Xia Wu
NeuroCLIP: Brain-Inspired Prompt Tuning for EEG-to-Image Multimodal Contrastive Learning
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in brain-inspired artificial intelligence have sought to align neural signals with visual semantics using multimodal models such as CLIP. However, existing methods often treat CLIP as a static feature extractor, overlooking its adaptability to neural representations and the inherent physiological-symbolic gap in EEG-image alignment. To address these challenges, we present NeuroCLIP, a prompt tuning framework tailored for EEG-to-image contrastive learning. Our approach introduces three core innovations: (1) We design a dual-stream visual embedding pipeline that combines dynamic filtering and token-level fusion to generate instance-level adaptive prompts, which guide the adjustment of patch embedding tokens based on image content, thereby enabling fine-grained modulation of visual representations under neural constraints; (2) We are the first to introduce visual prompt tokens into EEG-image alignment, acting as global, modality-level prompts that work in conjunction with instance-level adjustments. These visual prompt tokens are inserted into the Transformer architecture to facilitate neural-aware adaptation and parameter optimization at a global level; (3) Inspired by neuroscientific principles of human visual encoding, we propose a refined contrastive loss that better model the semantic ambiguity and cross-modal noise present in EEG signals. On the THINGS-EEG2 dataset, NeuroCLIP achieves a Top-1 accuracy of 63.2% in zero-shot image retrieval, surpassing the previous best method by +12.3%, and demonstrates strong generalization under inter-subject conditions (+4.6% Top-1), highlighting the potential of physiology-aware prompt tuning for bridging brain signals and visual semantics.
Brain Inspired Adaptive Memory Dual-Net for Few-Shot Image Classification
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:Few-shot image classification has become a popular research topic for its wide application in real-world scenarios, however the problem of supervision collapse induced by single image-level annotation remains a major challenge. Existing methods aim to tackle this problem by locating and aligning relevant local features. However, the high intra-class variability in real-world images poses significant challenges in locating semantically relevant local regions under few-shot settings. Drawing inspiration from the human's complementary learning system, which excels at rapidly capturing and integrating semantic features from limited examples, we propose the generalization-optimized Systems Consolidation Adaptive Memory Dual-Network, SCAM-Net. This approach simulates the systems consolidation of complementary learning system with an adaptive memory module, which successfully addresses the difficulty of identifying meaningful features in few-shot scenarios. Specifically, we construct a Hippocampus-Neocortex dual-network that consolidates structured representation of each category, the structured representation is then stored and adaptively regulated following the generalization optimization principle in a long-term memory inside Neocortex. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets show that the proposed model has achieved state-of-the-art performance.
Embedded Multi-label Feature Selection via Orthogonal Regression
Mar 01, 2024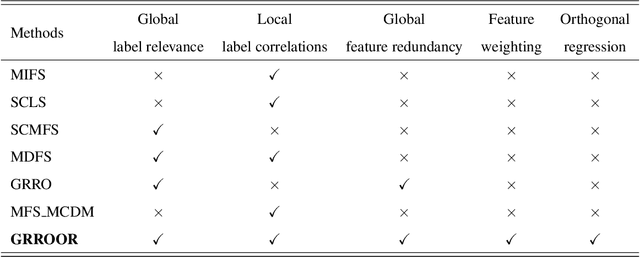
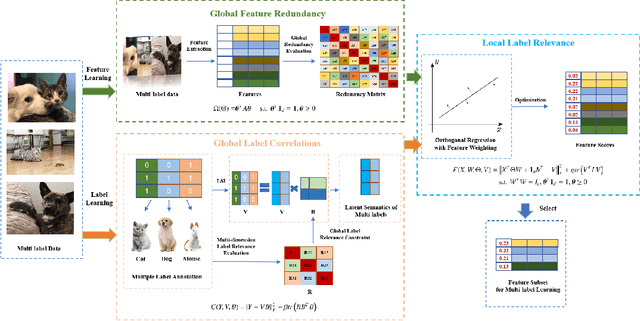

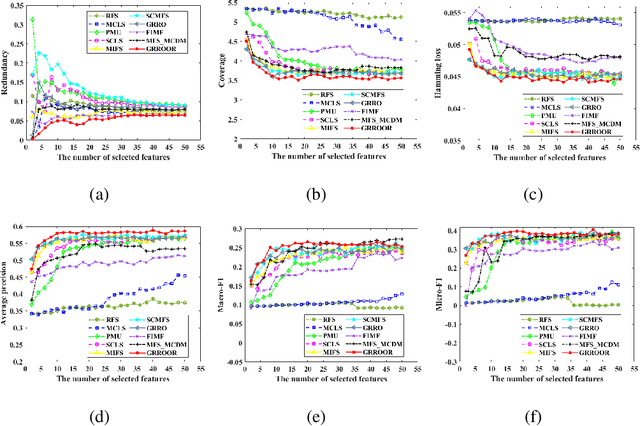
Abstract:In the last decade, embedded multi-label feature selection methods, incorporating the search for feature subsets into model optimization, have attracted considerable attention in accurately evaluating the importance of features in multi-label classification tasks. Nevertheless, the state-of-the-art embedded multi-label feature selection algorithms based on least square regression usually cannot preserve sufficient discriminative information in multi-label data. To tackle the aforementioned challenge, a novel embedded multi-label feature selection method, termed global redundancy and relevance optimization in orthogonal regression (GRROOR), is proposed to facilitate the multi-label feature selection. The method employs orthogonal regression with feature weighting to retain sufficient statistical and structural information related to local label correlations of the multi-label data in the feature learning process. Additionally, both global feature redundancy and global label relevancy information have been considered in the orthogonal regression model, which could contribute to the search for discriminative and non-redundant feature subsets in the multi-label data. The cost function of GRROOR is an unbalanced orthogonal Procrustes problem on the Stiefel manifold. A simple yet effective scheme is utilized to obtain an optimal solution. Extensive experimental results on ten multi-label data sets demonstrate the effectiveness of GRROOR.
DTVNet: Dynamic Time-lapse Video Generation via Single Still Image
Aug 11, 2020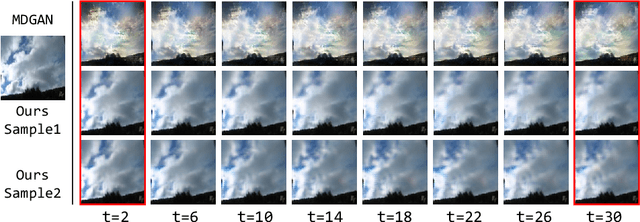
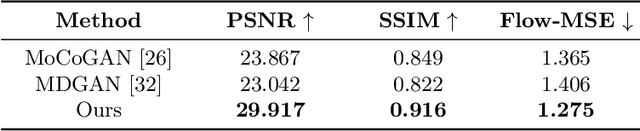
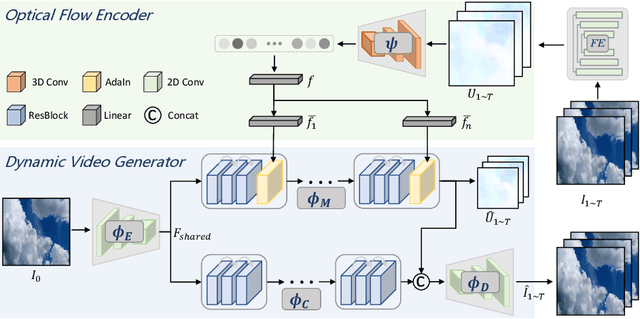
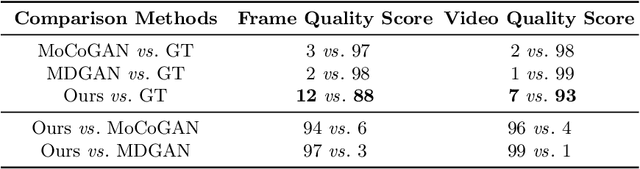
Abstract:This paper presents a novel end-to-end dynamic time-lapse video generation framework, named DTVNet, to generate diversified time-lapse videos from a single landscape image, which are conditioned on normalized motion vectors. The proposed DTVNet consists of two submodules: \emph{Optical Flow Encoder} (OFE) and \emph{Dynamic Video Generator} (DVG). The OFE maps a sequence of optical flow maps to a \emph{normalized motion vector} that encodes the motion information inside the generated video. The DVG contains motion and content streams that learn from the motion vector and the single image respectively, as well as an encoder and a decoder to learn shared content features and construct video frames with corresponding motion respectively. Specifically, the \emph{motion stream} introduces multiple \emph{adaptive instance normalization} (AdaIN) layers to integrate multi-level motion information that are processed by linear layers. In the testing stage, videos with the same content but various motion information can be generated by different \emph{normalized motion vectors} based on only one input image. We further conduct experiments on Sky Time-lapse dataset, and the results demonstrate the superiority of our approach over the state-of-the-art methods for generating high-quality and dynamic videos, as well as the variety for generating videos with various motion information.
Multiform Fonts-to-Fonts Translation via Style and Content Disentangled Representations of Chinese Character
Mar 28, 2020



Abstract:This paper mainly discusses the generation of personalized fonts as the problem of image style transfer. The main purpose of this paper is to design a network framework that can extract and recombine the content and style of the characters. These attempts can be used to synthesize the entire set of fonts with only a small amount of characters. The paper combines various depth networks such as Convolutional Neural Network, Multi-layer Perceptron and Residual Network to find the optimal model to extract the features of the fonts character. The result shows that those characters we have generated is very close to real characters, using Structural Similarity index and Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio evaluation criterions.
Automatic Generation of Chinese Handwriting via Fonts Style Representation Learning
Mar 27, 2020



Abstract:In this paper, we propose and end-to-end deep Chinese font generation system. This system can generate new style fonts by interpolation of latent style-related embeding variables that could achieve smooth transition between different style. Our method is simpler and more effective than other methods, which will help to improve the font design efficiency
Inverse design of multilayer nanoparticles using artificial neural networks and genetic algorithm
Mar 16, 2020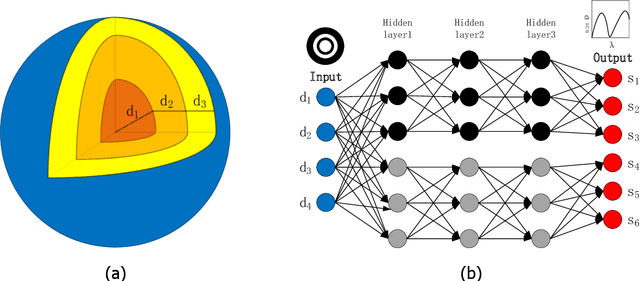
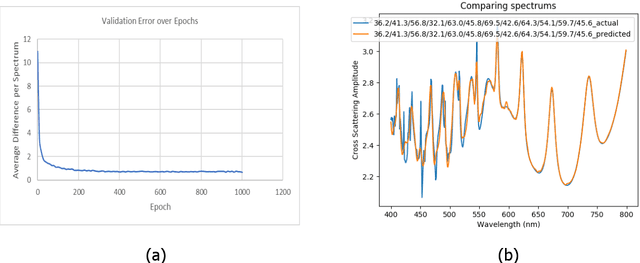
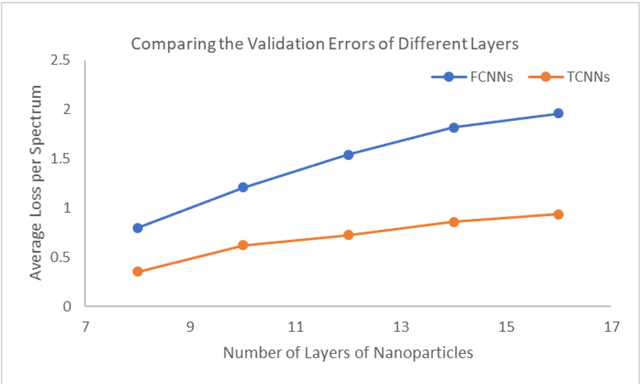
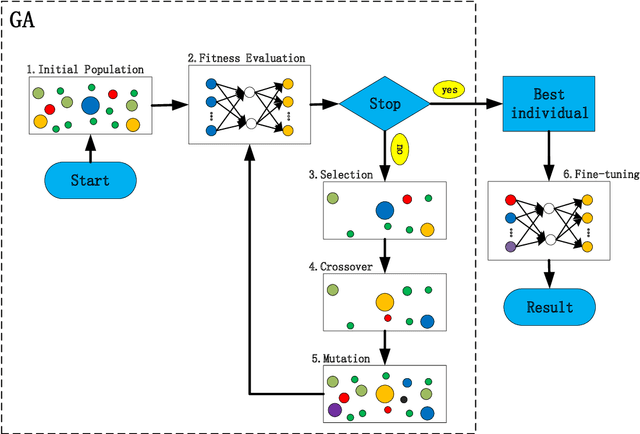
Abstract:The light scattering of multilayer nanoparticles can be solved by Maxwell equations. However, it is difficult to solve the inverse design of multilayer nanoparticles by using the traditional trial-and-error method. Here, we present a method for forward simulation and inverse design of multilayer nanoparticles. We combine the global search ability of genetic algorithm with the local search ability of neural network. First, the genetic algorithm is used to find a suitable solution, and then the neural network is used to fine-tune it. Due to the non-unique relationship between physical structures and optical responses, we first train a forward neural network, and then it is applied to the inverse design of multilayer nanoparticles. Not only here, this method can easily be extended to predict and find the best design parameters for other optical structures.
u-net CNN based fourier ptychography
Mar 16, 2020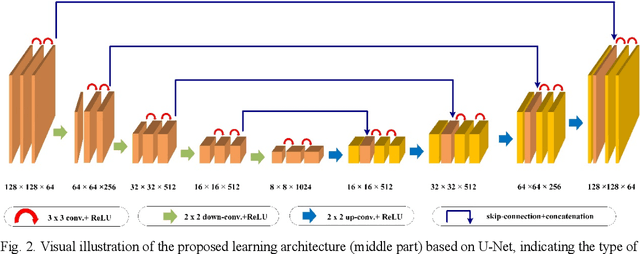
Abstract:Fourier ptychography is a recently explored imaging method for overcoming the diffraction limit of conventional cameras with applications in microscopy and yielding high-resolution images. In order to splice together low-resolution images taken under different illumination angles of coherent light source, an iterative phase retrieval algorithm is adopted. However, the reconstruction procedure is slow and needs a good many of overlap in the Fourier domain for the continuous recorded low-resolution images and is also worse under system aberrations such as noise or random update sequence. In this paper, we propose a new retrieval algorithm that is based on convolutional neural networks. Once well trained, our model can perform high-quality reconstruction rapidly by using the graphics processing unit. The experiments demonstrate that our model achieves better reconstruction results and is more robust under system aberrations.
Robotic Cane as a Soft SuperLimb for Elderly Sit-to-Stand Assistance
Feb 29, 2020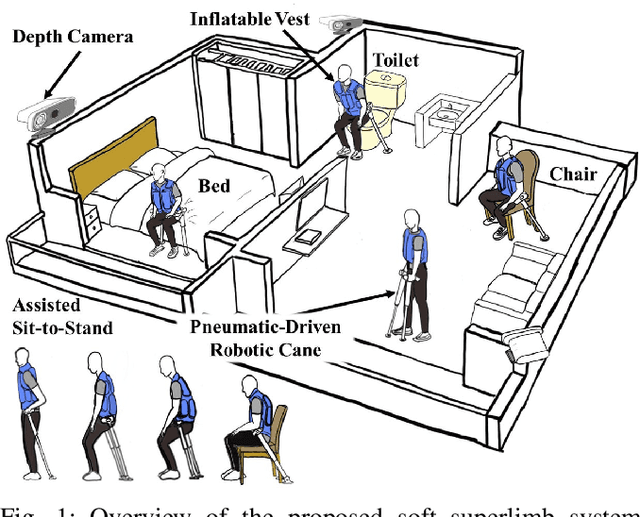
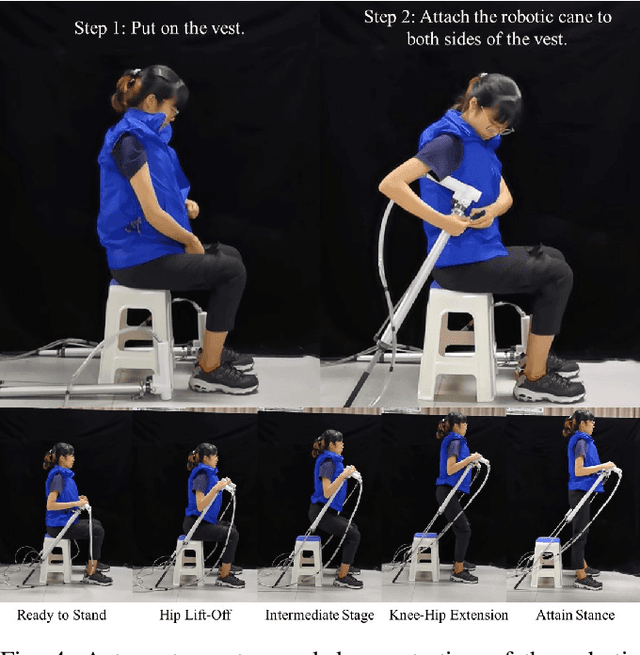
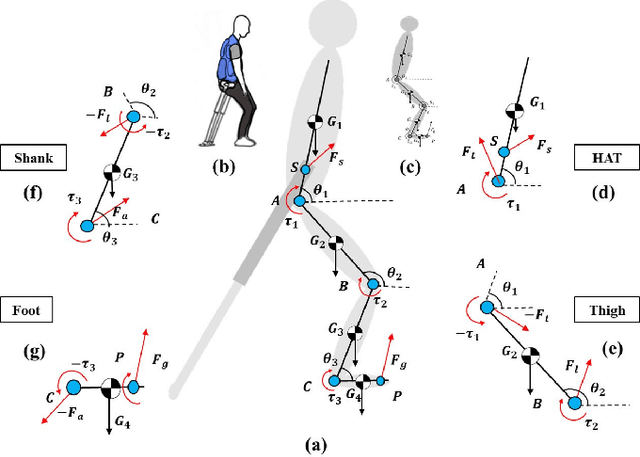
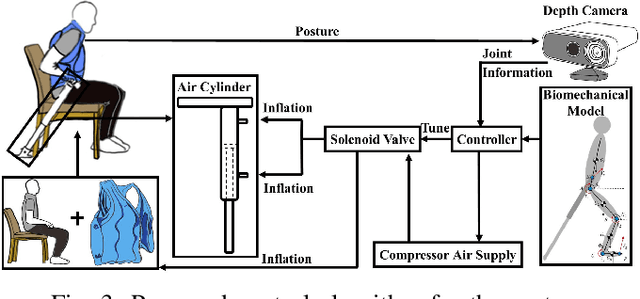

Abstract:Many researchers have identified robotics as a potential solution to the aging population faced by many developed and developing countries. If so, how should we address the cognitive acceptance and ambient control of elderly assistive robots through design? In this paper, we proposed an explorative design of an ambient SuperLimb (Supernumerary Robotic Limb) system that involves a pneumatically-driven robotic cane for at-home motion assistance, an inflatable vest for compliant human-robot interaction, and a depth sensor for ambient intention detection. The proposed system aims at providing active assistance during the sit-to-stand transition for at-home usage by the elderly at the bedside, in the chair, and on the toilet. We proposed a modified biomechanical model with a linear cane robot for closed-loop control implementation. We validated the design feasibility of the proposed ambient SuperLimb system including the biomechanical model, our result showed the advantages in reducing lower limb efforts and elderly fall risks, yet the detection accuracy using depth sensing and adjustments on the model still require further research in the future. Nevertheless, we summarized empirical guidelines to support the ambient design of elderly-assistive SuperLimb systems for lower limb functional augmentation.
Supervised feature selection with orthogonal regression and feature weighting
Oct 09, 2019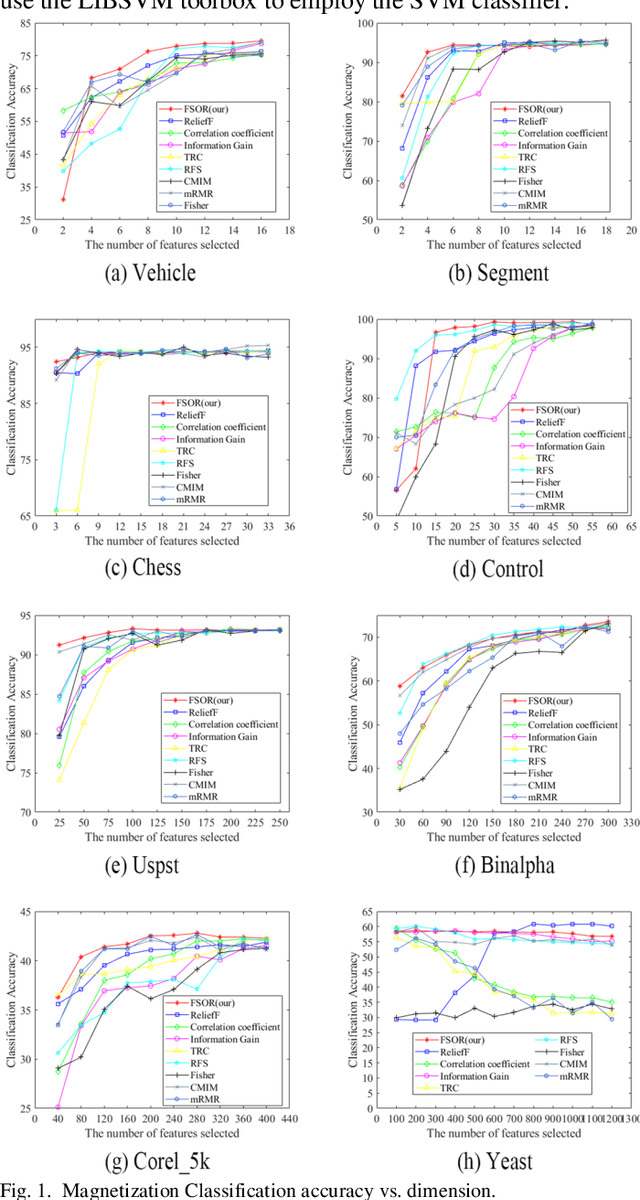
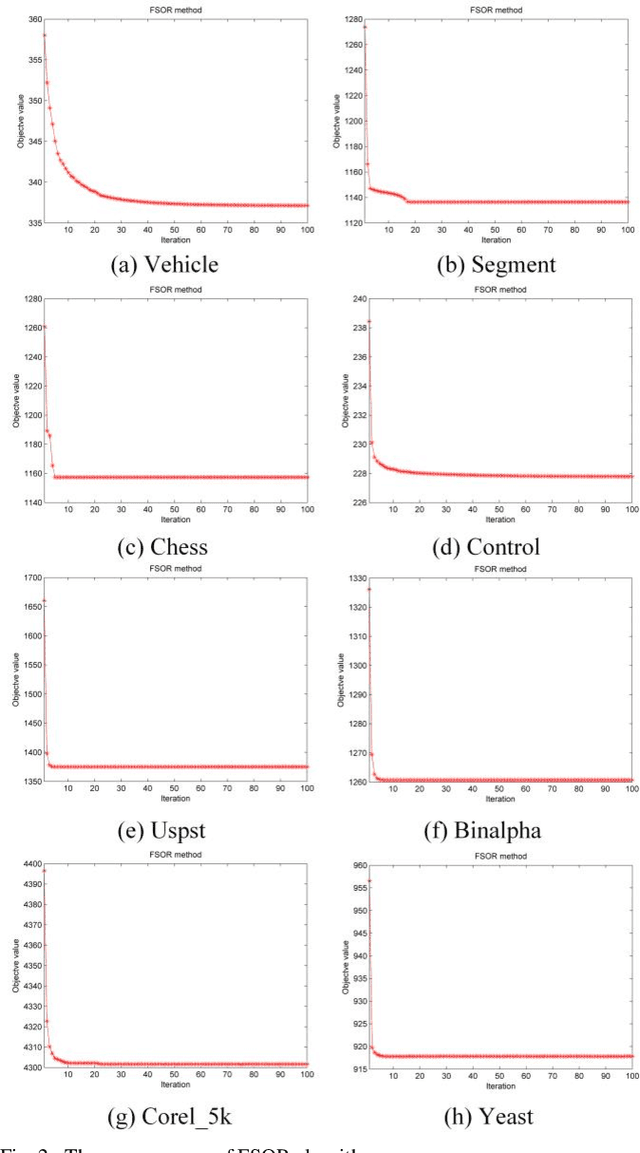

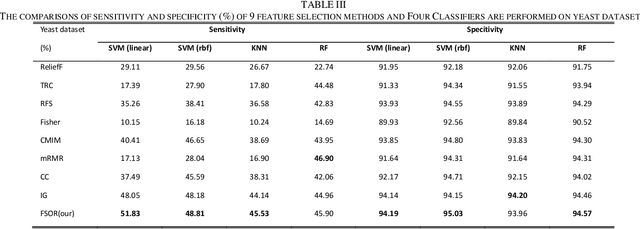
Abstract:Effective features can improve the performance of a model, which can thus help us understand the characteristics and underlying structure of complex data. Previous feature selection methods usually cannot keep more local structure information. To address the defects previously mentioned, we propose a novel supervised orthogonal least square regression model with feature weighting for feature selection. The optimization problem of the objection function can be solved by employing generalized power iteration (GPI) and augmented Lagrangian multiplier (ALM) methods. Experimental results show that the proposed method can more effectively reduce the feature dimensionality and obtain better classification results than traditional feature selection methods. The convergence of our iterative method is proved as well. Consequently, the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed method are verified both theoretically and experimentally.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge