Weidong Wang
Exposure-Aware Beamforming for mmWave Systems: From EM Theory to Thermal Compliance
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Electromagnetic (EM) exposure compliance has long been recognized as a crucial aspect of communications terminal designs. However, accurately assessing the impact of EM exposure for proper design strategies remains challenging. In this paper, we develop a long-term thermal EM exposure constraint model and propose a novel adaptive exposure-aware beamforming design for an mmWave uplink system. Specifically, we first establish an equivalent channel model based on Maxwell's radiation equations, which accurately captures the EM physical effects. Then, we derive a closed-form thermal impulse response model from the Pennes bioheat transfer equation (BHTE), characterizing the thermal inertia of tissue. Inspired by this model, we formulate a beamforming optimization problem that translates rigid instantaneous exposure limits into a flexible long-term thermal budget constraint. Furthermore, we develop a low-complexity online beamforming algorithm based on Lyapunov optimization theory, obtaining a closed-form near-optimal solution. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm effectively stabilizes tissue temperature near a predefined safety threshold and significantly outperforms the conventional scheme with instantaneous exposure constraints.
Automating Safety Enhancement for LLM-based Agents with Synthetic Risk Scenarios
May 23, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents are increasingly deployed in real-world applications such as "digital assistants, autonomous customer service, and decision-support systems", where their ability to "interact in multi-turn, tool-augmented environments" makes them indispensable. However, ensuring the safety of these agents remains a significant challenge due to the diverse and complex risks arising from dynamic user interactions, external tool usage, and the potential for unintended harmful behaviors. To address this critical issue, we propose AutoSafe, the first framework that systematically enhances agent safety through fully automated synthetic data generation. Concretely, 1) we introduce an open and extensible threat model, OTS, which formalizes how unsafe behaviors emerge from the interplay of user instructions, interaction contexts, and agent actions. This enables precise modeling of safety risks across diverse scenarios. 2) we develop a fully automated data generation pipeline that simulates unsafe user behaviors, applies self-reflective reasoning to generate safe responses, and constructs a large-scale, diverse, and high-quality safety training dataset-eliminating the need for hazardous real-world data collection. To evaluate the effectiveness of our framework, we design comprehensive experiments on both synthetic and real-world safety benchmarks. Results demonstrate that AutoSafe boosts safety scores by 45% on average and achieves a 28.91% improvement on real-world tasks, validating the generalization ability of our learned safety strategies. These results highlight the practical advancement and scalability of AutoSafe in building safer LLM-based agents for real-world deployment. We have released the project page at https://auto-safe.github.io/.
A Purely Data-Driven Adaptive Impedance Matching Method Robust to Parasitic Effects
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:Adaptive impedance matching between antennas and radio frequency front-end (RFFE) power modules is essential for mobile communication systems. To address the matching performance degradation caused by parasitic effects in practical tunable matching networks (TMN), this paper proposes a purely data-driven adaptive impedance matching method that avoids trial-and-error physical adjustment. First, we propose the residual enhanced circuit behavior modeling network (RECBM-Net), a deep learning model that maps TMN operating states to their scattering parameters (S-parameters). Then, we formulate the matching process based on the trained surrogate model as a mathematical optimization problem. We employ two classic numerical methods with different online computational overhead, namely simulated annealing particle swarm optimization (SAPSO) and adaptive moment estimation with automatic differentiation (AD-Adam), to search for the matching solution. To further reduce the online inference overhead caused by repeated forward propagation through RECBM-Net, we train an inverse mapping solver network (IMS-Net) to directly predict the optimal solution. Simulation results show that RECBM-Net achieves exceptionally high modeling accuracy. While AD-Adam significantly reduces computational overhead compared to SAPSO, it sacrifices slight accuracy. IMS-Net offers the lowest online overhead while maintaining excellent matching accuracy.
Beyond Traditional Coherence Time: An Electromagnetic Perspective for Mobile Channels
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:Channel coherence time has been widely regarded as a critical parameter in the design of mobile systems. However, a prominent challenge lies in integrating electromagnetic (EM) polarization effects into the derivation of the channel coherence time. In this paper, we develop a framework to analyze the impact of polarization mismatch on the channel coherence time. Specifically, we first establish an EM channel model to capture the essence of EM wave propagation. Based on this model, we then derive the EM temporal correlation function, incorporating the effects of polarization mismatch and beam misalignment. Further, considering the random orientation of the mobile user equipment (UE), we derive a closed-form solution for the EM coherence time in the turning scenario. When the trajectory degenerates into a straight line, we also provide a closed-form lower bound on the EM coherence time. The simulation results validate our theoretical analysis and reveal that neglecting the EM polarization effects leads to overly optimistic estimates of the EM coherence time.
Low-Complexity MUSIC Algorithm: From Finite-Precision Perspective
Mar 16, 2025Abstract:The high computational complexity of the multiple signal classification (MUSIC) algorithm is mainly caused by the subspace decomposition and spectrum search, especially for frequent real-time applications or massive sensors. In this paper, we propose a low-complexity MUSIC algorithm from finite-precision arithmetic perspective. First, we analyze the computational bottlenecks of the classic low-complexity randomized unitary-based MUSIC (RU-MUSIC), formulating this computational issue as an inner product problem. Then, a mixed-precision method is introduced to address this problem. Specifically, this method partitions summations in inner products into blocks, where intra-block computations use low-precision arithmetic and inter-block sums use high-precision arithmetic. To further improve computational accuracy, we develop an adaptive-precision method that supports adaptive block sizes and multiple precision levels. Finally, simulation results show that the proposed finite-precision MUSIC design achieves direction-of-arrival (DOA) estimation performance similar to that using full-precision arithmetic while reducing more than 50\% computational cost.
Large Reasoning Models in Agent Scenarios: Exploring the Necessity of Reasoning Capabilities
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:The rise of Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) signifies a paradigm shift toward advanced computational reasoning. Yet, this progress disrupts traditional agent frameworks, traditionally anchored by execution-oriented Large Language Models (LLMs). To explore this transformation, we propose the LaRMA framework, encompassing nine tasks across Tool Usage, Plan Design, and Problem Solving, assessed with three top LLMs (e.g., Claude3.5-sonnet) and five leading LRMs (e.g., DeepSeek-R1). Our findings address four research questions: LRMs surpass LLMs in reasoning-intensive tasks like Plan Design, leveraging iterative reflection for superior outcomes; LLMs excel in execution-driven tasks such as Tool Usage, prioritizing efficiency; hybrid LLM-LRM configurations, pairing LLMs as actors with LRMs as reflectors, optimize agent performance by blending execution speed with reasoning depth; and LRMs' enhanced reasoning incurs higher computational costs, prolonged processing, and behavioral challenges, including overthinking and fact-ignoring tendencies. This study fosters deeper inquiry into LRMs' balance of deep thinking and overthinking, laying a critical foundation for future agent design advancements.
Mixed-Precision Quantization: Make the Best Use of Bits Where They Matter Most
Dec 05, 2024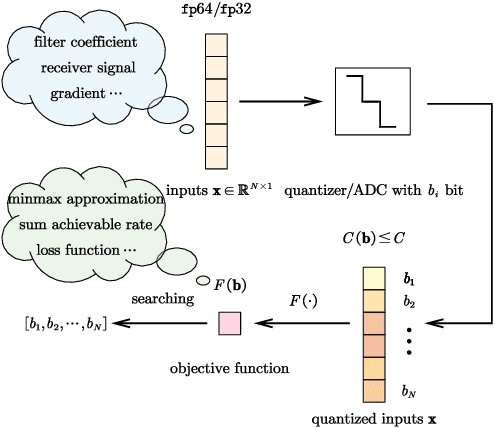
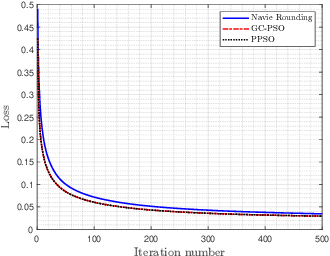
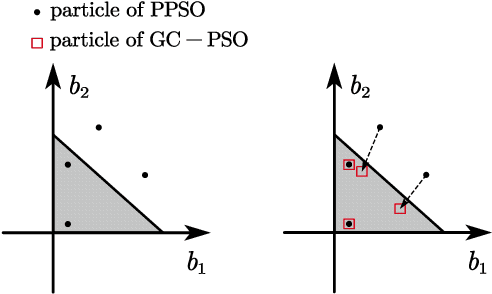
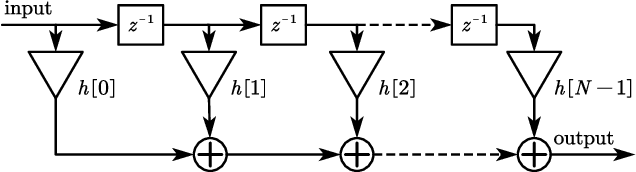
Abstract:Mixed-precision quantization offers superior performance to fixed-precision quantization. It has been widely used in signal processing, communication systems, and machine learning. In mixed-precision quantization, bit allocation is essential. Hence, in this paper, we propose a new bit allocation framework for mixed-precision quantization from a search perspective. First, we formulate a general bit allocation problem for mixed-precision quantization. Then we introduce the penalized particle swarm optimization (PPSO) algorithm to address the integer consumption constraint. To improve efficiency and avoid iterations on infeasible solutions within the PPSO algorithm, a greedy criterion particle swarm optimization (GC-PSO) algorithm is proposed. The corresponding convergence analysis is derived based on dynamical system theory. Furthermore, we apply the above framework to some specific classic fields, i.e., finite impulse response (FIR) filters, receivers, and gradient descent. Numerical examples in each application underscore the superiority of the proposed framework to the existing algorithms.
SpikeAtConv: An Integrated Spiking-Convolutional Attention Architecture for Energy-Efficient Neuromorphic Vision Processing
Nov 26, 2024



Abstract:Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) offer a biologically inspired alternative to conventional artificial neural networks, with potential advantages in power efficiency due to their event-driven computation. Despite their promise, SNNs have yet to achieve competitive performance on complex visual tasks, such as image classification. This study introduces a novel SNN architecture designed to enhance computational efficacy and task accuracy. The architecture features optimized pulse modules that facilitate the processing of spatio-temporal patterns in visual data, aiming to reconcile the computational demands of high-level vision tasks with the energy-efficient processing of SNNs. Our evaluations on standard image classification benchmarks indicate that the proposed architecture narrows the performance gap with traditional neural networks, providing insights into the design of more efficient and capable neuromorphic computing systems.
EPIC: Efficient Position-Independent Context Caching for Serving Large Language Models
Oct 20, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are critical for a wide range of applications, but serving them efficiently becomes increasingly challenging as inputs become more complex. Context caching improves serving performance by exploiting inter-request dependency and reusing key-value (KV) cache across requests, thus improving time-to-first-token (TTFT). However, existing prefix-based context caching requires exact token prefix matches, limiting cache reuse in few-shot learning, multi-document QA, or retrieval-augmented generation, where prefixes may vary. In this paper, we present EPIC, an LLM serving system that introduces position-independent context caching (PIC), enabling modular KV cache reuse regardless of token chunk position (or prefix). EPIC features two key designs: AttnLink, which leverages static attention sparsity to minimize recomputation for accuracy recovery, and KVSplit, a customizable chunking method that preserves semantic coherence. Our experiments demonstrate that Epic delivers up to 8x improvements in TTFT and 7x throughput over existing systems, with negligible or no accuracy loss. By addressing the limitations of traditional caching approaches, Epic enables more scalable and efficient LLM inference.
Out-of-distribution Detection in Medical Image Analysis: A survey
Apr 28, 2024
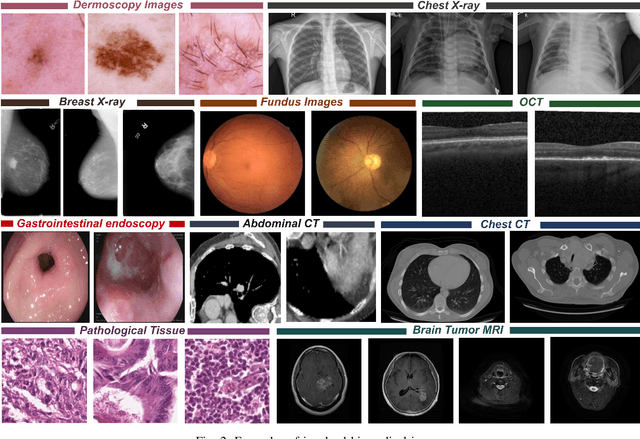
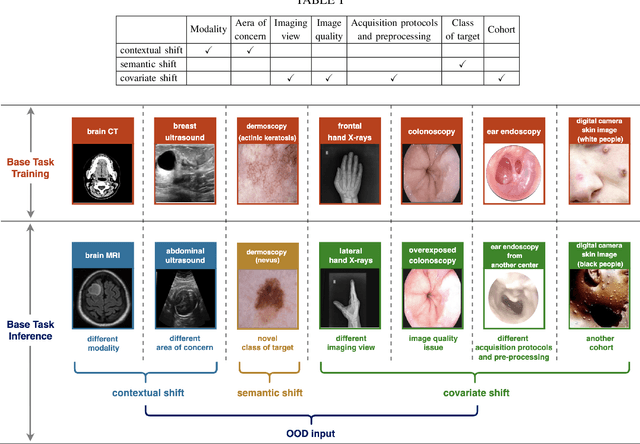

Abstract:Computer-aided diagnostics has benefited from the development of deep learning-based computer vision techniques in these years. Traditional supervised deep learning methods assume that the test sample is drawn from the identical distribution as the training data. However, it is possible to encounter out-of-distribution samples in real-world clinical scenarios, which may cause silent failure in deep learning-based medical image analysis tasks. Recently, research has explored various out-of-distribution (OOD) detection situations and techniques to enable a trustworthy medical AI system. In this survey, we systematically review the recent advances in OOD detection in medical image analysis. We first explore several factors that may cause a distributional shift when using a deep-learning-based model in clinic scenarios, with three different types of distributional shift well defined on top of these factors. Then a framework is suggested to categorize and feature existing solutions, while the previous studies are reviewed based on the methodology taxonomy. Our discussion also includes evaluation protocols and metrics, as well as the challenge and a research direction lack of exploration.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge