Aiying Zhang
Uncovering Latent Communication Patterns in Brain Networks via Adaptive Flow Routing
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Unraveling how macroscopic cognitive phenotypes emerge from microscopic neuronal connectivity remains one of the core pursuits of neuroscience. To this end, researchers typically leverage multi-modal information from structural connectivity (SC) and functional connectivity (FC) to complete downstream tasks. Recent methodologies explore the intricate coupling mechanisms between SC and FC, attempting to fuse their representations at the regional level. However, lacking fundamental neuroscientific insight, these approaches fail to uncover the latent interactions between neural regions underlying these connectomes, and thus cannot explain why SC and FC exhibit dynamic states of both coupling and heterogeneity. In this paper, we formulate multi-modal fusion through the lens of neural communication dynamics and propose the Adaptive Flow Routing Network (AFR-Net), a physics-informed framework that models how structural constraints (SC) give rise to functional communication patterns (FC), enabling interpretable discovery of critical neural pathways. Extensive experiments demonstrate that AFR-Net significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines. The code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/DIAL-F0D1.
A Privacy-Preserving Domain Adversarial Federated learning for multi-site brain functional connectivity analysis
Feb 03, 2025
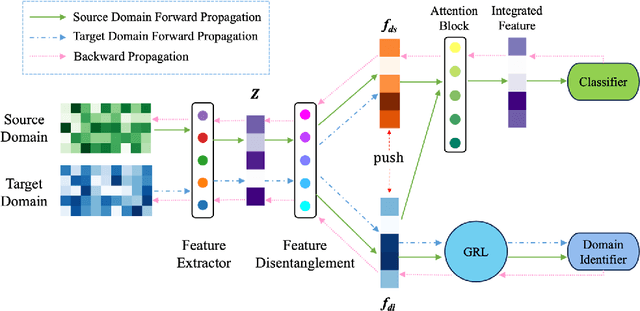
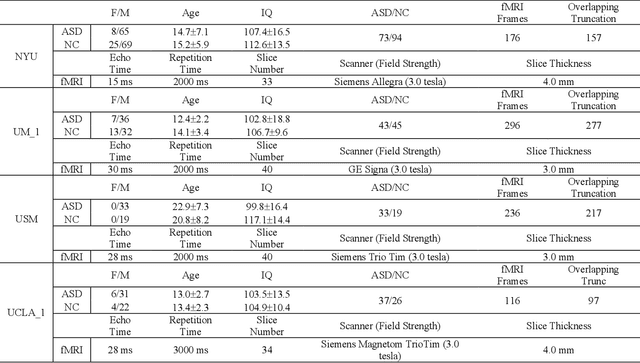
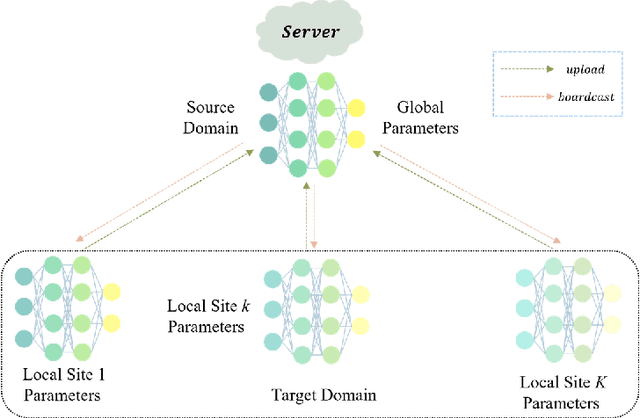
Abstract:Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rs-fMRI) and its derived functional connectivity networks (FCNs) have become critical for understanding neurological disorders. However, collaborative analyses and the generalizability of models still face significant challenges due to privacy regulations and the non-IID (non-independent and identically distributed) property of multiple data sources. To mitigate these difficulties, we propose Domain Adversarial Federated Learning (DAFed), a novel federated deep learning framework specifically designed for non-IID fMRI data analysis in multi-site settings. DAFed addresses these challenges through feature disentanglement, decomposing the latent feature space into domain-invariant and domain-specific components, to ensure robust global learning while preserving local data specificity. Furthermore, adversarial training facilitates effective knowledge transfer between labeled and unlabeled datasets, while a contrastive learning module enhances the global representation of domain-invariant features. We evaluated DAFed on the diagnosis of ASD and further validated its generalizability in the classification of AD, demonstrating its superior classification accuracy compared to state-of-the-art methods. Additionally, an enhanced Score-CAM module identifies key brain regions and functional connectivity significantly associated with ASD and MCI, respectively, uncovering shared neurobiological patterns across sites. These findings highlight the potential of DAFed to advance multi-site collaborative research in neuroimaging while protecting data confidentiality.
BrainMAP: Learning Multiple Activation Pathways in Brain Networks
Dec 23, 2024Abstract:Functional Magnetic Resonance Image (fMRI) is commonly employed to study human brain activity, since it offers insight into the relationship between functional fluctuations and human behavior. To enhance analysis and comprehension of brain activity, Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have been widely applied to the analysis of functional connectivities (FC) derived from fMRI data, due to their ability to capture the synergistic interactions among brain regions. However, in the human brain, performing complex tasks typically involves the activation of certain pathways, which could be represented as paths across graphs. As such, conventional GNNs struggle to learn from these pathways due to the long-range dependencies of multiple pathways. To address these challenges, we introduce a novel framework BrainMAP to learn Multiple Activation Pathways in Brain networks. BrainMAP leverages sequential models to identify long-range correlations among sequentialized brain regions and incorporates an aggregation module based on Mixture of Experts (MoE) to learn from multiple pathways. Our comprehensive experiments highlight BrainMAP's superior performance. Furthermore, our framework enables explanatory analyses of crucial brain regions involved in tasks. Our code is provided at https://github.com/LzyFischer/Graph-Mamba.
Integrated Brain Connectivity Analysis with fMRI, DTI, and sMRI Powered by Interpretable Graph Neural Networks
Aug 26, 2024Abstract:Multimodal neuroimaging modeling has becomes a widely used approach but confronts considerable challenges due to heterogeneity, which encompasses variability in data types, scales, and formats across modalities. This variability necessitates the deployment of advanced computational methods to integrate and interpret these diverse datasets within a cohesive analytical framework. In our research, we amalgamate functional magnetic resonance imaging, diffusion tensor imaging, and structural MRI into a cohesive framework. This integration capitalizes on the unique strengths of each modality and their inherent interconnections, aiming for a comprehensive understanding of the brain's connectivity and anatomical characteristics. Utilizing the Glasser atlas for parcellation, we integrate imaging derived features from various modalities: functional connectivity from fMRI, structural connectivity from DTI, and anatomical features from sMRI within consistent regions. Our approach incorporates a masking strategy to differentially weight neural connections, thereby facilitating a holistic amalgamation of multimodal imaging data. This technique enhances interpretability at connectivity level, transcending traditional analyses centered on singular regional attributes. The model is applied to the Human Connectome Project's Development study to elucidate the associations between multimodal imaging and cognitive functions throughout youth. The analysis demonstrates improved predictive accuracy and uncovers crucial anatomical features and essential neural connections, deepening our understanding of brain structure and function.
Exploring General Intelligence via Gated Graph Transformer in Functional Connectivity Studies
Jan 18, 2024Abstract:Functional connectivity (FC) as derived from fMRI has emerged as a pivotal tool in elucidating the intricacies of various psychiatric disorders and delineating the neural pathways that underpin cognitive and behavioral dynamics inherent to the human brain. While Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) offer a structured approach to represent neuroimaging data, they are limited by their need for a predefined graph structure to depict associations between brain regions, a detail not solely provided by FCs. To bridge this gap, we introduce the Gated Graph Transformer (GGT) framework, designed to predict cognitive metrics based on FCs. Empirical validation on the Philadelphia Neurodevelopmental Cohort (PNC) underscores the superior predictive prowess of our model, further accentuating its potential in identifying pivotal neural connectivities that correlate with human cognitive processes.
Causal inference of brain connectivity from fMRI with $ψ$-Learning Incorporated Linear non-Gaussian Acyclic Model ($ψ$-LiNGAM)
Jun 16, 2020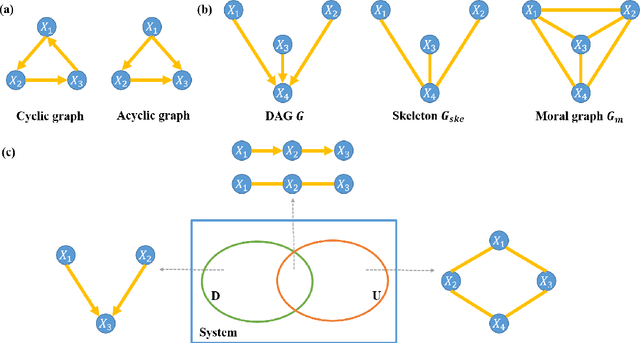
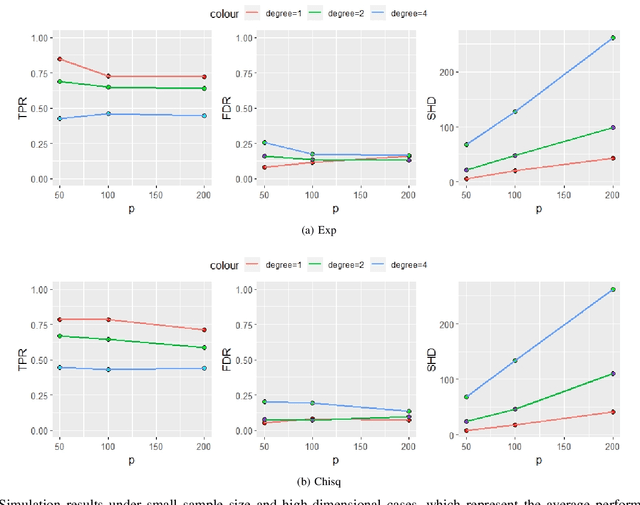
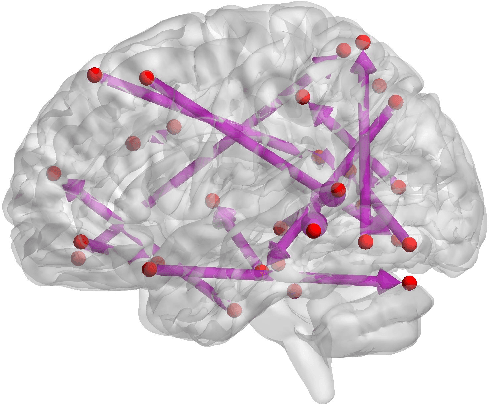
Abstract:Functional connectivity (FC) has become a primary means of understanding brain functions by identifying brain network interactions and, ultimately, how those interactions produce cognitions. A popular definition of FC is by statistical associations between measured brain regions. However, this could be problematic since the associations can only provide spatial connections but not causal interactions among regions of interests. Hence, it is necessary to study their causal relationship. Directed acyclic graph (DAG) models have been applied in recent FC studies but often encountered problems such as limited sample sizes and large number of variables (namely high-dimensional problems), which lead to both computational difficulty and convergence issues. As a result, the use of DAG models is problematic, where the identification of DAG models in general is nondeterministic polynomial time hard (NP-hard). To this end, we propose a $\psi$-learning incorporated linear non-Gaussian acyclic model ($\psi$-LiNGAM). We use the association model ($\psi$-learning) to facilitate causal inferences and the model works well especially for high-dimensional cases. Our simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method is more robust and accurate than several existing ones in detecting graph structure and direction. We then applied it to the resting state fMRI (rsfMRI) data obtained from the publicly available Philadelphia Neurodevelopmental Cohort (PNC) to study the cognitive variance, which includes 855 individuals aged 8-22 years. Therein, we have identified three types of hub structure: the in-hub, out-hub and sum-hub, which correspond to the centers of receiving, sending and relaying information, respectively. We also detected 16 most important pairs of causal flows. Several of the results have been verified to be biologically significant.
A Bayesian incorporated linear non-Gaussian acyclic model for multiple directed graph estimation to study brain emotion circuit development in adolescence
Jun 16, 2020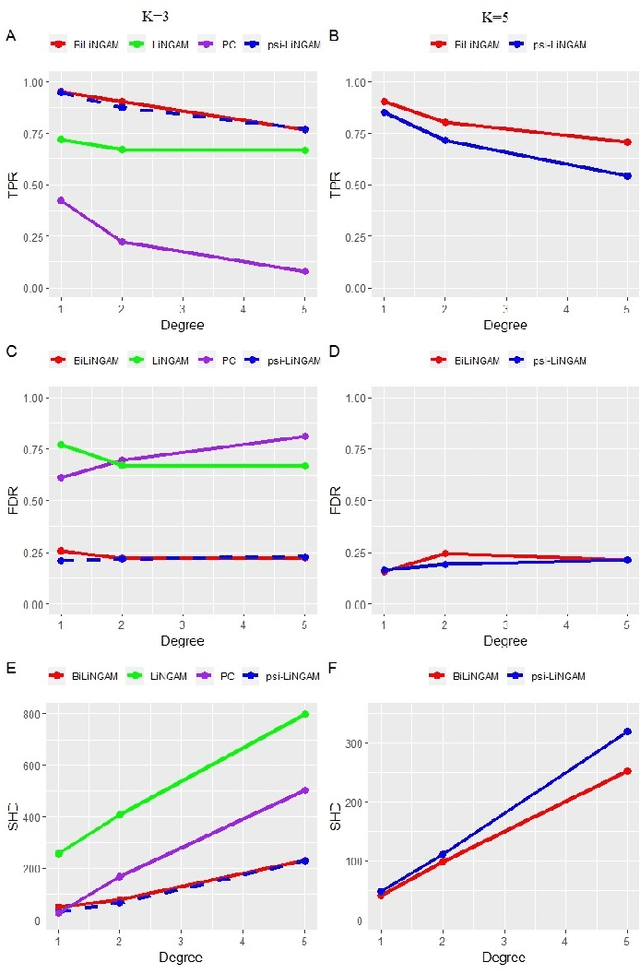
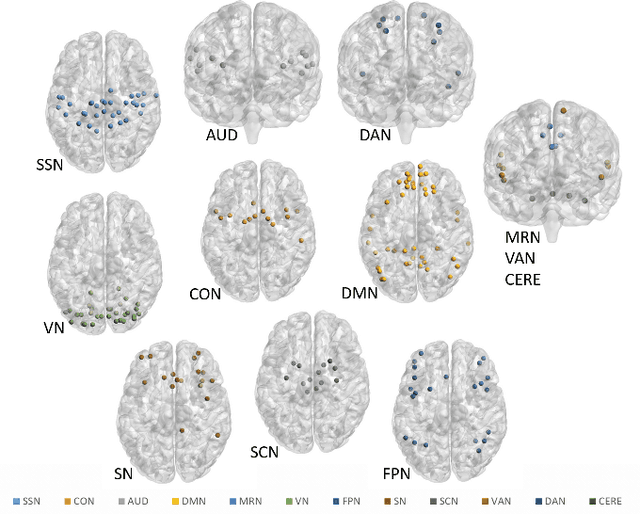
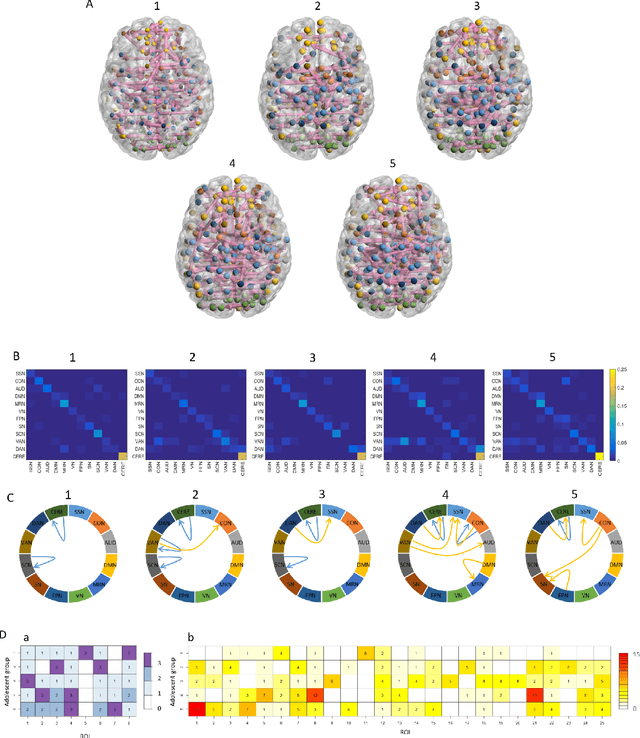
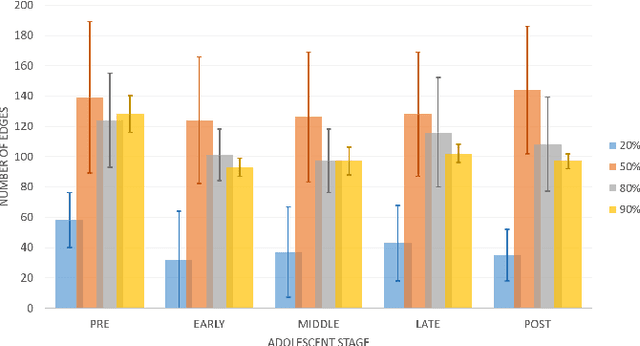
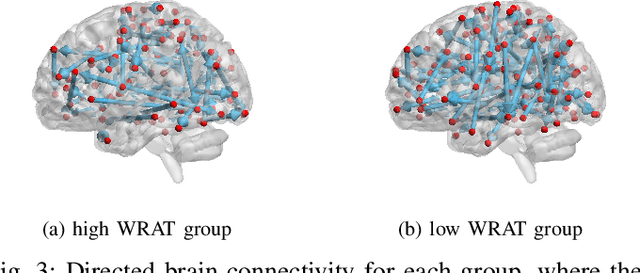
Abstract:Emotion perception is essential to affective and cognitive development which involves distributed brain circuits. The ability of emotion identification begins in infancy and continues to develop throughout childhood and adolescence. Understanding the development of brain's emotion circuitry may help us explain the emotional changes observed during adolescence. Our previous study delineated the trajectory of brain functional connectivity (FC) from late childhood to early adulthood during emotion identification tasks. In this work, we endeavour to deepen our understanding from association to causation. We proposed a Bayesian incorporated linear non-Gaussian acyclic model (BiLiNGAM), which incorporated our previous association model into the prior estimation pipeline. In particular, it can jointly estimate multiple directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) for multiple age groups at different developmental stages. Simulation results indicated more stable and accurate performance over various settings, especially when the sample size was small (high-dimensional cases). We then applied to the analysis of real data from the Philadelphia Neurodevelopmental Cohort (PNC). This included 855 individuals aged 8-22 years who were divided into five different adolescent stages. Our network analysis revealed the development of emotion-related intra- and inter- modular connectivity and pinpointed several emotion-related hubs. We further categorized the hubs into two types: in-hubs and out-hubs, as the center of receiving and distributing information. Several unique developmental hub structures and group-specific patterns were also discovered. Our findings help provide a causal understanding of emotion development in the human brain.
Interpretable multimodal fusion networks reveal mechanisms of brain cognition
Jun 16, 2020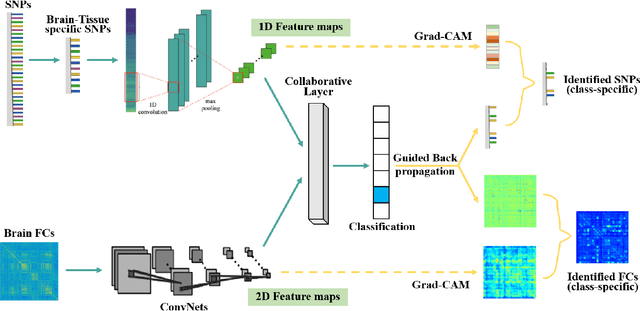
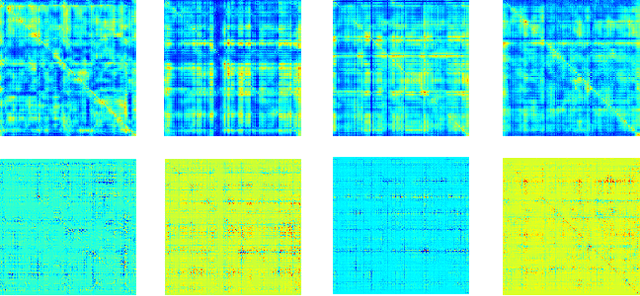
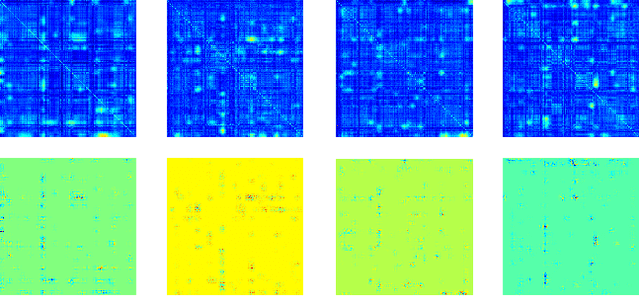
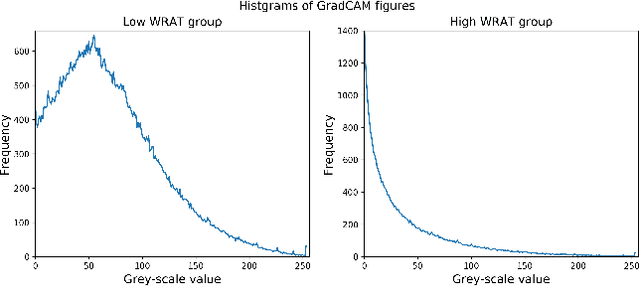
Abstract:Multimodal fusion benefits disease diagnosis by providing a more comprehensive perspective. Developing algorithms is challenging due to data heterogeneity and the complex within- and between-modality associations. Deep-network-based data-fusion models have been developed to capture the complex associations and the performance in diagnosis has been improved accordingly. Moving beyond diagnosis prediction, evaluation of disease mechanisms is critically important for biomedical research. Deep-network-based data-fusion models, however, are difficult to interpret, bringing about difficulties for studying biological mechanisms. In this work, we develop an interpretable multimodal fusion model, namely gCAM-CCL, which can perform automated diagnosis and result interpretation simultaneously. The gCAM-CCL model can generate interpretable activation maps, which quantify pixel-level contributions of the input features. This is achieved by combining intermediate feature maps using gradient-based weights. Moreover, the estimated activation maps are class-specific, and the captured cross-data associations are interest/label related, which further facilitates class-specific analysis and biological mechanism analysis. We validate the gCAM-CCL model on a brain imaging-genetic study, and show gCAM-CCL's performed well for both classification and mechanism analysis. Mechanism analysis suggests that during task-fMRI scans, several object recognition related regions of interests (ROIs) are first activated and then several downstream encoding ROIs get involved. Results also suggest that the higher cognition performing group may have stronger neurotransmission signaling while the lower cognition performing group may have problem in brain/neuron development, resulting from genetic variations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge