sources. To mitigate these difficulties, we propose Domain Adversarial Federated Learning (DAFed), a novel federated deep learning framework specifically designed for non-IID fMRI data analysis in multi-site settings. DAFed addresses these challenges through feature disentanglement, decomposing the latent feature space into domain-invariant and domain-specific components, to ensure robust global learning while preserving local data specificity. Furthermore, adversarial training facilitates effective knowledge transfer between labeled and unlabeled datasets, while a contrastive learning module enhances the global representation of domain-invariant features. We evaluated DAFed on the diagnosis of ASD and further validated its generalizability in the classification of AD, demonstrating its superior classification accuracy compared to state-of-the-art methods. Additionally, an enhanced Score-CAM module identifies key brain regions and functional connectivity significantly associated with ASD and MCI, respectively, uncovering shared neurobiological patterns across sites. These findings highlight the potential of DAFed to advance multi-site collaborative research in neuroimaging while protecting data confidentiality.
Fast LiDAR Data Generation with Rectified Flows
Dec 03, 2024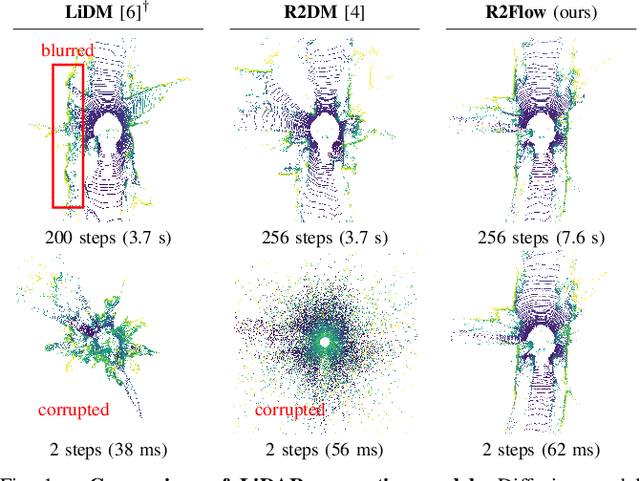
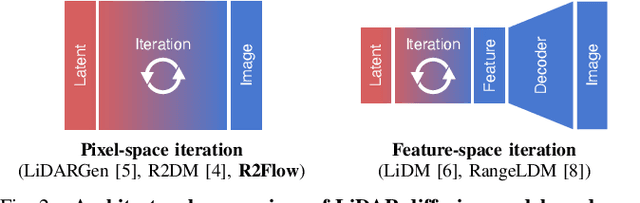

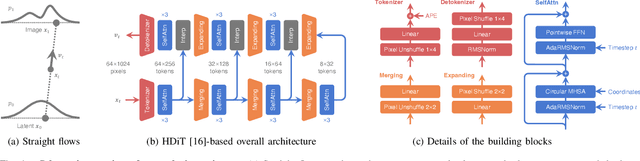
Abstract:Building LiDAR generative models holds promise as powerful data priors for restoration, scene manipulation, and scalable simulation in autonomous mobile robots. In recent years, approaches using diffusion models have emerged, significantly improving training stability and generation quality. Despite the success of diffusion models, generating high-quality samples requires numerous iterations of running neural networks, and the increasing computational cost can pose a barrier to robotics applications. To address this challenge, this paper presents R2Flow, a fast and high-fidelity generative model for LiDAR data. Our method is based on rectified flows that learn straight trajectories, simulating data generation with much fewer sampling steps against diffusion models. We also propose a efficient Transformer-based model architecture for processing the image representation of LiDAR range and reflectance measurements. Our experiments on the unconditional generation of the KITTI-360 dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in terms of both efficiency and quality.
HSFusion: A high-level vision task-driven infrared and visible image fusion network via semantic and geometric domain transformation
Jul 14, 2024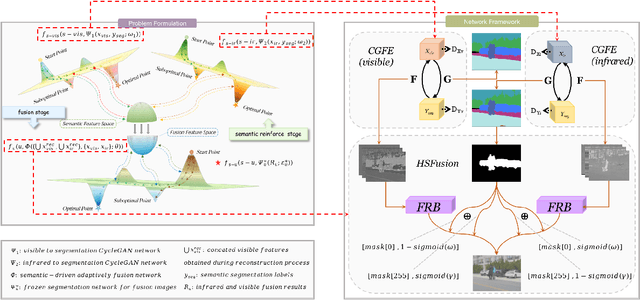
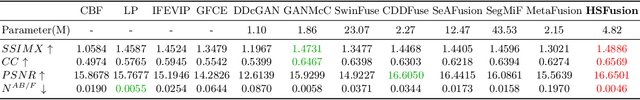
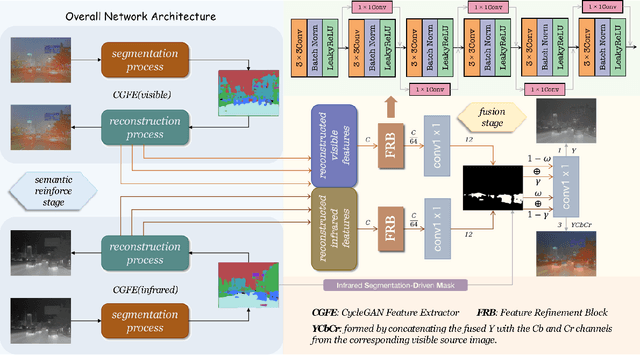
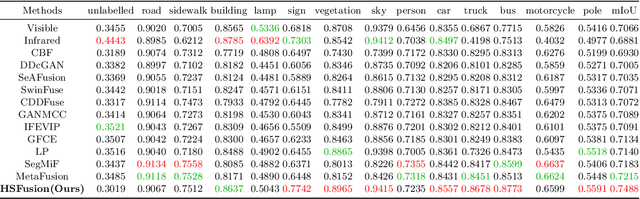
Abstract:Infrared and visible image fusion has been developed from vision perception oriented fusion methods to strategies which both consider the vision perception and high-level vision task. However, the existing task-driven methods fail to address the domain gap between semantic and geometric representation. To overcome these issues, we propose a high-level vision task-driven infrared and visible image fusion network via semantic and geometric domain transformation, terms as HSFusion. Specifically, to minimize the gap between semantic and geometric representation, we design two separate domain transformation branches by CycleGAN framework, and each includes two processes: the forward segmentation process and the reverse reconstruction process. CycleGAN is capable of learning domain transformation patterns, and the reconstruction process of CycleGAN is conducted under the constraint of these patterns. Thus, our method can significantly facilitate the integration of semantic and geometric information and further reduces the domain gap. In fusion stage, we integrate the infrared and visible features that extracted from the reconstruction process of two seperate CycleGANs to obtain the fused result. These features, containing varying proportions of semantic and geometric information, can significantly enhance the high level vision tasks. Additionally, we generate masks based on segmentation results to guide the fusion task. These masks can provide semantic priors, and we design adaptive weights for two distinct areas in the masks to facilitate image fusion. Finally, we conducted comparative experiments between our method and eleven other state-of-the-art methods, demonstrating that our approach surpasses others in both visual appeal and semantic segmentation task.
CTC-based Non-autoregressive Speech Translation
May 27, 2023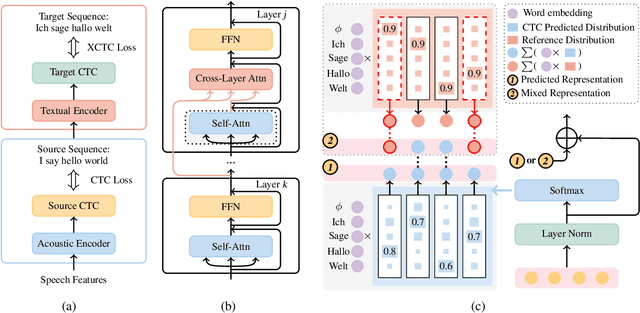
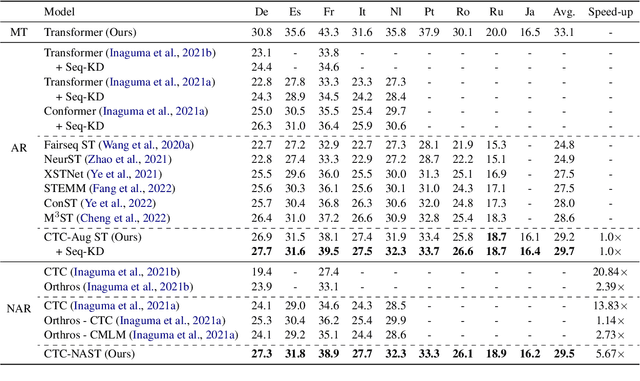
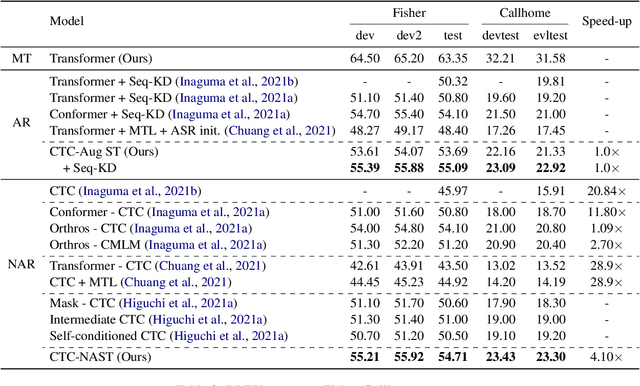
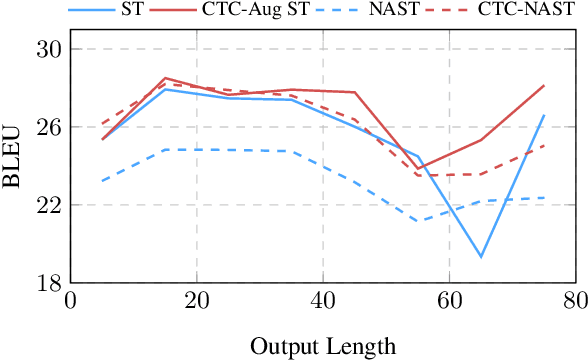
Abstract:Combining end-to-end speech translation (ST) and non-autoregressive (NAR) generation is promising in language and speech processing for their advantages of less error propagation and low latency. In this paper, we investigate the potential of connectionist temporal classification (CTC) for non-autoregressive speech translation (NAST). In particular, we develop a model consisting of two encoders that are guided by CTC to predict the source and target texts, respectively. Introducing CTC into NAST on both language sides has obvious challenges: 1) the conditional independent generation somewhat breaks the interdependency among tokens, and 2) the monotonic alignment assumption in standard CTC does not hold in translation tasks. In response, we develop a prediction-aware encoding approach and a cross-layer attention approach to address these issues. We also use curriculum learning to improve convergence of training. Experiments on the MuST-C ST benchmarks show that our NAST model achieves an average BLEU score of 29.5 with a speed-up of 5.67$\times$, which is comparable to the autoregressive counterpart and even outperforms the previous best result of 0.9 BLEU points.
The NiuTrans End-to-End Speech Translation System for IWSLT 2021 Offline Task
Jul 08, 2021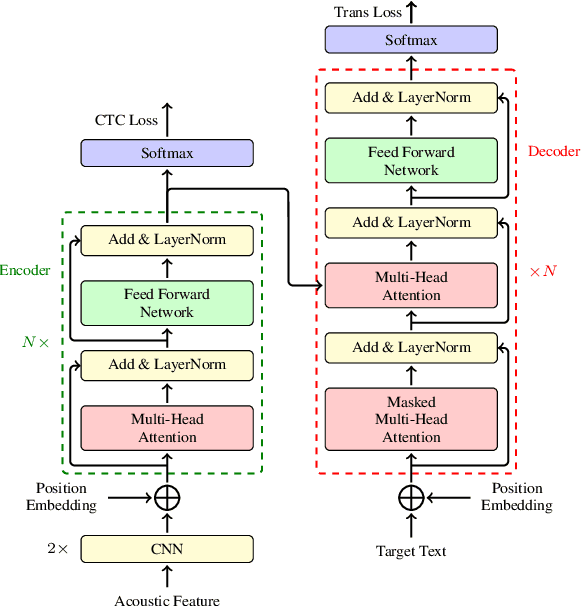
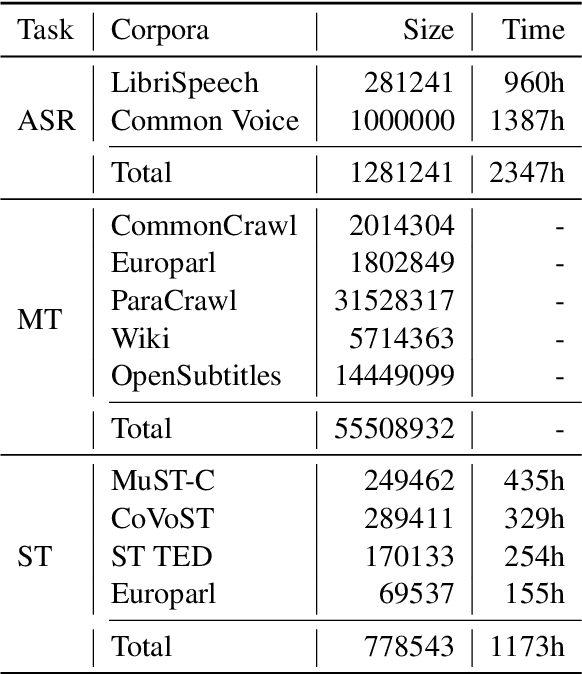
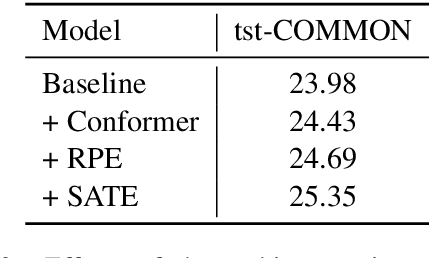
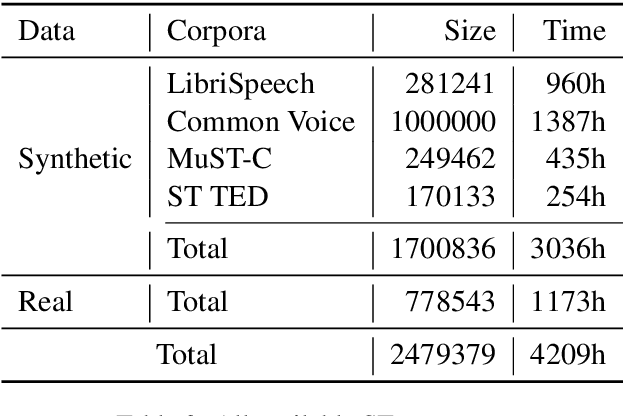
Abstract:This paper describes the submission of the NiuTrans end-to-end speech translation system for the IWSLT 2021 offline task, which translates from the English audio to German text directly without intermediate transcription. We use the Transformer-based model architecture and enhance it by Conformer, relative position encoding, and stacked acoustic and textual encoding. To augment the training data, the English transcriptions are translated to German translations. Finally, we employ ensemble decoding to integrate the predictions from several models trained with the different datasets. Combining these techniques, we achieve 33.84 BLEU points on the MuST-C En-De test set, which shows the enormous potential of the end-to-end model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge