Tianyang Chen
Whole-Body Control Through Narrow Gaps From Pixels To Action
Sep 02, 2024


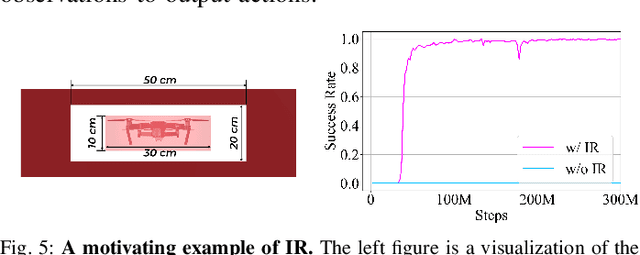
Abstract:Flying through body-size narrow gaps in the environment is one of the most challenging moments for an underactuated multirotor. We explore a purely data-driven method to master this flight skill in simulation, where a neural network directly maps pixels and proprioception to continuous low-level control commands. This learned policy enables whole-body control through gaps with different geometries demanding sharp attitude changes (e.g., near-vertical roll angle). The policy is achieved by successive model-free reinforcement learning (RL) and online observation space distillation. The RL policy receives (virtual) point clouds of the gaps' edges for scalable simulation and is then distilled into the high-dimensional pixel space. However, this flight skill is fundamentally expensive to learn by exploring due to restricted feasible solution space. We propose to reset the agent as states on the trajectories by a model-based trajectory optimizer to alleviate this problem. The presented training pipeline is compared with baseline methods, and ablation studies are conducted to identify the key ingredients of our method. The immediate next step is to scale up the variation of gap sizes and geometries in anticipation of emergent policies and demonstrate the sim-to-real transformation.
Large Language Model based Situational Dialogues for Second Language Learning
Mar 29, 2024Abstract:In second language learning, scenario-based conversation practice is important for language learners to achieve fluency in speaking, but students often lack sufficient opportunities to practice their conversational skills with qualified instructors or native speakers. To bridge this gap, we propose situational dialogue models for students to engage in conversational practice. Our situational dialogue models are fine-tuned on large language models (LLMs), with the aim of combining the engaging nature of an open-ended conversation with the focused practice of scenario-based tasks. Leveraging the generalization capabilities of LLMs, we demonstrate that our situational dialogue models perform effectively not only on training topics but also on topics not encountered during training. This offers a promising solution to support a wide range of conversational topics without extensive manual work. Additionally, research in the field of dialogue systems still lacks reliable automatic evaluation metrics, leading to human evaluation as the gold standard (Smith et al., 2022), which is typically expensive. To address the limitations of existing evaluation methods, we present a novel automatic evaluation method that employs fine-tuned LLMs to efficiently and effectively assess the performance of situational dialogue models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge