Travis Manderson
Toward Learning POMDPs Beyond Full-Rank Actions and State Observability
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:We are interested in enabling autonomous agents to learn and reason about systems with hidden states, such as furniture with hidden locking mechanisms. We cast this problem as learning the parameters of a discrete Partially Observable Markov Decision Process (POMDP). The agent begins with knowledge of the POMDP's actions and observation spaces, but not its state space, transitions, or observation models. These properties must be constructed from action-observation sequences. Spectral approaches to learning models of partially observable domains, such as learning Predictive State Representations (PSRs), are known to directly estimate the number of hidden states. These methods cannot, however, yield direct estimates of transition and observation likelihoods, which are important for many downstream reasoning tasks. Other approaches leverage tensor decompositions to estimate transition and observation likelihoods but often assume full state observability and full-rank transition matrices for all actions. To relax these assumptions, we study how PSRs learn transition and observation matrices up to a similarity transform, which may be estimated via tensor methods. Our method learns observation matrices and transition matrices up to a partition of states, where the states in a single partition have the same observation distributions corresponding to actions whose transition matrices are full-rank. Our experiments suggest that these partition-level transition models learned by our method, with a sufficient amount of data, meets the performance of PSRs as models to be used by standard sampling-based POMDP solvers. Furthermore, the explicit observation and transition likelihoods can be leveraged to specify planner behavior after the model has been learned.
Anomalies by Synthesis: Anomaly Detection using Generative Diffusion Models for Off-Road Navigation
May 28, 2025Abstract:In order to navigate safely and reliably in off-road and unstructured environments, robots must detect anomalies that are out-of-distribution (OOD) with respect to the training data. We present an analysis-by-synthesis approach for pixel-wise anomaly detection without making any assumptions about the nature of OOD data. Given an input image, we use a generative diffusion model to synthesize an edited image that removes anomalies while keeping the remaining image unchanged. Then, we formulate anomaly detection as analyzing which image segments were modified by the diffusion model. We propose a novel inference approach for guided diffusion by analyzing the ideal guidance gradient and deriving a principled approximation that bootstraps the diffusion model to predict guidance gradients. Our editing technique is purely test-time that can be integrated into existing workflows without the need for retraining or fine-tuning. Finally, we use a combination of vision-language foundation models to compare pixels in a learned feature space and detect semantically meaningful edits, enabling accurate anomaly detection for off-road navigation. Project website: https://siddancha.github.io/anomalies-by-diffusion-synthesis/
Constrained Robotic Navigation on Preferred Terrains Using LLMs and Speech Instruction: Exploiting the Power of Adverbs
Apr 02, 2024Abstract:This paper explores leveraging large language models for map-free off-road navigation using generative AI, reducing the need for traditional data collection and annotation. We propose a method where a robot receives verbal instructions, converted to text through Whisper, and a large language model (LLM) model extracts landmarks, preferred terrains, and crucial adverbs translated into speed settings for constrained navigation. A language-driven semantic segmentation model generates text-based masks for identifying landmarks and terrain types in images. By translating 2D image points to the vehicle's motion plane using camera parameters, an MPC controller can guides the vehicle towards the desired terrain. This approach enhances adaptation to diverse environments and facilitates the use of high-level instructions for navigating complex and challenging terrains.
Trajectory-Constrained Deep Latent Visual Attention for Improved Local Planning in Presence of Heterogeneous Terrain
Dec 09, 2021



Abstract:We present a reward-predictive, model-based deep learning method featuring trajectory-constrained visual attention for use in mapless, local visual navigation tasks. Our method learns to place visual attention at locations in latent image space which follow trajectories caused by vehicle control actions to enhance predictive accuracy during planning. The attention model is jointly optimized by the task-specific loss and an additional trajectory-constraint loss, allowing adaptability yet encouraging a regularized structure for improved generalization and reliability. Importantly, visual attention is applied in latent feature map space instead of raw image space to promote efficient planning. We validated our model in visual navigation tasks of planning low turbulence, collision-free trajectories in off-road settings and hill climbing with locking differentials in the presence of slippery terrain. Experiments involved randomized procedural generated simulation and real-world environments. We found our method improved generalization and learning efficiency when compared to no-attention and self-attention alternatives.
Multimodal dynamics modeling for off-road autonomous vehicles
Nov 23, 2020



Abstract:Dynamics modeling in outdoor and unstructured environments is difficult because different elements in the environment interact with the robot in ways that can be hard to predict. Leveraging multiple sensors to perceive maximal information about the robot's environment is thus crucial when building a model to perform predictions about the robot's dynamics with the goal of doing motion planning. We design a model capable of long-horizon motion predictions, leveraging vision, lidar and proprioception, which is robust to arbitrarily missing modalities at test time. We demonstrate in simulation that our model is able to leverage vision to predict traction changes. We then test our model using a real-world challenging dataset of a robot navigating through a forest, performing predictions in trajectories unseen during training. We try different modality combinations at test time and show that, while our model performs best when all modalities are present, it is still able to perform better than the baseline even when receiving only raw vision input and no proprioception, as well as when only receiving proprioception. Overall, our study demonstrates the importance of leveraging multiple sensors when doing dynamics modeling in outdoor conditions.
Vision-Based Goal-Conditioned Policies for Underwater Navigation in the Presence of Obstacles
Jun 29, 2020


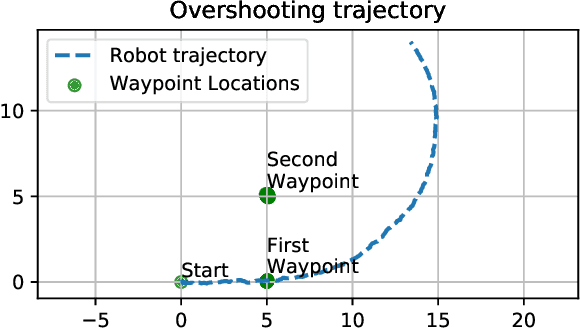
Abstract:We present Nav2Goal, a data-efficient and end-to-end learning method for goal-conditioned visual navigation. Our technique is used to train a navigation policy that enables a robot to navigate close to sparse geographic waypoints provided by a user without any prior map, all while avoiding obstacles and choosing paths that cover user-informed regions of interest. Our approach is based on recent advances in conditional imitation learning. General-purpose, safe and informative actions are demonstrated by a human expert. The learned policy is subsequently extended to be goal-conditioned by training with hindsight relabelling, guided by the robot's relative localization system, which requires no additional manual annotation. We deployed our method on an underwater vehicle in the open ocean to collect scientifically relevant data of coral reefs, which allowed our robot to operate safely and autonomously, even at very close proximity to the coral. Our field deployments have demonstrated over a kilometer of autonomous visual navigation, where the robot reaches on the order of 40 waypoints, while collecting scientifically relevant data. This is done while travelling within 0.5 m altitude from sensitive corals and exhibiting significant learned agility to overcome turbulent ocean conditions and to actively avoid collisions.
Learning to Drive Off Road on Smooth Terrain in Unstructured Environments Using an On-Board Camera and Sparse Aerial Images
Apr 09, 2020



Abstract:We present a method for learning to drive on smooth terrain while simultaneously avoiding collisions in challenging off-road and unstructured outdoor environments using only visual inputs. Our approach applies a hybrid model-based and model-free reinforcement learning method that is entirely self-supervised in labeling terrain roughness and collisions using on-board sensors. Notably, we provide both first-person and overhead aerial image inputs to our model. We find that the fusion of these complementary inputs improves planning foresight and makes the model robust to visual obstructions. Our results show the ability to generalize to environments with plentiful vegetation, various types of rock, and sandy trails. During evaluation, our policy attained 90% smooth terrain traversal and reduced the proportion of rough terrain driven over by 6.1 times compared to a model using only first-person imagery.
One-Shot Informed Robotic Visual Search in the Wild
Mar 22, 2020



Abstract:We consider the task of underwater robot navigation for the purpose of collecting scientifically-relevant video data for environmental monitoring. The majority of field robots that currently perform monitoring tasks in unstructured natural environments navigate via path-tracking a pre-specified sequence of waypoints. Although this navigation method is often necessary, it is limiting because the robot does not have a model of what the scientist deems to be relevant visual observations. Thus, the robot can neither visually search for particular types of objects, nor focus its attention on parts of the scene that might be more relevant than the pre-specified waypoints and viewpoints. In this paper we propose a method that enables informed visual navigation via a learned visual similarity operator that guides the robot's visual search towards parts of the scene that look like an exemplar image, which is given by the user as a high-level specification for data collection. We propose and evaluate a weakly-supervised video representation learning method that outperforms ImageNet embeddings for similarity tasks in the underwater domain. We also demonstrate the deployment of this similarity operator during informed visual navigation in collaborative environmental monitoring scenarios, in large-scale field trials, where the robot and a human scientist jointly search for relevant visual content.
DeepURL: Deep Pose Estimation Framework for Underwater Relative Localization
Mar 13, 2020
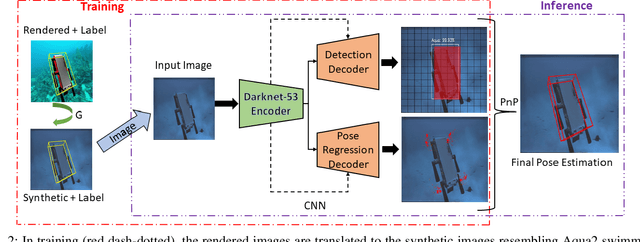
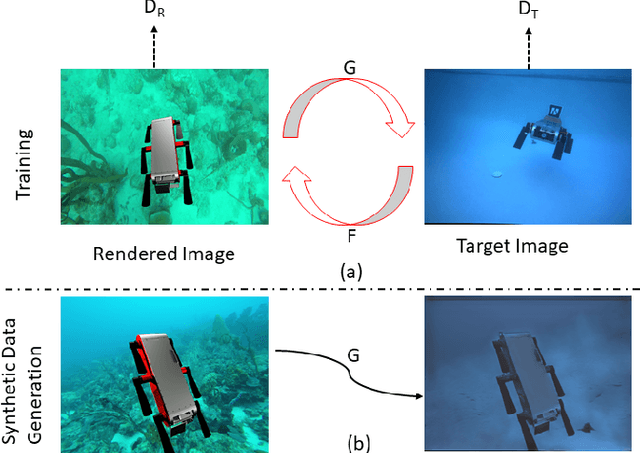
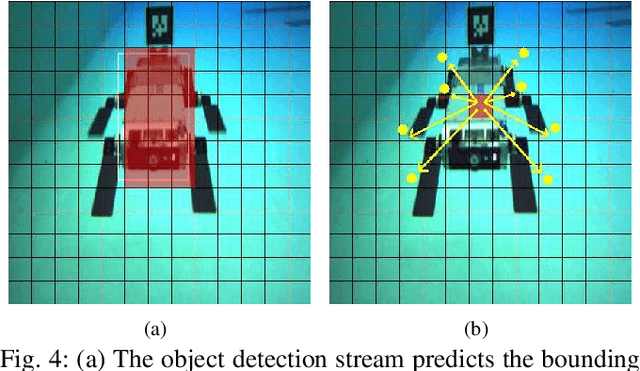
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a real-time deep-learning approach for determining the 6D relative pose of Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUV) from a single image. A team of autonomous robots localizing themselves, in a communication-constrained underwater environment, is essential for many applications such as underwater exploration, mapping, multi-robot convoying, and other multi-robot tasks. Due to the profound difficulty of collecting ground truth images with accurate 6D poses underwater, this work utilizes rendered images from the Unreal Game Engine simulation for training. An image translation network is employed to bridge the gap between the rendered and the real images producing synthetic images for training. The proposed method predicts the 6D pose of an AUV from a single image as 2D image keypoints representing 8 corners of the 3D model of the AUV, and then the 6D pose in the camera coordinates is determined using RANSAC-based PnP. Experimental results in underwater environments (swimming pool and ocean) with different cameras demonstrate the robustness of the proposed technique, where the trained system decreased translation error by 75.5% and orientation error by 64.6% over the state-of-the-art methods.
Heterogeneous Robot Teams for Informative Sampling
Jun 17, 2019



Abstract:In this paper we present a cooperative multi-robot strategy to adaptively explore and sample environments that are unfavorable for humans. We propose a methodology for a team of heterogeneous robots to collaborate on information based planning for applications like sampling thermal imagery in a wildfire affected site to assist with detecting spot fires and areas of residual fires, fire mapping and monitoring fire progression or applications in marine domain for coral reef monitoring and survey. We use Gabor filter based texture classifier on aerial images from an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) to segment the region of interest into classes. A policy gradient based path planner is used on the texture classified aerial image to plan a path for the Unmanned Ground Vehicle (UGV). The UGV then uses a local planner to reach the goals set by the global planner by avoiding obstacles. The UGV also learns the labels for the segmented classes as drivable and non-drivable using the feedback from the performance while reaching the planned waypoints. We evaluated the building blocks of our approach and present the results with application of these strategies to different domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge