Weizhi Wang
MiroThinker: Pushing the Performance Boundaries of Open-Source Research Agents via Model, Context, and Interactive Scaling
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:We present MiroThinker v1.0, an open-source research agent designed to advance tool-augmented reasoning and information-seeking capabilities. Unlike previous agents that only scale up model size or context length, MiroThinker explores interaction scaling at the model level, systematically training the model to handle deeper and more frequent agent-environment interactions as a third dimension of performance improvement. Unlike LLM test-time scaling, which operates in isolation and risks degradation with longer reasoning chains, interactive scaling leverages environment feedback and external information acquisition to correct errors and refine trajectories. Through reinforcement learning, the model achieves efficient interaction scaling: with a 256K context window, it can perform up to 600 tool calls per task, enabling sustained multi-turn reasoning and complex real-world research workflows. Across four representative benchmarks-GAIA, HLE, BrowseComp, and BrowseComp-ZH-the 72B variant achieves up to 81.9%, 37.7%, 47.1%, and 55.6% accuracy respectively, surpassing previous open-source agents and approaching commercial counterparts such as GPT-5-high. Our analysis reveals that MiroThinker benefits from interactive scaling consistently: research performance improves predictably as the model engages in deeper and more frequent agent-environment interactions, demonstrating that interaction depth exhibits scaling behaviors analogous to model size and context length. These findings establish interaction scaling as a third critical dimension for building next-generation open research agents, complementing model capacity and context windows.
Identity-GRPO: Optimizing Multi-Human Identity-preserving Video Generation via Reinforcement Learning
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:While advanced methods like VACE and Phantom have advanced video generation for specific subjects in diverse scenarios, they struggle with multi-human identity preservation in dynamic interactions, where consistent identities across multiple characters are critical. To address this, we propose Identity-GRPO, a human feedback-driven optimization pipeline for refining multi-human identity-preserving video generation. First, we construct a video reward model trained on a large-scale preference dataset containing human-annotated and synthetic distortion data, with pairwise annotations focused on maintaining human consistency throughout the video. We then employ a GRPO variant tailored for multi-human consistency, which greatly enhances both VACE and Phantom. Through extensive ablation studies, we evaluate the impact of annotation quality and design choices on policy optimization. Experiments show that Identity-GRPO achieves up to 18.9% improvement in human consistency metrics over baseline methods, offering actionable insights for aligning reinforcement learning with personalized video generation.
Controlling Language Difficulty in Dialogues with Linguistic Features
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have emerged as powerful tools for supporting second language acquisition, particularly in simulating interactive dialogues for speaking practice. However, adapting the language difficulty of LLM-generated responses to match learners' proficiency levels remains a challenge. This work addresses this issue by proposing a framework for controlling language proficiency in educational dialogue systems. Our approach leverages three categories of linguistic features, readability features (e.g., Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level), syntactic features (e.g., syntactic tree depth), and lexical features (e.g., simple word ratio), to quantify and regulate text complexity. We demonstrate that training LLMs on linguistically annotated dialogue data enables precise modulation of language proficiency, outperforming prompt-based methods in both flexibility and stability. To evaluate this, we introduce Dilaprix, a novel metric integrating the aforementioned features, which shows strong correlation with expert judgments of language difficulty. Empirical results reveal that our approach achieves superior controllability of language proficiency while maintaining high dialogue quality.
Open-Qwen2VL: Compute-Efficient Pre-Training of Fully-Open Multimodal LLMs on Academic Resources
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:The reproduction of state-of-the-art multimodal LLM pre-training faces barriers at every stage of the pipeline, including high-quality data filtering, multimodal data mixture strategies, sequence packing techniques, and training frameworks. We introduce Open-Qwen2VL, a fully open-source 2B-parameter Multimodal Large Language Model pre-trained efficiently on 29M image-text pairs using only 220 A100-40G GPU hours. Our approach employs low-to-high dynamic image resolution and multimodal sequence packing to significantly enhance pre-training efficiency. The training dataset was carefully curated using both MLLM-based filtering techniques (e.g., MLM-Filter) and conventional CLIP-based filtering methods, substantially improving data quality and training efficiency. The Open-Qwen2VL pre-training is conducted on academic level 8xA100-40G GPUs at UCSB on 5B packed multimodal tokens, which is 0.36% of 1.4T multimodal pre-training tokens of Qwen2-VL. The final instruction-tuned Open-Qwen2VL outperforms partially-open state-of-the-art MLLM Qwen2-VL-2B on various multimodal benchmarks of MMBench, SEEDBench, MMstar, and MathVista, indicating the remarkable training efficiency of Open-Qwen2VL. We open-source all aspects of our work, including compute-efficient and data-efficient training details, data filtering methods, sequence packing scripts, pre-training data in WebDataset format, FSDP-based training codebase, and both base and instruction-tuned model checkpoints. We redefine "fully open" for multimodal LLMs as the complete release of: 1) the training codebase, 2) detailed data filtering techniques, and 3) all pre-training and supervised fine-tuning data used to develop the model.
Adaptive Layer-skipping in Pre-trained LLMs
Mar 31, 2025



Abstract:Various layer-skipping methods have been proposed to accelerate token generation in large language models (LLMs). However, they have overlooked a fundamental question: How do computational demands vary across the generation of different tokens? In this work, we introduce FlexiDepth, a method that dynamically adjusts the number of Transformer layers used in text generation. By incorporating a plug-in router and adapter, FlexiDepth enables adaptive layer-skipping in LLMs without modifying their original parameters. Introducing FlexiDepth to Llama-3-8B model achieves layer skipping of 8 layers out of 32, and meanwhile maintains the full 100\% benchmark performance. Experimental results with FlexiDepth demonstrate that computational demands in LLMs significantly vary based on token type. Specifically, generating repetitive tokens or fixed phrases requires fewer layers, whereas producing tokens involving computation or high uncertainty requires more layers. Interestingly, this adaptive allocation pattern aligns with human intuition. To advance research in this area, we open sourced FlexiDepth and a dataset documenting FlexiDepth's layer allocation patterns for future exploration.
Tora: Trajectory-oriented Diffusion Transformer for Video Generation
Jul 31, 2024Abstract:Recent advancements in Diffusion Transformer (DiT) have demonstrated remarkable proficiency in producing high-quality video content. Nonetheless, the potential of transformer-based diffusion models for effectively generating videos with controllable motion remains an area of limited exploration. This paper introduces Tora, the first trajectory-oriented DiT framework that integrates textual, visual, and trajectory conditions concurrently for video generation. Specifically, Tora consists of a Trajectory Extractor~(TE), a Spatial-Temporal DiT, and a Motion-guidance Fuser~(MGF). The TE encodes arbitrary trajectories into hierarchical spacetime motion patches with a 3D video compression network. The MGF integrates the motion patches into the DiT blocks to generate consistent videos following trajectories. Our design aligns seamlessly with DiT's scalability, allowing precise control of video content's dynamics with diverse durations, aspect ratios, and resolutions. Extensive experiments demonstrate Tora's excellence in achieving high motion fidelity, while also meticulously simulating the movement of the physical world. Page can be found at https://ali-videoai.github.io/tora_video.
Large Language Model based Situational Dialogues for Second Language Learning
Mar 29, 2024Abstract:In second language learning, scenario-based conversation practice is important for language learners to achieve fluency in speaking, but students often lack sufficient opportunities to practice their conversational skills with qualified instructors or native speakers. To bridge this gap, we propose situational dialogue models for students to engage in conversational practice. Our situational dialogue models are fine-tuned on large language models (LLMs), with the aim of combining the engaging nature of an open-ended conversation with the focused practice of scenario-based tasks. Leveraging the generalization capabilities of LLMs, we demonstrate that our situational dialogue models perform effectively not only on training topics but also on topics not encountered during training. This offers a promising solution to support a wide range of conversational topics without extensive manual work. Additionally, research in the field of dialogue systems still lacks reliable automatic evaluation metrics, leading to human evaluation as the gold standard (Smith et al., 2022), which is typically expensive. To address the limitations of existing evaluation methods, we present a novel automatic evaluation method that employs fine-tuned LLMs to efficiently and effectively assess the performance of situational dialogue models.
MM-Diff: High-Fidelity Image Personalization via Multi-Modal Condition Integration
Mar 22, 2024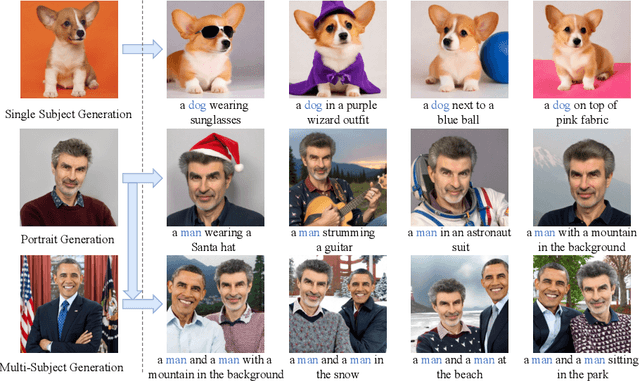
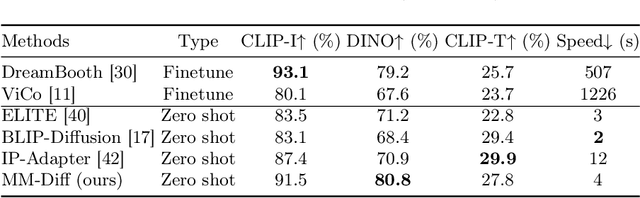
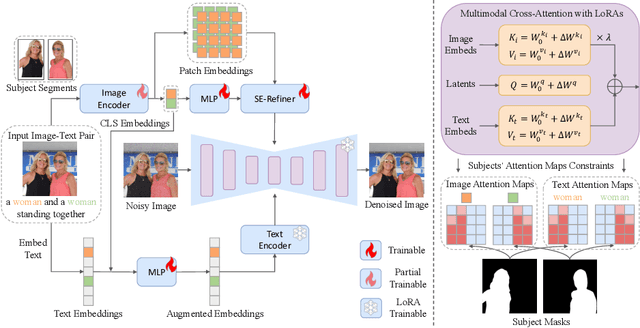
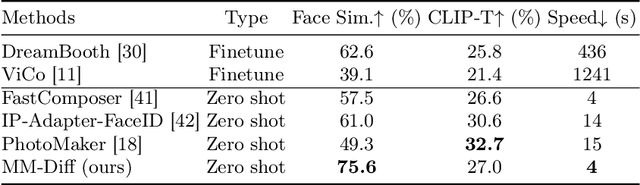
Abstract:Recent advances in tuning-free personalized image generation based on diffusion models are impressive. However, to improve subject fidelity, existing methods either retrain the diffusion model or infuse it with dense visual embeddings, both of which suffer from poor generalization and efficiency. Also, these methods falter in multi-subject image generation due to the unconstrained cross-attention mechanism. In this paper, we propose MM-Diff, a unified and tuning-free image personalization framework capable of generating high-fidelity images of both single and multiple subjects in seconds. Specifically, to simultaneously enhance text consistency and subject fidelity, MM-Diff employs a vision encoder to transform the input image into CLS and patch embeddings. CLS embeddings are used on the one hand to augment the text embeddings, and on the other hand together with patch embeddings to derive a small number of detail-rich subject embeddings, both of which are efficiently integrated into the diffusion model through the well-designed multimodal cross-attention mechanism. Additionally, MM-Diff introduces cross-attention map constraints during the training phase, ensuring flexible multi-subject image sampling during inference without any predefined inputs (e.g., layout). Extensive experiments demonstrate the superior performance of MM-Diff over other leading methods.
EffiVED:Efficient Video Editing via Text-instruction Diffusion Models
Mar 18, 2024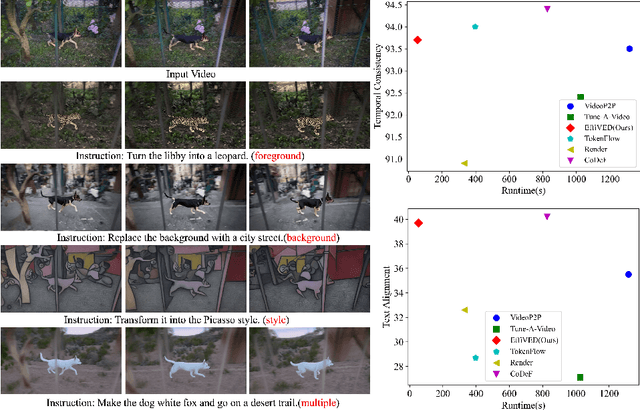
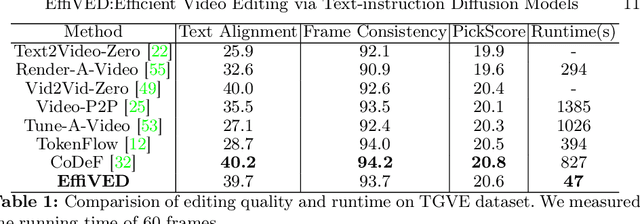
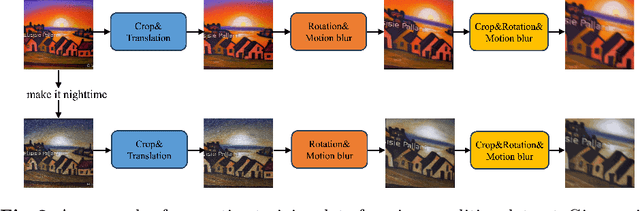
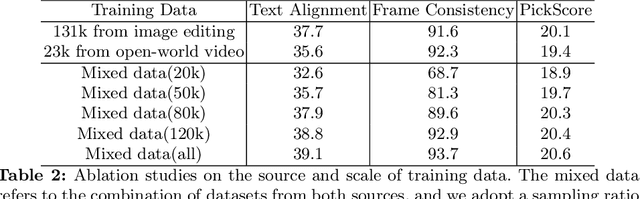
Abstract:Large-scale text-to-video models have shown remarkable abilities, but their direct application in video editing remains challenging due to limited available datasets. Current video editing methods commonly require per-video fine-tuning of diffusion models or specific inversion optimization to ensure high-fidelity edits. In this paper, we introduce EffiVED, an efficient diffusion-based model that directly supports instruction-guided video editing. To achieve this, we present two efficient workflows to gather video editing pairs, utilizing augmentation and fundamental vision-language techniques. These workflows transform vast image editing datasets and open-world videos into a high-quality dataset for training EffiVED. Experimental results reveal that EffiVED not only generates high-quality editing videos but also executes rapidly. Finally, we demonstrate that our data collection method significantly improves editing performance and can potentially tackle the scarcity of video editing data. The datasets will be made publicly available upon publication.
Finetuned Multimodal Language Models Are High-Quality Image-Text Data Filters
Mar 05, 2024



Abstract:We propose a novel framework for filtering image-text data by leveraging fine-tuned Multimodal Language Models (MLMs). Our approach outperforms predominant filtering methods (e.g., CLIPScore) via integrating the recent advances in MLMs. We design four distinct yet complementary metrics to holistically measure the quality of image-text data. A new pipeline is established to construct high-quality instruction data for fine-tuning MLMs as data filters. Comparing with CLIPScore, our MLM filters produce more precise and comprehensive scores that directly improve the quality of filtered data and boost the performance of pre-trained models. We achieve significant improvements over CLIPScore on popular foundation models (i.e., CLIP and BLIP2) and various downstream tasks. Our MLM filter can generalize to different models and tasks, and be used as a drop-in replacement for CLIPScore. An additional ablation study is provided to verify our design choices for the MLM filter.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge