Weisong Zhao
UPA: Unsupervised Prompt Agent via Tree-Based Search and Selection
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Prompt agents have recently emerged as a promising paradigm for automated prompt optimization, framing refinement as a sequential decision-making problem over a structured prompt space. While this formulation enables the use of advanced planning algorithms, these methods typically assume access to supervised reward signals, which are often unavailable in practical scenarios. In this work, we propose UPA, an Unsupervised Prompt Agent that realizes structured search and selection without relying on supervised feedback. Specifically, during search, UPA iteratively constructs an evolving tree structure to navigate the prompt space, guided by fine-grained and order-invariant pairwise comparisons from Large Language Models (LLMs). Crucially, as these local comparisons do not inherently yield a consistent global scale, we decouple systematic prompt exploration from final selection, introducing a two-stage framework grounded in the Bradley-Terry-Luce (BTL) model. This framework first performs path-wise Bayesian aggregation of local comparisons to filter candidates under uncertainty, followed by global tournament-style comparisons to infer latent prompt quality and identify the optimal prompt. Experiments across multiple tasks demonstrate that UPA consistently outperforms existing prompt optimization methods, showing that agent-style optimization remains highly effective even in fully unsupervised settings.
One Ring to Rule Them All: Unifying Group-Based RL via Dynamic Power-Mean Geometry
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Group-based reinforcement learning has evolved from the arithmetic mean of GRPO to the geometric mean of GMPO. While GMPO improves stability by constraining a conservative objective, it shares a fundamental limitation with GRPO: reliance on a fixed aggregation geometry that ignores the evolving and heterogeneous nature of each trajectory. In this work, we unify these approaches under Power-Mean Policy Optimization (PMPO), a generalized framework that parameterizes the aggregation geometry via the power-mean geometry exponent p. Within this framework, GRPO and GMPO are recovered as special cases. Theoretically, we demonstrate that adjusting p modulates the concentration of gradient updates, effectively reweighting tokens based on their advantage contribution. To determine p adaptively, we introduce a Clip-aware Effective Sample Size (ESS) mechanism. Specifically, we propose a deterministic rule that maps a trajectory clipping fraction to a target ESS. Then, we solve for the specific p to align the trajectory induced ESS with this target one. This allows PMPO to dynamically transition between the aggressive arithmetic mean for reliable trajectories and the conservative geometric mean for unstable ones. Experiments on multiple mathematical reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that PMPO outperforms strong baselines.
Second FRCSyn-onGoing: Winning Solutions and Post-Challenge Analysis to Improve Face Recognition with Synthetic Data
Dec 02, 2024Abstract:Synthetic data is gaining increasing popularity for face recognition technologies, mainly due to the privacy concerns and challenges associated with obtaining real data, including diverse scenarios, quality, and demographic groups, among others. It also offers some advantages over real data, such as the large amount of data that can be generated or the ability to customize it to adapt to specific problem-solving needs. To effectively use such data, face recognition models should also be specifically designed to exploit synthetic data to its fullest potential. In order to promote the proposal of novel Generative AI methods and synthetic data, and investigate the application of synthetic data to better train face recognition systems, we introduce the 2nd FRCSyn-onGoing challenge, based on the 2nd Face Recognition Challenge in the Era of Synthetic Data (FRCSyn), originally launched at CVPR 2024. This is an ongoing challenge that provides researchers with an accessible platform to benchmark i) the proposal of novel Generative AI methods and synthetic data, and ii) novel face recognition systems that are specifically proposed to take advantage of synthetic data. We focus on exploring the use of synthetic data both individually and in combination with real data to solve current challenges in face recognition such as demographic bias, domain adaptation, and performance constraints in demanding situations, such as age disparities between training and testing, changes in the pose, or occlusions. Very interesting findings are obtained in this second edition, including a direct comparison with the first one, in which synthetic databases were restricted to DCFace and GANDiffFace.
Enhancing Instruction-Following Capability of Visual-Language Models by Reducing Image Redundancy
Nov 23, 2024


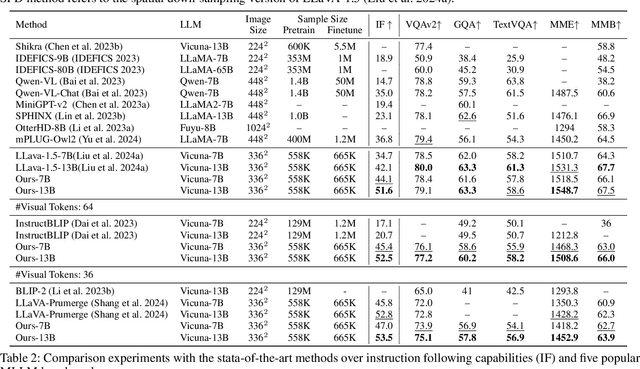
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have strong instruction-following capability to interpret and execute tasks as directed by human commands. Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have inferior instruction-following ability compared to LLMs. However, there is a significant gap in the instruction-following capabilities between the MLLMs and LLMs. In this study, we conduct a pilot experiment, which demonstrates that spatially down-sampling visual tokens significantly enhances the instruction-following capability of MLLMs. This is attributed to the substantial redundancy in visual modality. However, this intuitive method severely impairs the MLLM's multimodal understanding capability. In this paper, we propose Visual-Modality Token Compression (VMTC) and Cross-Modality Attention Inhibition (CMAI) strategies to alleviate this gap between MLLMs and LLMs by inhibiting the influence of irrelevant visual tokens during content generation, increasing the instruction-following ability of the MLLMs while retaining their multimodal understanding capacity. In VMTC module, the primary tokens are retained and the redundant tokens are condensed by token clustering and merging. In CMAI process, we aggregate text-to-image attentions by text-to-text attentions to obtain a text-to-image focus score. Attention inhibition is performed on the text-image token pairs with low scores. Our comprehensive experiments over instruction-following capabilities and VQA-V2, GQA, TextVQA, MME and MMBench five benchmarks, demonstrate that proposed strategy significantly enhances the instruction following capability of MLLMs while preserving the ability to understand and process multimodal inputs.
Second Edition FRCSyn Challenge at CVPR 2024: Face Recognition Challenge in the Era of Synthetic Data
Apr 16, 2024



Abstract:Synthetic data is gaining increasing relevance for training machine learning models. This is mainly motivated due to several factors such as the lack of real data and intra-class variability, time and errors produced in manual labeling, and in some cases privacy concerns, among others. This paper presents an overview of the 2nd edition of the Face Recognition Challenge in the Era of Synthetic Data (FRCSyn) organized at CVPR 2024. FRCSyn aims to investigate the use of synthetic data in face recognition to address current technological limitations, including data privacy concerns, demographic biases, generalization to novel scenarios, and performance constraints in challenging situations such as aging, pose variations, and occlusions. Unlike the 1st edition, in which synthetic data from DCFace and GANDiffFace methods was only allowed to train face recognition systems, in this 2nd edition we propose new sub-tasks that allow participants to explore novel face generative methods. The outcomes of the 2nd FRCSyn Challenge, along with the proposed experimental protocol and benchmarking contribute significantly to the application of synthetic data to face recognition.
* arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2311.10476
FRCSyn Challenge at WACV 2024:Face Recognition Challenge in the Era of Synthetic Data
Nov 17, 2023



Abstract:Despite the widespread adoption of face recognition technology around the world, and its remarkable performance on current benchmarks, there are still several challenges that must be covered in more detail. This paper offers an overview of the Face Recognition Challenge in the Era of Synthetic Data (FRCSyn) organized at WACV 2024. This is the first international challenge aiming to explore the use of synthetic data in face recognition to address existing limitations in the technology. Specifically, the FRCSyn Challenge targets concerns related to data privacy issues, demographic biases, generalization to unseen scenarios, and performance limitations in challenging scenarios, including significant age disparities between enrollment and testing, pose variations, and occlusions. The results achieved in the FRCSyn Challenge, together with the proposed benchmark, contribute significantly to the application of synthetic data to improve face recognition technology.
Cross Architecture Distillation for Face Recognition
Jun 26, 2023Abstract:Transformers have emerged as the superior choice for face recognition tasks, but their insufficient platform acceleration hinders their application on mobile devices. In contrast, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) capitalize on hardware-compatible acceleration libraries. Consequently, it has become indispensable to preserve the distillation efficacy when transferring knowledge from a Transformer-based teacher model to a CNN-based student model, known as Cross-Architecture Knowledge Distillation (CAKD). Despite its potential, the deployment of CAKD in face recognition encounters two challenges: 1) the teacher and student share disparate spatial information for each pixel, obstructing the alignment of feature space, and 2) the teacher network is not trained in the role of a teacher, lacking proficiency in handling distillation-specific knowledge. To surmount these two constraints, 1) we first introduce a Unified Receptive Fields Mapping module (URFM) that maps pixel features of the teacher and student into local features with unified receptive fields, thereby synchronizing the pixel-wise spatial information of teacher and student. Subsequently, 2) we develop an Adaptable Prompting Teacher network (APT) that integrates prompts into the teacher, enabling it to manage distillation-specific knowledge while preserving the model's discriminative capacity. Extensive experiments on popular face benchmarks and two large-scale verification sets demonstrate the superiority of our method.
Grouped Knowledge Distillation for Deep Face Recognition
Apr 10, 2023Abstract:Compared with the feature-based distillation methods, logits distillation can liberalize the requirements of consistent feature dimension between teacher and student networks, while the performance is deemed inferior in face recognition. One major challenge is that the light-weight student network has difficulty fitting the target logits due to its low model capacity, which is attributed to the significant number of identities in face recognition. Therefore, we seek to probe the target logits to extract the primary knowledge related to face identity, and discard the others, to make the distillation more achievable for the student network. Specifically, there is a tail group with near-zero values in the prediction, containing minor knowledge for distillation. To provide a clear perspective of its impact, we first partition the logits into two groups, i.e., Primary Group and Secondary Group, according to the cumulative probability of the softened prediction. Then, we reorganize the Knowledge Distillation (KD) loss of grouped logits into three parts, i.e., Primary-KD, Secondary-KD, and Binary-KD. Primary-KD refers to distilling the primary knowledge from the teacher, Secondary-KD aims to refine minor knowledge but increases the difficulty of distillation, and Binary-KD ensures the consistency of knowledge distribution between teacher and student. We experimentally found that (1) Primary-KD and Binary-KD are indispensable for KD, and (2) Secondary-KD is the culprit restricting KD at the bottleneck. Therefore, we propose a Grouped Knowledge Distillation (GKD) that retains the Primary-KD and Binary-KD but omits Secondary-KD in the ultimate KD loss calculation. Extensive experimental results on popular face recognition benchmarks demonstrate the superiority of proposed GKD over state-of-the-art methods.
Modeling Based on Elman Wavelet Neural Network for Class-D Power Amplifiers
Sep 12, 2013



Abstract:In Class-D Power Amplifiers (CDPAs), the power supply noise can intermodulate with the input signal, manifesting into power-supply induced intermodulation distortion (PS-IMD) and due to the memory effects of the system, there exist asymmetries in the PS-IMDs. In this paper, a new behavioral modeling based on the Elman Wavelet Neural Network (EWNN) is proposed to study the nonlinear distortion of the CDPAs. In EWNN model, the Morlet wavelet functions are employed as the activation function and there is a normalized operation in the hidden layer, the modification of the scale factor and translation factor in the wavelet functions are ignored to avoid the fluctuations of the error curves. When there are 30 neurons in the hidden layer, to achieve the same square sum error (SSE) $\epsilon_{min}=10^{-3}$, EWNN needs 31 iteration steps, while the basic Elman neural network (BENN) model needs 86 steps. The Volterra-Laguerre model has 605 parameters to be estimated but still can't achieve the same magnitude accuracy of EWNN. Simulation results show that the proposed approach of EWNN model has fewer parameters and higher accuracy than the Volterra-Laguerre model and its convergence rate is much faster than the BENN model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge