GB-CosFace: Rethinking Softmax-based Face Recognition from the Perspective of Open Set Classification
Paper and Code
Nov 22, 2021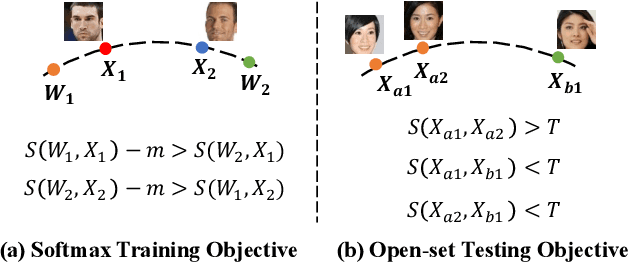
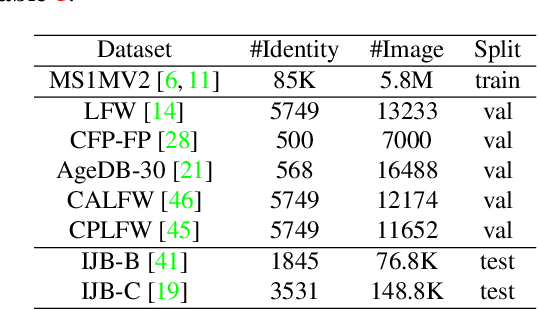
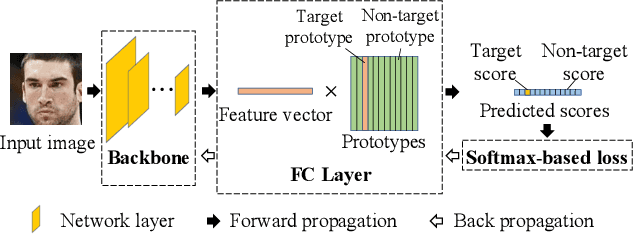
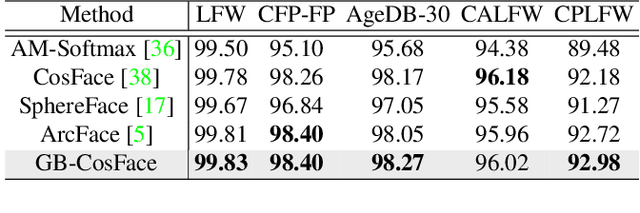
State-of-the-art face recognition methods typically take the multi-classification pipeline and adopt the softmax-based loss for optimization. Although these methods have achieved great success, the softmax-based loss has its limitation from the perspective of open set classification: the multi-classification objective in the training phase does not strictly match the objective of open set classification testing. In this paper, we derive a new loss named global boundary CosFace (GB-CosFace). Our GB-CosFace introduces an adaptive global boundary to determine whether two face samples belong to the same identity so that the optimization objective is aligned with the testing process from the perspective of open set classification. Meanwhile, since the loss formulation is derived from the softmax-based loss, our GB-CosFace retains the excellent properties of the softmax-based loss, and CosFace is proved to be a special case of the proposed loss. We analyze and explain the proposed GB-CosFace geometrically. Comprehensive experiments on multiple face recognition benchmarks indicate that the proposed GB-CosFace outperforms current state-of-the-art face recognition losses in mainstream face recognition tasks. Compared to CosFace, our GB-CosFace improves 1.58%, 0.57%, and 0.28% at TAR@FAR=1e-6, 1e-5, 1e-4 on IJB-C benchmark.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge