Xiaomeng Zhao
MinerU2.5: A Decoupled Vision-Language Model for Efficient High-Resolution Document Parsing
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:We introduce MinerU2.5, a 1.2B-parameter document parsing vision-language model that achieves state-of-the-art recognition accuracy while maintaining exceptional computational efficiency. Our approach employs a coarse-to-fine, two-stage parsing strategy that decouples global layout analysis from local content recognition. In the first stage, the model performs efficient layout analysis on downsampled images to identify structural elements, circumventing the computational overhead of processing high-resolution inputs. In the second stage, guided by the global layout, it performs targeted content recognition on native-resolution crops extracted from the original image, preserving fine-grained details in dense text, complex formulas, and tables. To support this strategy, we developed a comprehensive data engine that generates diverse, large-scale training corpora for both pretraining and fine-tuning. Ultimately, MinerU2.5 demonstrates strong document parsing ability, achieving state-of-the-art performance on multiple benchmarks, surpassing both general-purpose and domain-specific models across various recognition tasks, while maintaining significantly lower computational overhead.
OmniDocBench: Benchmarking Diverse PDF Document Parsing with Comprehensive Annotations
Dec 10, 2024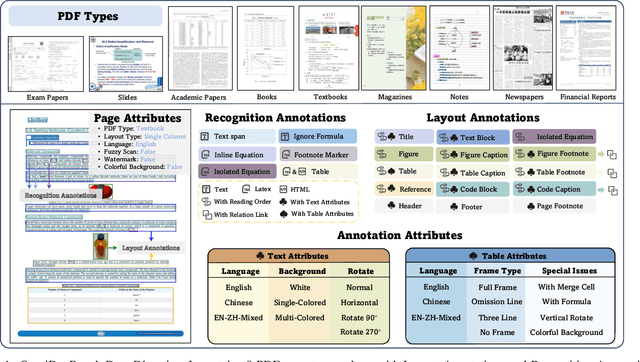
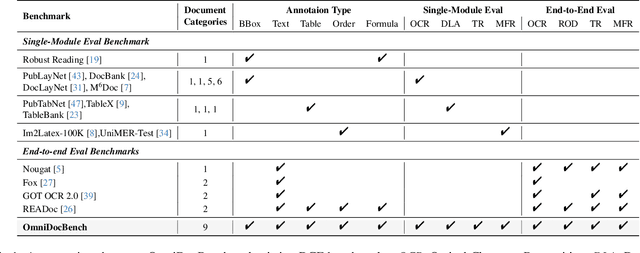
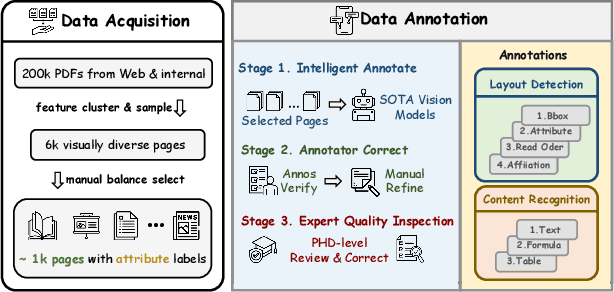
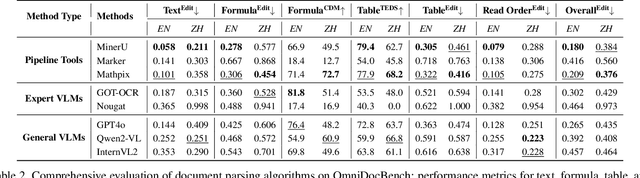
Abstract:Document content extraction is crucial in computer vision, especially for meeting the high-quality data needs of large language models (LLMs) and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) technologies. However, current document parsing methods suffer from significant limitations in terms of diversity and comprehensive evaluation. To address these challenges, we introduce OmniDocBench, a novel multi-source benchmark designed to advance automated document content extraction. OmniDocBench includes a meticulously curated and annotated high-quality evaluation dataset comprising nine diverse document types, such as academic papers, textbooks, slides, among others. Our benchmark provides a flexible and comprehensive evaluation framework with 19 layout category labels and 14 attribute labels, enabling multi-level assessments across entire datasets, individual modules, or specific data types. Using OmniDocBench, we perform an exhaustive comparative analysis of existing modular pipelines and multimodal end-to-end methods, highlighting their limitations in handling document diversity and ensuring fair evaluation. OmniDocBench establishes a robust, diverse, and fair evaluation standard for the document content extraction field, offering crucial insights for future advancements and fostering the development of document parsing technologies. The codes and dataset is available in https://github.com/opendatalab/OmniDocBench.
MinerU: An Open-Source Solution for Precise Document Content Extraction
Sep 27, 2024



Abstract:Document content analysis has been a crucial research area in computer vision. Despite significant advancements in methods such as OCR, layout detection, and formula recognition, existing open-source solutions struggle to consistently deliver high-quality content extraction due to the diversity in document types and content. To address these challenges, we present MinerU, an open-source solution for high-precision document content extraction. MinerU leverages the sophisticated PDF-Extract-Kit models to extract content from diverse documents effectively and employs finely-tuned preprocessing and postprocessing rules to ensure the accuracy of the final results. Experimental results demonstrate that MinerU consistently achieves high performance across various document types, significantly enhancing the quality and consistency of content extraction. The MinerU open-source project is available at https://github.com/opendatalab/MinerU.
LIMP: Large Language Model Enhanced Intent-aware Mobility Prediction
Aug 23, 2024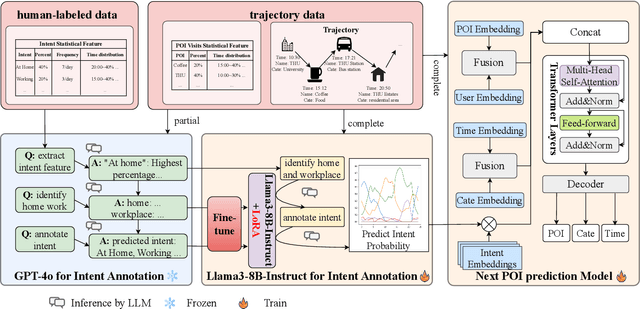
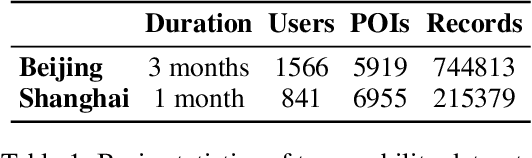
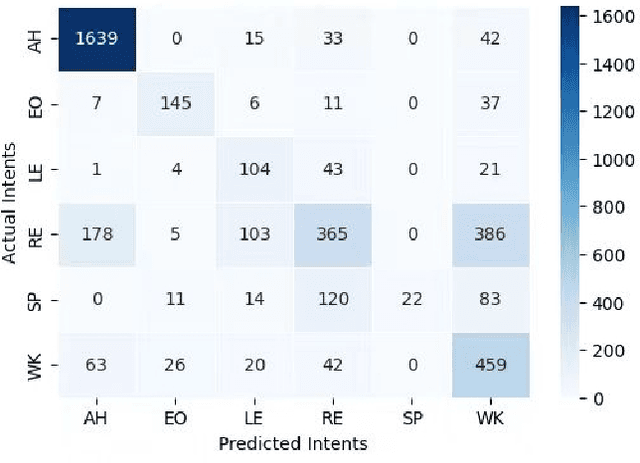
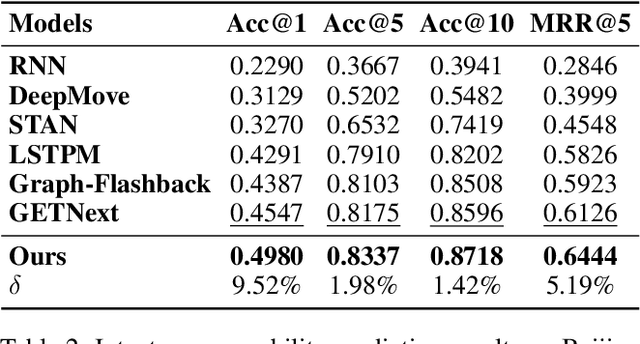
Abstract:Human mobility prediction is essential for applications like urban planning and transportation management, yet it remains challenging due to the complex, often implicit, intentions behind human behavior. Existing models predominantly focus on spatiotemporal patterns, paying less attention to the underlying intentions that govern movements. Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) offer a promising alternative research angle for integrating commonsense reasoning into mobility prediction. However, it is a non-trivial problem because LLMs are not natively built for mobility intention inference, and they also face scalability issues and integration difficulties with spatiotemporal models. To address these challenges, we propose a novel LIMP (LLMs for Intent-ware Mobility Prediction) framework. Specifically, LIMP introduces an "Analyze-Abstract-Infer" (A2I) agentic workflow to unleash LLM's commonsense reasoning power for mobility intention inference. Besides, we design an efficient fine-tuning scheme to transfer reasoning power from commercial LLM to smaller-scale, open-source language model, ensuring LIMP's scalability to millions of mobility records. Moreover, we propose a transformer-based intention-aware mobility prediction model to effectively harness the intention inference ability of LLM. Evaluated on two real-world datasets, LIMP significantly outperforms baseline models, demonstrating improved accuracy in next-location prediction and effective intention inference. The interpretability of intention-aware mobility prediction highlights our LIMP framework's potential for real-world applications. Codes and data can be found in https://github.com/tsinghua-fib-lab/LIMP .
InternLM2 Technical Report
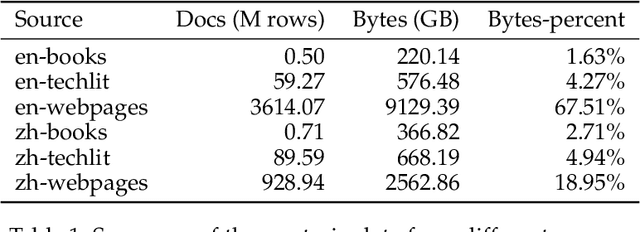
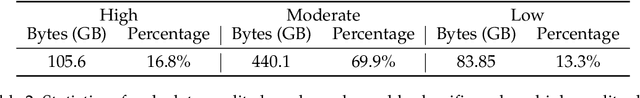
Mar 26, 2024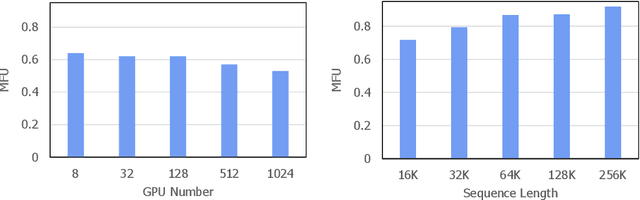

Abstract:The evolution of Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT and GPT-4 has sparked discussions on the advent of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). However, replicating such advancements in open-source models has been challenging. This paper introduces InternLM2, an open-source LLM that outperforms its predecessors in comprehensive evaluations across 6 dimensions and 30 benchmarks, long-context modeling, and open-ended subjective evaluations through innovative pre-training and optimization techniques. The pre-training process of InternLM2 is meticulously detailed, highlighting the preparation of diverse data types including text, code, and long-context data. InternLM2 efficiently captures long-term dependencies, initially trained on 4k tokens before advancing to 32k tokens in pre-training and fine-tuning stages, exhibiting remarkable performance on the 200k ``Needle-in-a-Haystack" test. InternLM2 is further aligned using Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) and a novel Conditional Online Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (COOL RLHF) strategy that addresses conflicting human preferences and reward hacking. By releasing InternLM2 models in different training stages and model sizes, we provide the community with insights into the model's evolution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge