Zhichao Wei
MM-Diff: High-Fidelity Image Personalization via Multi-Modal Condition Integration
Mar 22, 2024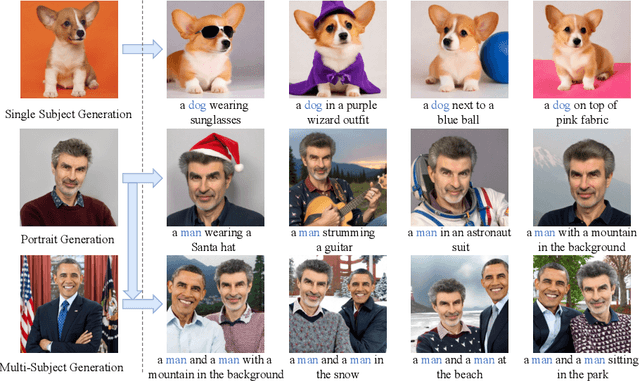
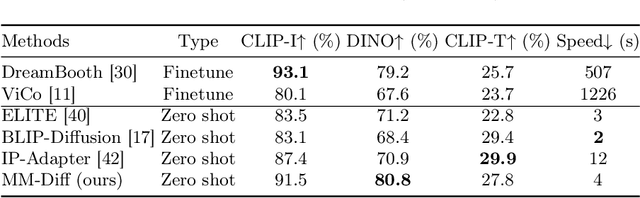
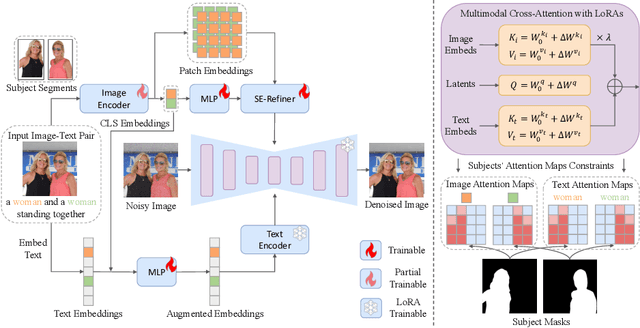
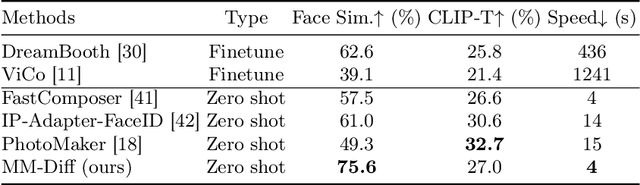
Abstract:Recent advances in tuning-free personalized image generation based on diffusion models are impressive. However, to improve subject fidelity, existing methods either retrain the diffusion model or infuse it with dense visual embeddings, both of which suffer from poor generalization and efficiency. Also, these methods falter in multi-subject image generation due to the unconstrained cross-attention mechanism. In this paper, we propose MM-Diff, a unified and tuning-free image personalization framework capable of generating high-fidelity images of both single and multiple subjects in seconds. Specifically, to simultaneously enhance text consistency and subject fidelity, MM-Diff employs a vision encoder to transform the input image into CLS and patch embeddings. CLS embeddings are used on the one hand to augment the text embeddings, and on the other hand together with patch embeddings to derive a small number of detail-rich subject embeddings, both of which are efficiently integrated into the diffusion model through the well-designed multimodal cross-attention mechanism. Additionally, MM-Diff introduces cross-attention map constraints during the training phase, ensuring flexible multi-subject image sampling during inference without any predefined inputs (e.g., layout). Extensive experiments demonstrate the superior performance of MM-Diff over other leading methods.
UVOSAM: A Mask-free Paradigm for Unsupervised Video Object Segmentation via Segment Anything Model
May 22, 2023



Abstract:Unsupervised video object segmentation has made significant progress in recent years, but the manual annotation of video mask datasets is expensive and limits the diversity of available datasets. The Segment Anything Model (SAM) has introduced a new prompt-driven paradigm for image segmentation, unlocking a range of previously unexplored capabilities. In this paper, we propose a novel paradigm called UVOSAM, which leverages SAM for unsupervised video object segmentation without requiring video mask labels. To address SAM's limitations in instance discovery and identity association, we introduce a video salient object tracking network that automatically generates trajectories for prominent foreground objects. These trajectories then serve as prompts for SAM to produce video masks on a frame-by-frame basis. Our experimental results demonstrate that UVOSAM significantly outperforms current mask-supervised methods. These findings suggest that UVOSAM has the potential to improve unsupervised video object segmentation and reduce the cost of manual annotation.
Learning Aligned Cross-modal Representations for Referring Image Segmentation
Jan 16, 2023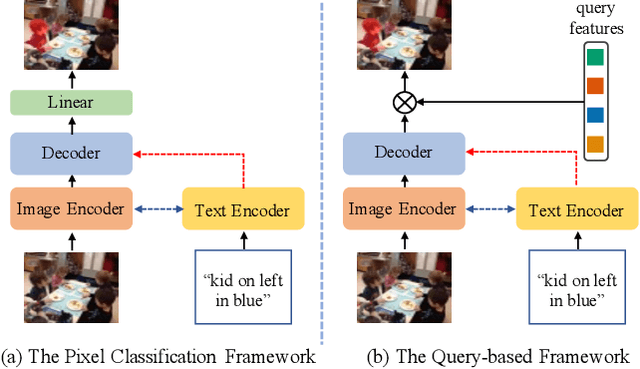
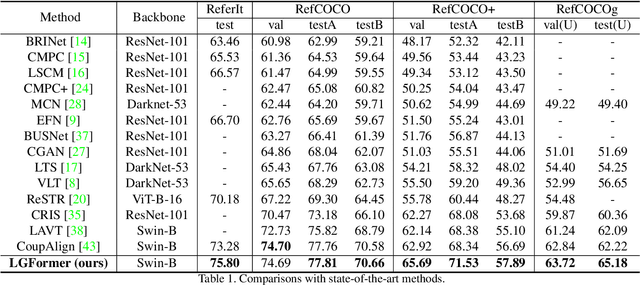
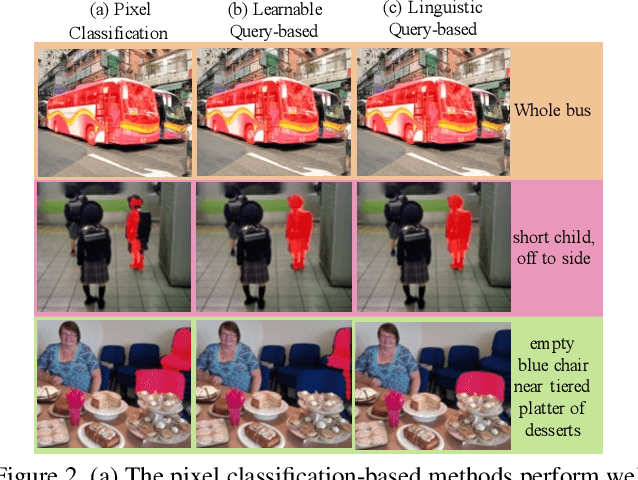
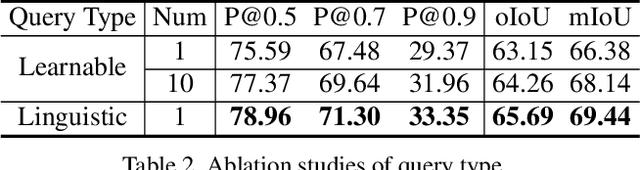
Abstract:Referring image segmentation aims to segment the image region of interest according to the given language expression, which is a typical multi-modal task. One of the critical challenges of this task is to align semantic representations for different modalities including vision and language. To achieve this, previous methods perform cross-modal interactions to update visual features but ignore the role of integrating fine-grained visual features into linguistic features. We present AlignFormer, an end-to-end framework for referring image segmentation. Our AlignFormer views the linguistic feature as the center embedding and segments the region of interest by pixels grouping based on the center embedding. For achieving the pixel-text alignment, we design a Vision-Language Bidirectional Attention module (VLBA) and resort contrastive learning. Concretely, the VLBA enhances visual features by propagating semantic text representations to each pixel and promotes linguistic features by fusing fine-grained image features. Moreover, we introduce the cross-modal instance contrastive loss to alleviate the influence of pixel samples in ambiguous regions and improve the ability to align multi-modal representations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our AlignFormer achieves a new state-of-the-art performance on RefCOCO, RefCOCO+, and RefCOCOg by large margins.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge