Xiaohao Chen
Learning Aligned Cross-modal Representations for Referring Image Segmentation
Jan 16, 2023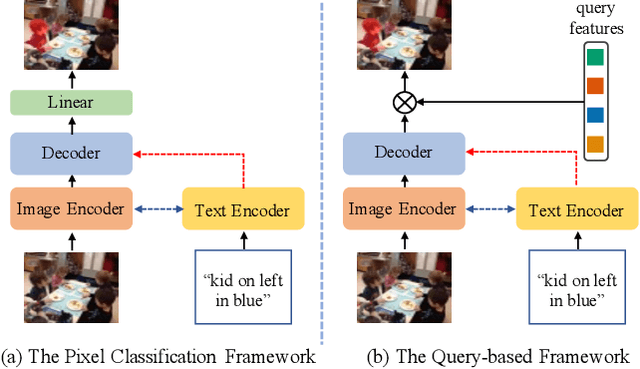
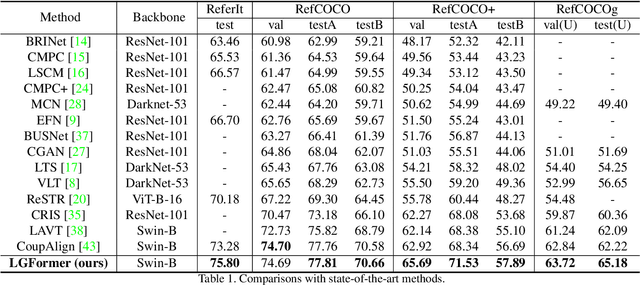
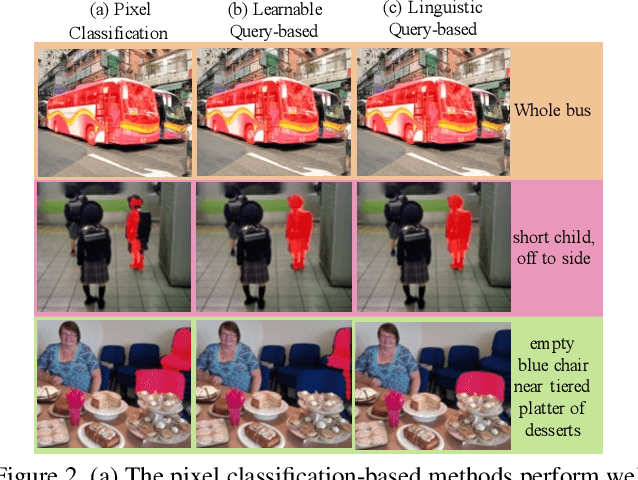
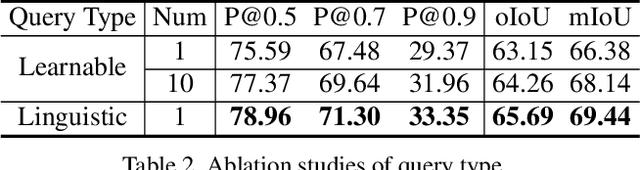
Abstract:Referring image segmentation aims to segment the image region of interest according to the given language expression, which is a typical multi-modal task. One of the critical challenges of this task is to align semantic representations for different modalities including vision and language. To achieve this, previous methods perform cross-modal interactions to update visual features but ignore the role of integrating fine-grained visual features into linguistic features. We present AlignFormer, an end-to-end framework for referring image segmentation. Our AlignFormer views the linguistic feature as the center embedding and segments the region of interest by pixels grouping based on the center embedding. For achieving the pixel-text alignment, we design a Vision-Language Bidirectional Attention module (VLBA) and resort contrastive learning. Concretely, the VLBA enhances visual features by propagating semantic text representations to each pixel and promotes linguistic features by fusing fine-grained image features. Moreover, we introduce the cross-modal instance contrastive loss to alleviate the influence of pixel samples in ambiguous regions and improve the ability to align multi-modal representations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our AlignFormer achieves a new state-of-the-art performance on RefCOCO, RefCOCO+, and RefCOCOg by large margins.
GB-CosFace: Rethinking Softmax-based Face Recognition from the Perspective of Open Set Classification
Nov 22, 2021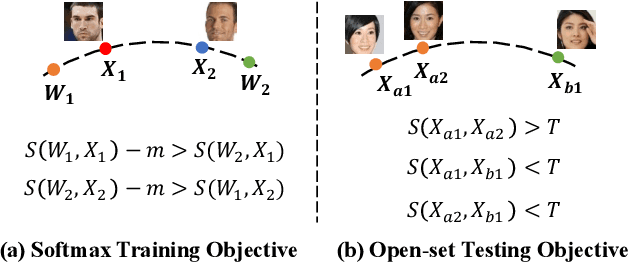
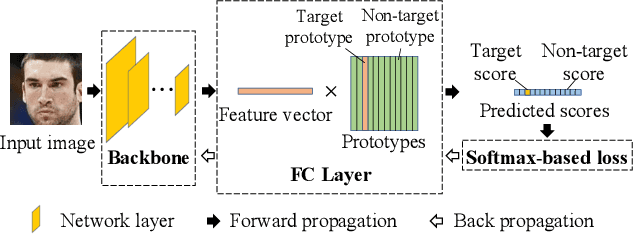
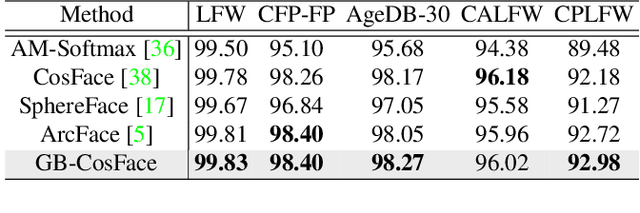
Abstract:State-of-the-art face recognition methods typically take the multi-classification pipeline and adopt the softmax-based loss for optimization. Although these methods have achieved great success, the softmax-based loss has its limitation from the perspective of open set classification: the multi-classification objective in the training phase does not strictly match the objective of open set classification testing. In this paper, we derive a new loss named global boundary CosFace (GB-CosFace). Our GB-CosFace introduces an adaptive global boundary to determine whether two face samples belong to the same identity so that the optimization objective is aligned with the testing process from the perspective of open set classification. Meanwhile, since the loss formulation is derived from the softmax-based loss, our GB-CosFace retains the excellent properties of the softmax-based loss, and CosFace is proved to be a special case of the proposed loss. We analyze and explain the proposed GB-CosFace geometrically. Comprehensive experiments on multiple face recognition benchmarks indicate that the proposed GB-CosFace outperforms current state-of-the-art face recognition losses in mainstream face recognition tasks. Compared to CosFace, our GB-CosFace improves 1.58%, 0.57%, and 0.28% at TAR@FAR=1e-6, 1e-5, 1e-4 on IJB-C benchmark.
FloorPlanCAD: A Large-Scale CAD Drawing Dataset for Panoptic Symbol Spotting
May 15, 2021



Abstract:Access to large and diverse computer-aided design (CAD) drawings is critical for developing symbol spotting algorithms. In this paper, we present FloorPlanCAD, a large-scale real-world CAD drawing dataset containing over 10,000 floor plans, ranging from residential to commercial buildings. CAD drawings in the dataset are all represented as vector graphics, which enable us to provide line-grained annotations of 30 object categories. Equipped by such annotations, we introduce the task of panoptic symbol spotting, which requires to spot not only instances of countable things, but also the semantic of uncountable stuff. Aiming to solve this task, we propose a novel method by combining Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) with Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), which captures both non-Euclidean and Euclidean features and can be trained end-to-end. The proposed CNN-GCN method achieved state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on the task of semantic symbol spotting, and help us build a baseline network for the panoptic symbol spotting task. Our contributions are three-fold: 1) to the best of our knowledge, the presented CAD drawing dataset is the first of its kind; 2) the panoptic symbol spotting task considers the spotting of both thing instances and stuff semantic as one recognition problem; and 3) we presented a baseline solution to the panoptic symbol spotting task based on a novel CNN-GCN method, which achieved SOTA performance on semantic symbol spotting. We believe that these contributions will boost research in related areas.
CondLaneNet: a Top-to-down Lane Detection Framework Based on Conditional Convolution
May 11, 2021
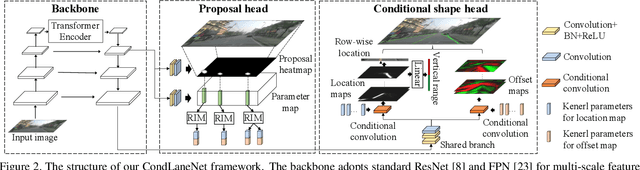

Abstract:Modern deep-learning-based lane detection methods are successful in most scenarios but struggling for lane lines with complex topologies. In this work, we propose CondLaneNet, a novel top-to-down lane detection framework that detects the lane instances first and then dynamically predicts the line shape for each instance. Aiming to resolve lane instance-level discrimination problem, we introduce a conditional lane detection strategy based on conditional convolution and row-wise formulation. Further, we design the Recurrent Instance Module(RIM) to overcome the problem of detecting lane lines with complex topologies such as dense lines and fork lines. Benefit from the end-to-end pipeline which requires little post-process, our method has real-time efficiency. We extensively evaluate our method on three benchmarks of lane detection. Results show that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on all three benchmark datasets. Moreover, our method has the coexistence of accuracy and efficiency, e.g. a 78.14 F1 score and 220 FPS on CULane.
Learning Selfie-Friendly Abstraction from Artistic Style Images
May 21, 2018



Abstract:Artistic style transfer can be thought as a process to generate different versions of abstraction of the original image. However, most of the artistic style transfer operators are not optimized for human faces thus mainly suffers from two undesirable features when applying them to selfies. First, the edges of human faces may unpleasantly deviate from the ones in the original image. Second, the skin color is far from faithful to the original one which is usually problematic in producing quality selfies. In this paper, we take a different approach and formulate this abstraction process as a gradient domain learning problem. We aim to learn a type of abstraction which not only achieves the specified artistic style but also circumvents the two aforementioned drawbacks thus highly applicable to selfie photography. We also show that our method can be directly generalized to videos with high inter-frame consistency. Our method is also robust to non-selfie images, and the generalization to various kinds of real-life scenes is discussed. We will make our code publicly available.
Robust Tracking Using Region Proposal Networks
May 30, 2017



Abstract:Recent advances in visual tracking showed that deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) trained for image classification can be strong feature extractors for discriminative trackers. However, due to the drastic difference between image classification and tracking, extra treatments such as model ensemble and feature engineering must be carried out to bridge the two domains. Such procedures are either time consuming or hard to generalize well across datasets. In this paper we discovered that the internal structure of Region Proposal Network (RPN)'s top layer feature can be utilized for robust visual tracking. We showed that such property has to be unleashed by a novel loss function which simultaneously considers classification accuracy and bounding box quality. Without ensemble and any extra treatment on feature maps, our proposed method achieved state-of-the-art results on several large scale benchmarks including OTB50, OTB100 and VOT2016. We will make our code publicly available.
Accurate Single Stage Detector Using Recurrent Rolling Convolution
Apr 19, 2017



Abstract:Most of the recent successful methods in accurate object detection and localization used some variants of R-CNN style two stage Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) where plausible regions were proposed in the first stage then followed by a second stage for decision refinement. Despite the simplicity of training and the efficiency in deployment, the single stage detection methods have not been as competitive when evaluated in benchmarks consider mAP for high IoU thresholds. In this paper, we proposed a novel single stage end-to-end trainable object detection network to overcome this limitation. We achieved this by introducing Recurrent Rolling Convolution (RRC) architecture over multi-scale feature maps to construct object classifiers and bounding box regressors which are "deep in context". We evaluated our method in the challenging KITTI dataset which measures methods under IoU threshold of 0.7. We showed that with RRC, a single reduced VGG-16 based model already significantly outperformed all the previously published results. At the time this paper was written our models ranked the first in KITTI car detection (the hard level), the first in cyclist detection and the second in pedestrian detection. These results were not reached by the previous single stage methods. The code is publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge