Honghua Li
GAT-CADNet: Graph Attention Network for Panoptic Symbol Spotting in CAD Drawings
Jan 10, 2022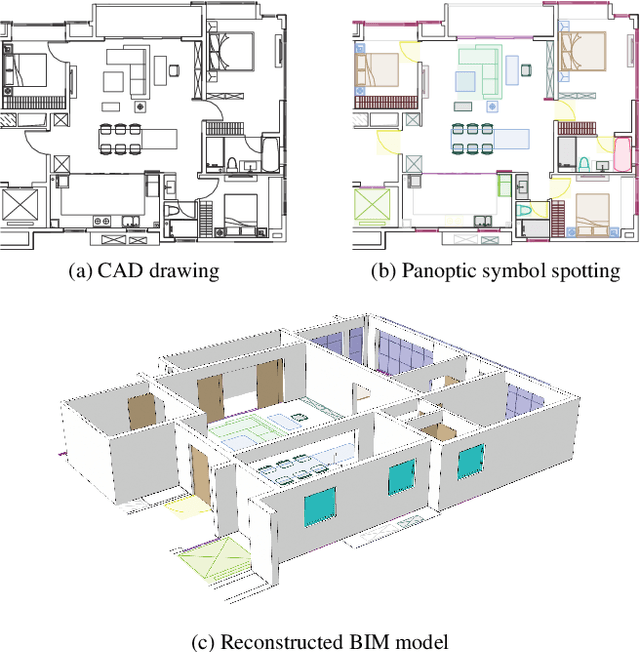
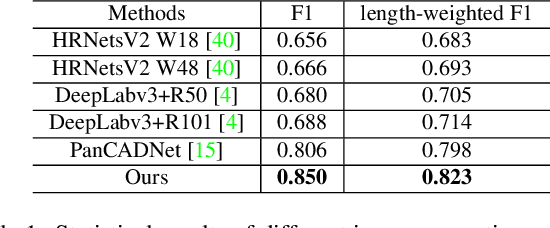
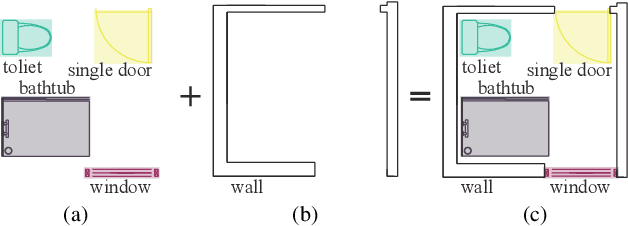
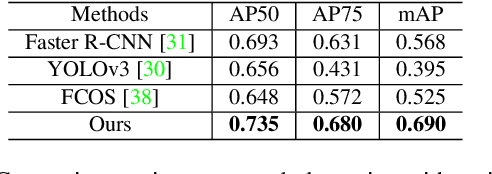
Abstract:Spotting graphical symbols from the computer-aided design (CAD) drawings is essential to many industrial applications. Different from raster images, CAD drawings are vector graphics consisting of geometric primitives such as segments, arcs, and circles. By treating each CAD drawing as a graph, we propose a novel graph attention network GAT-CADNet to solve the panoptic symbol spotting problem: vertex features derived from the GAT branch are mapped to semantic labels, while their attention scores are cascaded and mapped to instance prediction. Our key contributions are three-fold: 1) the instance symbol spotting task is formulated as a subgraph detection problem and solved by predicting the adjacency matrix; 2) a relative spatial encoding (RSE) module explicitly encodes the relative positional and geometric relation among vertices to enhance the vertex attention; 3) a cascaded edge encoding (CEE) module extracts vertex attentions from multiple stages of GAT and treats them as edge encoding to predict the adjacency matrix. The proposed GAT-CADNet is intuitive yet effective and manages to solve the panoptic symbol spotting problem in one consolidated network. Extensive experiments and ablation studies on the public benchmark show that our graph-based approach surpasses existing state-of-the-art methods by a large margin.
FloorPlanCAD: A Large-Scale CAD Drawing Dataset for Panoptic Symbol Spotting
May 15, 2021



Abstract:Access to large and diverse computer-aided design (CAD) drawings is critical for developing symbol spotting algorithms. In this paper, we present FloorPlanCAD, a large-scale real-world CAD drawing dataset containing over 10,000 floor plans, ranging from residential to commercial buildings. CAD drawings in the dataset are all represented as vector graphics, which enable us to provide line-grained annotations of 30 object categories. Equipped by such annotations, we introduce the task of panoptic symbol spotting, which requires to spot not only instances of countable things, but also the semantic of uncountable stuff. Aiming to solve this task, we propose a novel method by combining Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) with Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), which captures both non-Euclidean and Euclidean features and can be trained end-to-end. The proposed CNN-GCN method achieved state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on the task of semantic symbol spotting, and help us build a baseline network for the panoptic symbol spotting task. Our contributions are three-fold: 1) to the best of our knowledge, the presented CAD drawing dataset is the first of its kind; 2) the panoptic symbol spotting task considers the spotting of both thing instances and stuff semantic as one recognition problem; and 3) we presented a baseline solution to the panoptic symbol spotting task based on a novel CNN-GCN method, which achieved SOTA performance on semantic symbol spotting. We believe that these contributions will boost research in related areas.
Single-Shot is Enough: Panoramic Infrastructure Based Calibration of Multiple Cameras and 3D LiDARs
Mar 24, 2021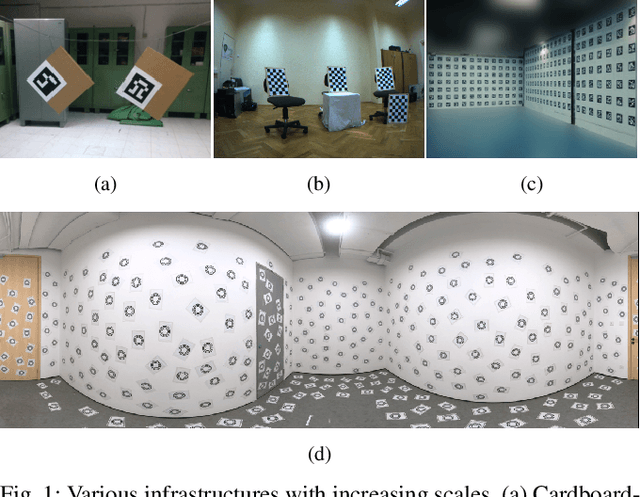
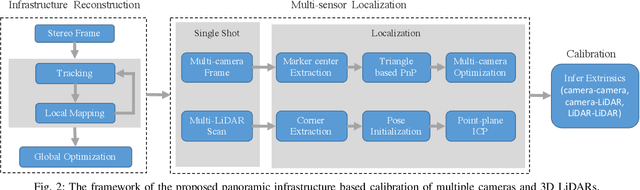
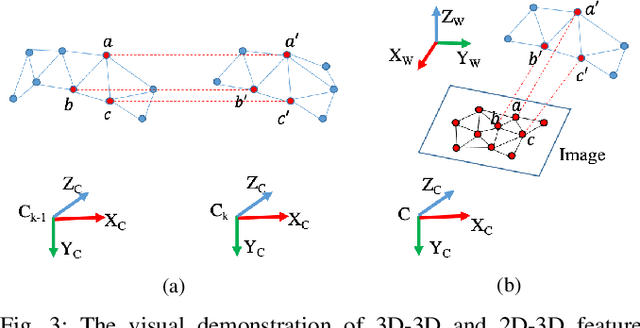
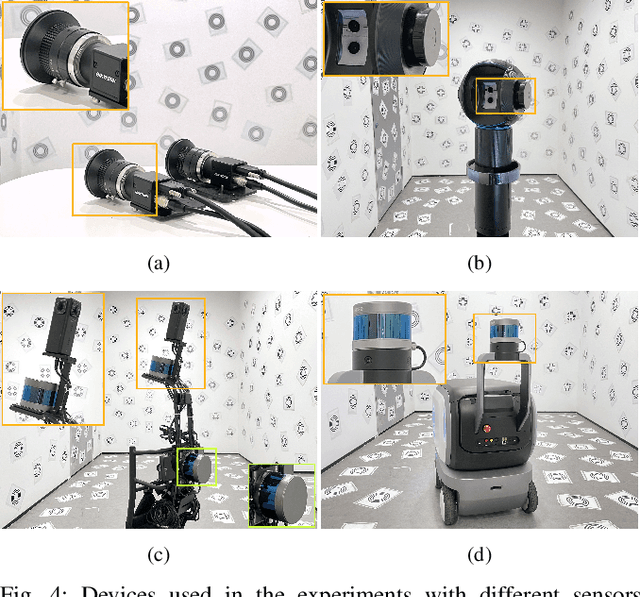
Abstract:The integration of multiple cameras and 3D Li- DARs has become basic configuration of augmented reality devices, robotics, and autonomous vehicles. The calibration of multi-modal sensors is crucial for a system to properly function, but it remains tedious and impractical for mass production. Moreover, most devices require re-calibration after usage for certain period of time. In this paper, we propose a single-shot solution for calibrating extrinsic transformations among multiple cameras and 3D LiDARs. We establish a panoramic infrastructure, in which a camera or LiDAR can be robustly localized using data from single frame. Experiments are conducted on three devices with different camera-LiDAR configurations, showing that our approach achieved comparable calibration accuracy with the state-of-the-art approaches but with much greater efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge