Tim Baldwin
Argument-Based Comparative Question Answering Evaluation Benchmark
Feb 20, 2025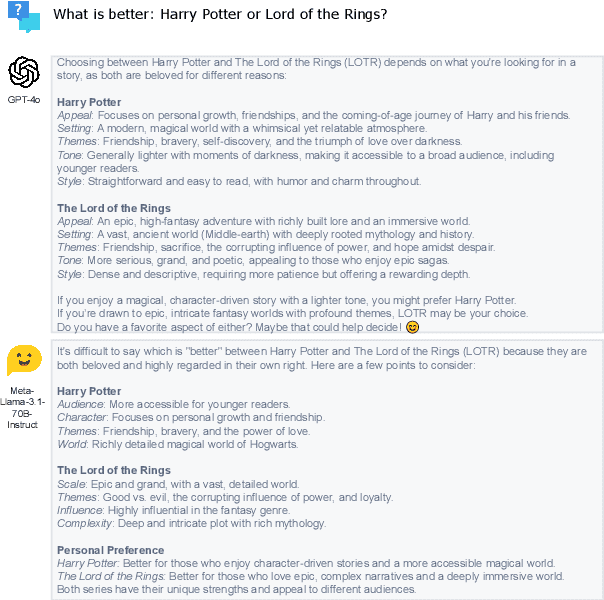
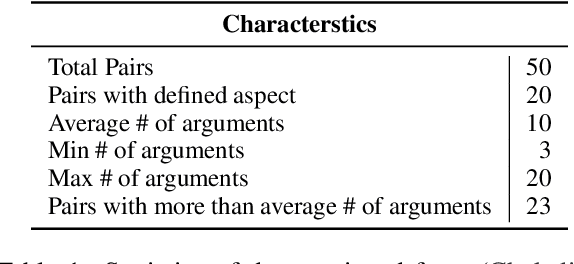
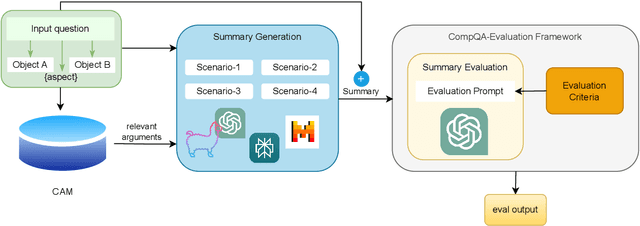
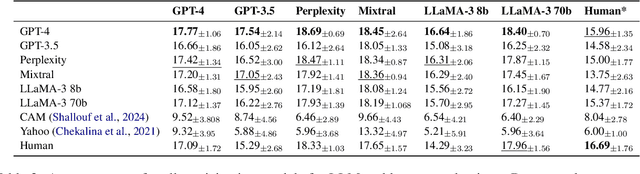
Abstract:In this paper, we aim to solve the problems standing in the way of automatic comparative question answering. To this end, we propose an evaluation framework to assess the quality of comparative question answering summaries. We formulate 15 criteria for assessing comparative answers created using manual annotation and annotation from 6 large language models and two comparative question asnwering datasets. We perform our tests using several LLMs and manual annotation under different settings and demonstrate the constituency of both evaluations. Our results demonstrate that the Llama-3 70B Instruct model demonstrates the best results for summary evaluation, while GPT-4 is the best for answering comparative questions. All used data, code, and evaluation results are publicly available\footnote{\url{https://anonymous.4open.science/r/cqa-evaluation-benchmark-4561/README.md}}.
PALO: A Polyglot Large Multimodal Model for 5B People
Mar 05, 2024



Abstract:In pursuit of more inclusive Vision-Language Models (VLMs), this study introduces a Large Multilingual Multimodal Model called PALO. PALO offers visual reasoning capabilities in 10 major languages, including English, Chinese, Hindi, Spanish, French, Arabic, Bengali, Russian, Urdu, and Japanese, that span a total of ~5B people (65% of the world population). Our approach involves a semi-automated translation approach to adapt the multimodal instruction dataset from English to the target languages using a fine-tuned Large Language Model, thereby ensuring high linguistic fidelity while allowing scalability due to minimal manual effort. The incorporation of diverse instruction sets helps us boost overall performance across multiple languages especially those that are underrepresented like Hindi, Arabic, Bengali, and Urdu. The resulting models are trained across three scales (1.7B, 7B and 13B parameters) to show the generalization and scalability where we observe substantial improvements compared to strong baselines. We also propose the first multilingual multimodal benchmark for the forthcoming approaches to evaluate their vision-language reasoning capabilities across languages. Code: https://github.com/mbzuai-oryx/PALO.
MobiLlama: Towards Accurate and Lightweight Fully Transparent GPT
Feb 26, 2024



Abstract:"Bigger the better" has been the predominant trend in recent Large Language Models (LLMs) development. However, LLMs do not suit well for scenarios that require on-device processing, energy efficiency, low memory footprint, and response efficiency. These requisites are crucial for privacy, security, and sustainable deployment. This paper explores the "less is more" paradigm by addressing the challenge of designing accurate yet efficient Small Language Models (SLMs) for resource constrained devices. Our primary contribution is the introduction of an accurate and fully transparent open-source 0.5 billion (0.5B) parameter SLM, named MobiLlama, catering to the specific needs of resource-constrained computing with an emphasis on enhanced performance with reduced resource demands. MobiLlama is a SLM design that initiates from a larger model and applies a careful parameter sharing scheme to reduce both the pre-training and the deployment cost. Our work strives to not only bridge the gap in open-source SLMs but also ensures full transparency, where complete training data pipeline, training code, model weights, and over 300 checkpoints along with evaluation codes is available at : https://github.com/mbzuai-oryx/MobiLlama.
LLM360: Towards Fully Transparent Open-Source LLMs
Dec 11, 2023



Abstract:The recent surge in open-source Large Language Models (LLMs), such as LLaMA, Falcon, and Mistral, provides diverse options for AI practitioners and researchers. However, most LLMs have only released partial artifacts, such as the final model weights or inference code, and technical reports increasingly limit their scope to high-level design choices and surface statistics. These choices hinder progress in the field by degrading transparency into the training of LLMs and forcing teams to rediscover many details in the training process. We present LLM360, an initiative to fully open-source LLMs, which advocates for all training code and data, model checkpoints, and intermediate results to be made available to the community. The goal of LLM360 is to support open and collaborative AI research by making the end-to-end LLM training process transparent and reproducible by everyone. As a first step of LLM360, we release two 7B parameter LLMs pre-trained from scratch, Amber and CrystalCoder, including their training code, data, intermediate checkpoints, and analyses (at https://www.llm360.ai). We are committed to continually pushing the boundaries of LLMs through this open-source effort. More large-scale and stronger models are underway and will be released in the future.
Just What do You Think You're Doing, Dave?' A Checklist for Responsible Data Use in NLP
Sep 14, 2021

Abstract:A key part of the NLP ethics movement is responsible use of data, but exactly what that means or how it can be best achieved remain unclear. This position paper discusses the core legal and ethical principles for collection and sharing of textual data, and the tensions between them. We propose a potential checklist for responsible data (re-)use that could both standardise the peer review of conference submissions, as well as enable a more in-depth view of published research across the community. Our proposal aims to contribute to the development of a consistent standard for data (re-)use, embraced across NLP conferences.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge