Weitian Chen
Department of Imaging and Interventional Radiology, the Chinese University of Hong Kong
Utilizing 3D Fast Spin Echo Anatomical Imaging to Reduce the Number of Contrast Preparations in $T_{1ρ}$ Quantification of Knee Cartilage Using Learning-Based Methods
Feb 13, 2025
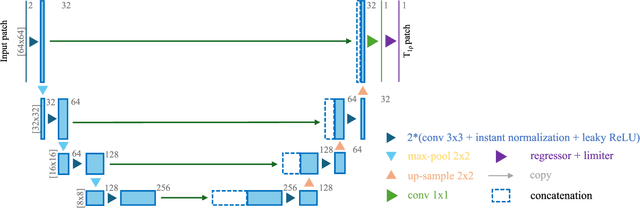
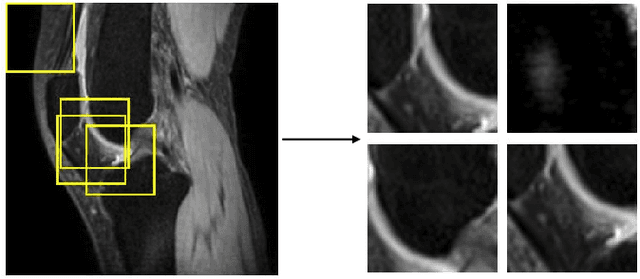

Abstract:Purpose: To propose and evaluate an accelerated $T_{1\rho}$ quantification method that combines $T_{1\rho}$-weighted fast spin echo (FSE) images and proton density (PD)-weighted anatomical FSE images, leveraging deep learning models for $T_{1\rho}$ mapping. The goal is to reduce scan time and facilitate integration into routine clinical workflows for osteoarthritis (OA) assessment. Methods: This retrospective study utilized MRI data from 40 participants (30 OA patients and 10 healthy volunteers). A volume of PD-weighted anatomical FSE images and a volume of $T_{1\rho}$-weighted images acquired at a non-zero spin-lock time were used as input to train deep learning models, including a 2D U-Net and a multi-layer perceptron (MLP). $T_{1\rho}$ maps generated by these models were compared with ground truth maps derived from a traditional non-linear least squares (NLLS) fitting method using four $T_{1\rho}$-weighted images. Evaluation metrics included mean absolute error (MAE), mean absolute percentage error (MAPE), regional error (RE), and regional percentage error (RPE). Results: Deep learning models achieved RPEs below 5% across all evaluated scenarios, outperforming NLLS methods, especially in low signal-to-noise conditions. The best results were obtained using the 2D U-Net, which effectively leveraged spatial information for accurate $T_{1\rho}$ fitting. The proposed method demonstrated compatibility with shorter TSLs, alleviating RF hardware and specific absorption rate (SAR) limitations. Conclusion: The proposed approach enables efficient $T_{1\rho}$ mapping using PD-weighted anatomical images, reducing scan time while maintaining clinical standards. This method has the potential to facilitate the integration of quantitative MRI techniques into routine clinical practice, benefiting OA diagnosis and monitoring.
ERANet: Edge Replacement Augmentation for Semi-Supervised Meniscus Segmentation with Prototype Consistency Alignment and Conditional Self-Training
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:Manual segmentation is labor-intensive, and automatic segmentation remains challenging due to the inherent variability in meniscal morphology, partial volume effects, and low contrast between the meniscus and surrounding tissues. To address these challenges, we propose ERANet, an innovative semi-supervised framework for meniscus segmentation that effectively leverages both labeled and unlabeled images through advanced augmentation and learning strategies. ERANet integrates three key components: edge replacement augmentation (ERA), prototype consistency alignment (PCA), and a conditional self-training (CST) strategy within a mean teacher architecture. ERA introduces anatomically relevant perturbations by simulating meniscal variations, ensuring that augmentations align with the structural context. PCA enhances segmentation performance by aligning intra-class features and promoting compact, discriminative feature representations, particularly in scenarios with limited labeled data. CST improves segmentation robustness by iteratively refining pseudo-labels and mitigating the impact of label noise during training. Together, these innovations establish ERANet as a robust and scalable solution for meniscus segmentation, effectively addressing key barriers to practical implementation. We validated ERANet comprehensively on 3D Double Echo Steady State (DESS) and 3D Fast/Turbo Spin Echo (FSE/TSE) MRI sequences. The results demonstrate the superior performance of ERANet compared to state-of-the-art methods. The proposed framework achieves reliable and accurate segmentation of meniscus structures, even when trained on minimal labeled data. Extensive ablation studies further highlight the synergistic contributions of ERA, PCA, and CST, solidifying ERANet as a transformative solution for semi-supervised meniscus segmentation in medical imaging.
Quantifying Knee Cartilage Shape and Lesion: From Image to Metrics
Sep 11, 2024



Abstract:Imaging features of knee articular cartilage have been shown to be potential imaging biomarkers for knee osteoarthritis. Despite recent methodological advancements in image analysis techniques like image segmentation, registration, and domain-specific image computing algorithms, only a few works focus on building fully automated pipelines for imaging feature extraction. In this study, we developed a deep-learning-based medical image analysis application for knee cartilage morphometrics, CartiMorph Toolbox (CMT). We proposed a 2-stage joint template learning and registration network, CMT-reg. We trained the model using the OAI-ZIB dataset and assessed its performance in template-to-image registration. The CMT-reg demonstrated competitive results compared to other state-of-the-art models. We integrated the proposed model into an automated pipeline for the quantification of cartilage shape and lesion (full-thickness cartilage loss, specifically). The toolbox provides a comprehensive, user-friendly solution for medical image analysis and data visualization. The software and models are available at https://github.com/YongchengYAO/CMT-AMAI24paper .
Chemical Shift Encoding based Double Bonds Quantification in Triglycerides using Deep Image Prior
Jul 02, 2024



Abstract:This study evaluated a deep learning-based method using Deep Image Prior (DIP) to quantify triglyceride double bonds from chemical-shift encoded multi-echo gradient echo images without network training. We employed a cost function based on signal constraints to iteratively update the neural network on a single dataset. The method was validated using phantom experiments and in vivo scans. Results showed close alignment between measured and reference double bond values, with phantom experiments yielding a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.96 (p = .0005). In vivo results demonstrated good agreement in subcutaneous fat. We conclude that Deep Image Prior shows feasibility for quantifying double bonds and fatty acid content from chemical-shift encoded multi-echo MRI.
The state-of-the-art in Cardiac MRI Reconstruction: Results of the CMRxRecon Challenge in MICCAI 2023
Apr 01, 2024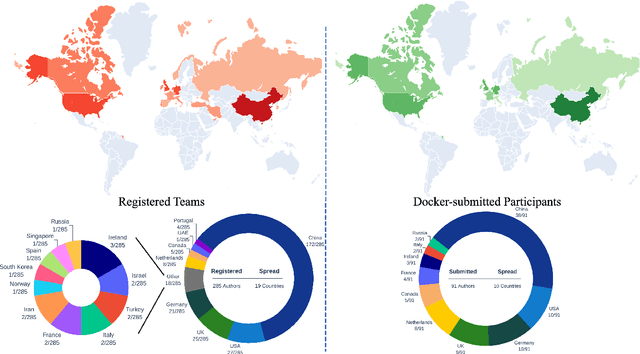
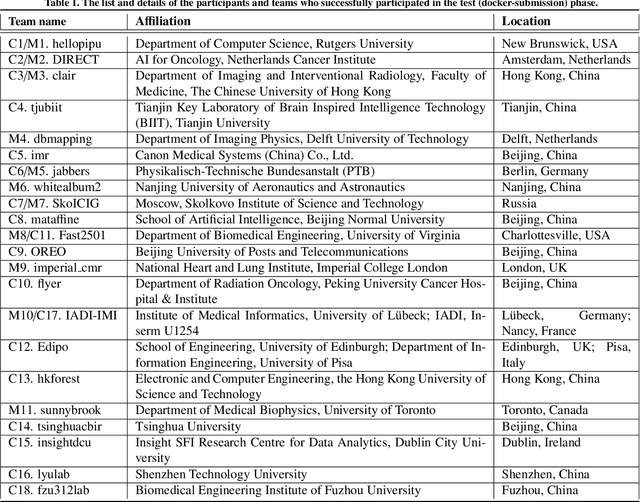
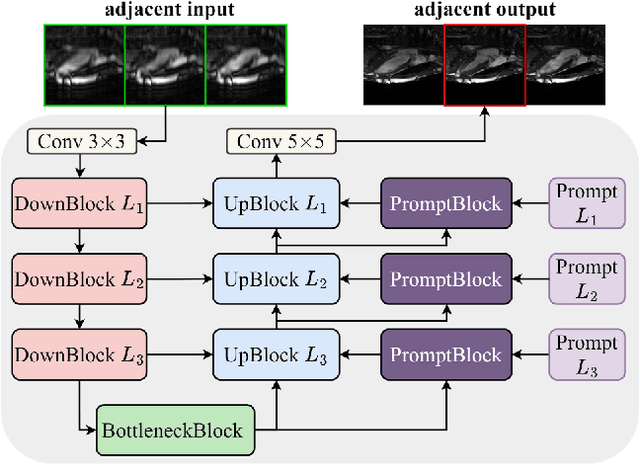
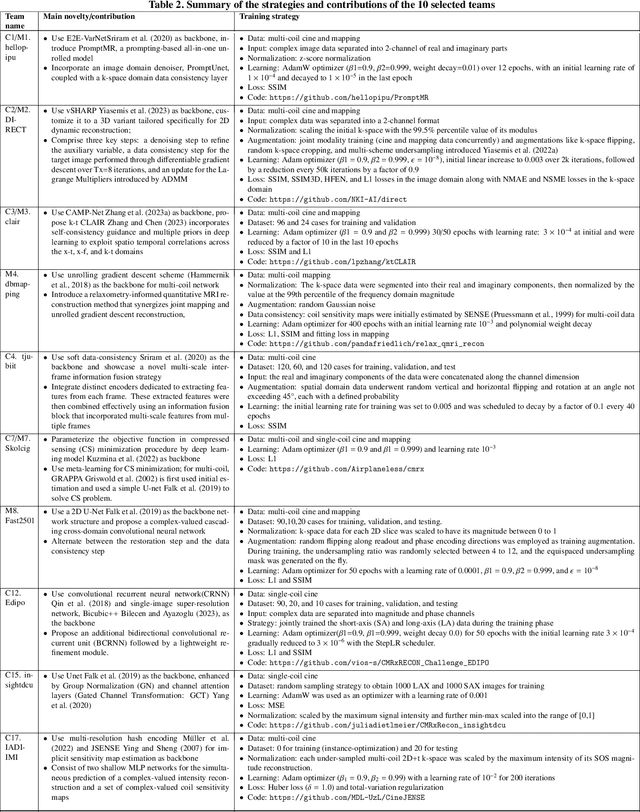
Abstract:Cardiac MRI, crucial for evaluating heart structure and function, faces limitations like slow imaging and motion artifacts. Undersampling reconstruction, especially data-driven algorithms, has emerged as a promising solution to accelerate scans and enhance imaging performance using highly under-sampled data. Nevertheless, the scarcity of publicly available cardiac k-space datasets and evaluation platform hinder the development of data-driven reconstruction algorithms. To address this issue, we organized the Cardiac MRI Reconstruction Challenge (CMRxRecon) in 2023, in collaboration with the 26th International Conference on MICCAI. CMRxRecon presented an extensive k-space dataset comprising cine and mapping raw data, accompanied by detailed annotations of cardiac anatomical structures. With overwhelming participation, the challenge attracted more than 285 teams and over 600 participants. Among them, 22 teams successfully submitted Docker containers for the testing phase, with 7 teams submitted for both cine and mapping tasks. All teams use deep learning based approaches, indicating that deep learning has predominately become a promising solution for the problem. The first-place winner of both tasks utilizes the E2E-VarNet architecture as backbones. In contrast, U-Net is still the most popular backbone for both multi-coil and single-coil reconstructions. This paper provides a comprehensive overview of the challenge design, presents a summary of the submitted results, reviews the employed methods, and offers an in-depth discussion that aims to inspire future advancements in cardiac MRI reconstruction models. The summary emphasizes the effective strategies observed in Cardiac MRI reconstruction, including backbone architecture, loss function, pre-processing techniques, physical modeling, and model complexity, thereby providing valuable insights for further developments in this field.
$k$-$t$ CLAIR: Self-Consistency Guided Multi-Prior Learning for Dynamic Parallel MR Image Reconstruction
Oct 17, 2023



Abstract:Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR) has been widely used in clinical practice for the medical diagnosis of cardiac diseases. However, the long acquisition time hinders its development in real-time applications. Here, we propose a novel self-consistency guided multi-prior learning framework named $k$-$t$ CLAIR to exploit spatiotemporal correlations from highly undersampled data for accelerated dynamic parallel MRI reconstruction. The $k$-$t$ CLAIR progressively reconstructs faithful images by leveraging multiple complementary priors learned in the $x$-$t$, $x$-$f$, and $k$-$t$ domains in an iterative fashion, as dynamic MRI exhibits high spatiotemporal redundancy. Additionally, $k$-$t$ CLAIR incorporates calibration information for prior learning, resulting in a more consistent reconstruction. Experimental results on cardiac cine and T1W/T2W images demonstrate that $k$-$t$ CLAIR achieves high-quality dynamic MR reconstruction in terms of both quantitative and qualitative performance.
CartiMorph: a framework for automated knee articular cartilage morphometrics
Aug 03, 2023Abstract:We introduce CartiMorph, a framework for automated knee articular cartilage morphometrics. It takes an image as input and generates quantitative metrics for cartilage subregions, including the percentage of full-thickness cartilage loss (FCL), mean thickness, surface area, and volume. CartiMorph leverages the power of deep learning models for hierarchical image feature representation. Deep learning models were trained and validated for tissue segmentation, template construction, and template-to-image registration. We established methods for surface-normal-based cartilage thickness mapping, FCL estimation, and rule-based cartilage parcellation. Our cartilage thickness map showed less error in thin and peripheral regions. We evaluated the effectiveness of the adopted segmentation model by comparing the quantitative metrics obtained from model segmentation and those from manual segmentation. The root-mean-squared deviation of the FCL measurements was less than 8%, and strong correlations were observed for the mean thickness (Pearson's correlation coefficient $\rho \in [0.82,0.97]$), surface area ($\rho \in [0.82,0.98]$) and volume ($\rho \in [0.89,0.98]$) measurements. We compared our FCL measurements with those from a previous study and found that our measurements deviated less from the ground truths. We observed superior performance of the proposed rule-based cartilage parcellation method compared with the atlas-based approach. CartiMorph has the potential to promote imaging biomarkers discovery for knee osteoarthritis.
An Uncertainty Aided Framework for Learning based Liver $T_1ρ$ Mapping and Analysis
Jul 07, 2023Abstract:Objective: Quantitative $T_1\rho$ imaging has potential for assessment of biochemical alterations of liver pathologies. Deep learning methods have been employed to accelerate quantitative $T_1\rho$ imaging. To employ artificial intelligence-based quantitative imaging methods in complicated clinical environment, it is valuable to estimate the uncertainty of the predicated $T_1\rho$ values to provide the confidence level of the quantification results. The uncertainty should also be utilized to aid the post-hoc quantitative analysis and model learning tasks. Approach: To address this need, we propose a parametric map refinement approach for learning-based $T_1\rho$ mapping and train the model in a probabilistic way to model the uncertainty. We also propose to utilize the uncertainty map to spatially weight the training of an improved $T_1\rho$ mapping network to further improve the mapping performance and to remove pixels with unreliable $T_1\rho$ values in the region of interest. The framework was tested on a dataset of 51 patients with different liver fibrosis stages. Main results: Our results indicate that the learning-based map refinement method leads to a relative mapping error of less than 3% and provides uncertainty estimation simultaneously. The estimated uncertainty reflects the actual error level, and it can be used to further reduce relative $T_1\rho$ mapping error to 2.60% as well as removing unreliable pixels in the region of interest effectively. Significance: Our studies demonstrate the proposed approach has potential to provide a learning-based quantitative MRI system for trustworthy $T_1\rho$ mapping of the liver.
CAMP-Net: Context-Aware Multi-Prior Network for Accelerated MRI Reconstruction
Jun 20, 2023



Abstract:Despite promising advances in deep learning-based MRI reconstruction methods, restoring high-frequency image details and textures remains a challenging problem for accelerated MRI. To tackle this challenge, we propose a novel context-aware multi-prior network (CAMP-Net) for MRI reconstruction. CAMP-Net leverages the complementary nature of multiple prior knowledge and explores data redundancy between adjacent slices in the hybrid domain to improve image quality. It incorporates three interleaved modules respectively for image enhancement, k-space restoration, and calibration consistency to jointly learn context-aware multiple priors in an end-to-end fashion. The image enhancement module learns a coil-combined image prior to suppress noise-like artifacts, while the k-space restoration module explores multi-coil k-space correlations to recover high-frequency details. The calibration consistency module embeds the known physical properties of MRI acquisition to ensure consistency of k-space correlations extracted from measurements and the artifact-free image intermediate. The resulting low- and high-frequency reconstructions are hierarchically aggregated in a frequency fusion module and iteratively refined to progressively reconstruct the final image. We evaluated the generalizability and robustness of our method on three large public datasets with various accelerations and sampling patterns. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that CAMP-Net outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of reconstruction quality and quantitative $T_2$ mapping.
Uncertainty-weighted Multi-tasking for $T_{1ρ}$ and T$_2$ Mapping in the Liver with Self-supervised Learning
Mar 14, 2023Abstract:Multi-parametric mapping of MRI relaxations in liver has the potential of revealing pathological information of the liver. A self-supervised learning based multi-parametric mapping method is proposed to map T$T_{1\rho}$ and T$_2$ simultaneously, by utilising the relaxation constraint in the learning process. Data noise of different mapping tasks is utilised to make the model uncertainty-aware, which adaptively weight different mapping tasks during learning. The method was examined on a dataset of 51 patients with non-alcoholic fatter liver disease. Results showed that the proposed method can produce comparable parametric maps to the traditional multi-contrast pixel wise fitting method, with a reduced number of images and less computation time. The uncertainty weighting also improves the model performance. It has the potential of accelerating MRI quantitative imaging.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge