Teng Fu
Interpretable Oracle Bone Script Decipherment through Radical and Pictographic Analysis with LVLMs
Aug 13, 2025Abstract:As the oldest mature writing system, Oracle Bone Script (OBS) has long posed significant challenges for archaeological decipherment due to its rarity, abstractness, and pictographic diversity. Current deep learning-based methods have made exciting progress on the OBS decipherment task, but existing approaches often ignore the intricate connections between glyphs and the semantics of OBS. This results in limited generalization and interpretability, especially when addressing zero-shot settings and undeciphered OBS. To this end, we propose an interpretable OBS decipherment method based on Large Vision-Language Models, which synergistically combines radical analysis and pictograph-semantic understanding to bridge the gap between glyphs and meanings of OBS. Specifically, we propose a progressive training strategy that guides the model from radical recognition and analysis to pictographic analysis and mutual analysis, thus enabling reasoning from glyph to meaning. We also design a Radical-Pictographic Dual Matching mechanism informed by the analysis results, significantly enhancing the model's zero-shot decipherment performance. To facilitate model training, we propose the Pictographic Decipherment OBS Dataset, which comprises 47,157 Chinese characters annotated with OBS images and pictographic analysis texts. Experimental results on public benchmarks demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art Top-10 accuracy and superior zero-shot decipherment capabilities. More importantly, our model delivers logical analysis processes, possibly providing archaeologically valuable reference results for undeciphered OBS, and thus has potential applications in digital humanities and historical research. The dataset and code will be released in https://github.com/PKXX1943/PD-OBS.
From Intent to Execution: Multimodal Chain-of-Thought Reinforcement Learning for Precise CAD Code Generation
Aug 13, 2025Abstract:Computer-Aided Design (CAD) plays a vital role in engineering and manufacturing, yet current CAD workflows require extensive domain expertise and manual modeling effort. Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have made it possible to generate code from natural language, opening new opportunities for automating parametric 3D modeling. However, directly translating human design intent into executable CAD code remains highly challenging, due to the need for logical reasoning, syntactic correctness, and numerical precision. In this work, we propose CAD-RL, a multimodal Chain-of-Thought (CoT) guided reinforcement learning post training framework for CAD modeling code generation. Our method combines CoT-based Cold Start with goal-driven reinforcement learning post training using three task-specific rewards: executability reward, geometric accuracy reward, and external evaluation reward. To ensure stable policy learning under sparse and high-variance reward conditions, we introduce three targeted optimization strategies: Trust Region Stretch for improved exploration, Precision Token Loss for enhanced dimensions parameter accuracy, and Overlong Filtering to reduce noisy supervision. To support training and benchmarking, we release ExeCAD, a noval dataset comprising 16,540 real-world CAD examples with paired natural language and structured design language descriptions, executable CADQuery scripts, and rendered 3D models. Experiments demonstrate that CAD-RL achieves significant improvements in reasoning quality, output precision, and code executability over existing VLMs.
The Role of Rank in Mismatched Low-Rank Symmetric Matrix Estimation
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:We investigate the performance of a Bayesian statistician tasked with recovering a rank-\(k\) signal matrix \(\bS \bS^{\top} \in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}\), corrupted by element-wise additive Gaussian noise. This problem lies at the core of numerous applications in machine learning, signal processing, and statistics. We derive an analytic expression for the asymptotic mean-square error (MSE) of the Bayesian estimator under mismatches in the assumed signal rank, signal power, and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), considering both sphere and Gaussian signals. Additionally, we conduct a rigorous analysis of how rank mismatch influences the asymptotic MSE. Our primary technical tools include the spectrum of Gaussian orthogonal ensembles (GOE) with low-rank perturbations and asymptotic behavior of \(k\)-dimensional spherical integrals.
CrowdTrack: A Benchmark for Difficult Multiple Pedestrian Tracking in Real Scenarios
Jul 03, 2025Abstract:Multi-object tracking is a classic field in computer vision. Among them, pedestrian tracking has extremely high application value and has become the most popular research category. Existing methods mainly use motion or appearance information for tracking, which is often difficult in complex scenarios. For the motion information, mutual occlusions between objects often prevent updating of the motion state; for the appearance information, non-robust results are often obtained due to reasons such as only partial visibility of the object or blurred images. Although learning how to perform tracking in these situations from the annotated data is the simplest solution, the existing MOT dataset fails to satisfy this solution. Existing methods mainly have two drawbacks: relatively simple scene composition and non-realistic scenarios. Although some of the video sequences in existing dataset do not have the above-mentioned drawbacks, the number is far from adequate for research purposes. To this end, we propose a difficult large-scale dataset for multi-pedestrian tracking, shot mainly from the first-person view and all from real-life complex scenarios. We name it ``CrowdTrack'' because there are numerous objects in most of the sequences. Our dataset consists of 33 videos, containing a total of 5,185 trajectories. Each object is annotated with a complete bounding box and a unique object ID. The dataset will provide a platform to facilitate the development of algorithms that remain effective in complex situations. We analyzed the dataset comprehensively and tested multiple SOTA models on our dataset. Besides, we analyzed the performance of the foundation models on our dataset. The dataset and project code is released at: https://github.com/loseevaya/CrowdTrack .
Prolonged Reasoning Is Not All You Need: Certainty-Based Adaptive Routing for Efficient LLM/MLLM Reasoning
May 21, 2025



Abstract:Recent advancements in reasoning have significantly enhanced the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) across diverse tasks. However, excessive reliance on chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning can impair model performance and brings unnecessarily lengthened outputs, reducing efficiency. Our work reveals that prolonged reasoning does not universally improve accuracy and even degrade performance on simpler tasks. To address this, we propose Certainty-based Adaptive Reasoning (CAR), a novel framework that dynamically switches between short answers and long-form reasoning based on the model perplexity. CAR first generates a short answer and evaluates its perplexity, triggering reasoning only when the model exhibits low confidence (i.e., high perplexity). Experiments across diverse multimodal VQA/KIE benchmarks and text reasoning datasets show that CAR outperforms both short-answer and long-form reasoning approaches, striking an optimal balance between accuracy and efficiency.
ChatReID: Open-ended Interactive Person Retrieval via Hierarchical Progressive Tuning for Vision Language Models
Feb 27, 2025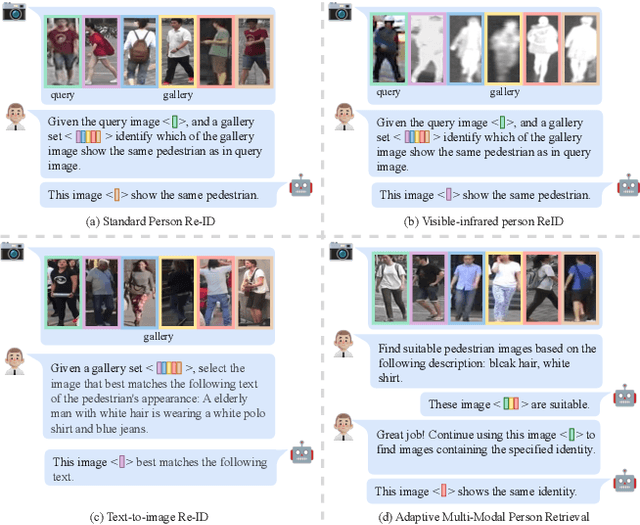
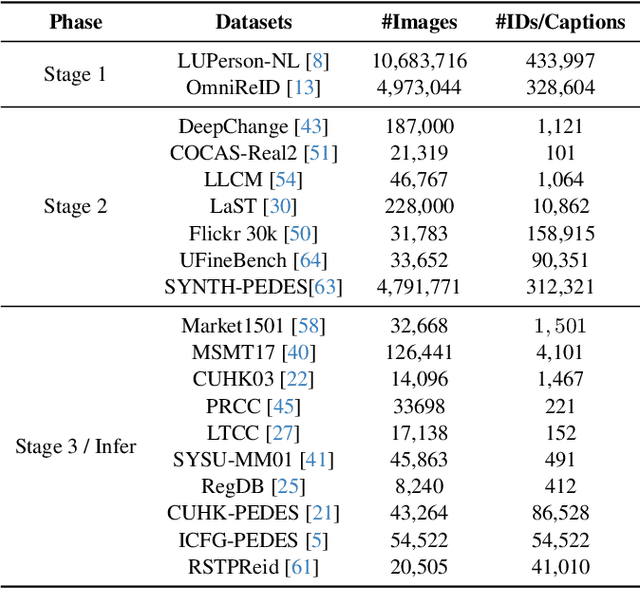
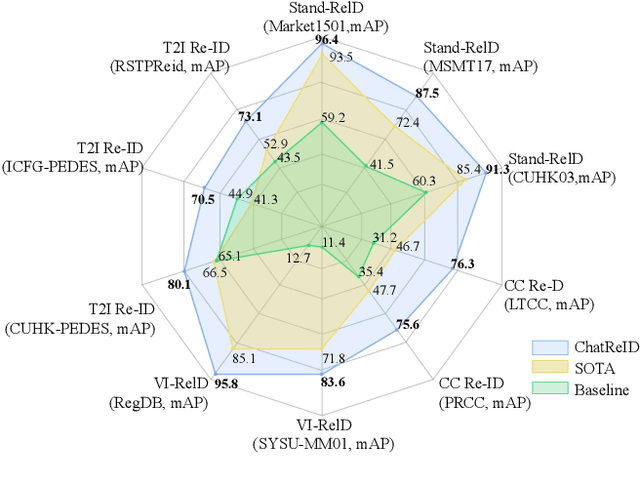
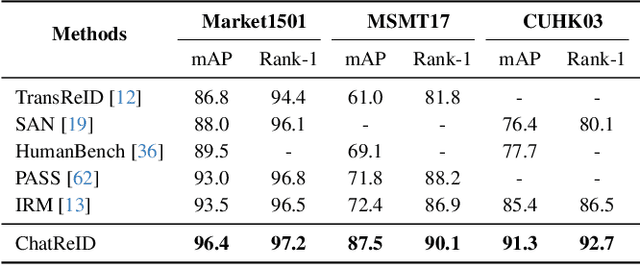
Abstract:Person re-identification (Re-ID) is a critical task in human-centric intelligent systems, enabling consistent identification of individuals across different camera views using multi-modal query information. Recent studies have successfully integrated LVLMs with person Re-ID, yielding promising results. However, existing LVLM-based methods face several limitations. They rely on extracting textual embeddings from fixed templates, which are used either as intermediate features for image representation or for prompt tuning in domain-specific tasks. Furthermore, they are unable to adopt the VQA inference format, significantly restricting their broader applicability. In this paper, we propose a novel, versatile, one-for-all person Re-ID framework, ChatReID. Our approach introduces a Hierarchical Progressive Tuning (HPT) strategy, which ensures fine-grained identity-level retrieval by progressively refining the model's ability to distinguish pedestrian identities. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach outperforms SOTA methods across ten benchmarks in four different Re-ID settings, offering enhanced flexibility and user-friendliness. ChatReID provides a scalable, practical solution for real-world person Re-ID applications, enabling effective multi-modal interaction and fine-grained identity discrimination.
EAFormer: Scene Text Segmentation with Edge-Aware Transformers
Jul 24, 2024Abstract:Scene text segmentation aims at cropping texts from scene images, which is usually used to help generative models edit or remove texts. The existing text segmentation methods tend to involve various text-related supervisions for better performance. However, most of them ignore the importance of text edges, which are significant for downstream applications. In this paper, we propose Edge-Aware Transformers, termed EAFormer, to segment texts more accurately, especially at the edge of texts. Specifically, we first design a text edge extractor to detect edges and filter out edges of non-text areas. Then, we propose an edge-guided encoder to make the model focus more on text edges. Finally, an MLP-based decoder is employed to predict text masks. We have conducted extensive experiments on commonly-used benchmarks to verify the effectiveness of EAFormer. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method can perform better than previous methods, especially on the segmentation of text edges. Considering that the annotations of several benchmarks (e.g., COCO_TS and MLT_S) are not accurate enough to fairly evaluate our methods, we have relabeled these datasets. Through experiments, we observe that our method can achieve a higher performance improvement when more accurate annotations are used for training.
Synthesizing Efficient Data with Diffusion Models for Person Re-Identification Pre-Training
Jun 10, 2024
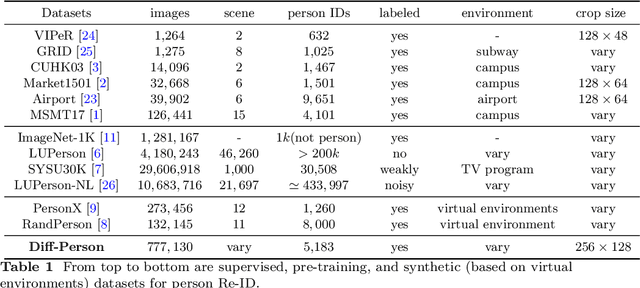
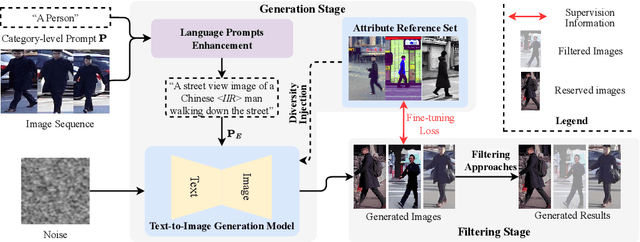
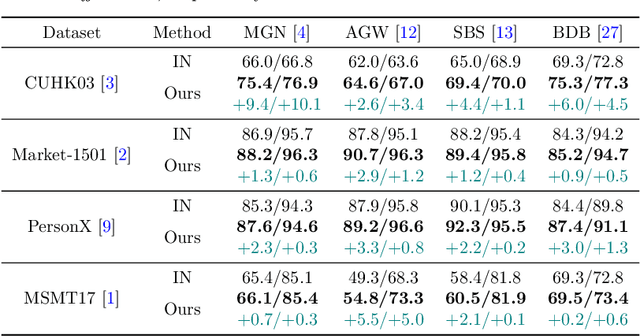
Abstract:Existing person re-identification (Re-ID) methods principally deploy the ImageNet-1K dataset for model initialization, which inevitably results in sub-optimal situations due to the large domain gap. One of the key challenges is that building large-scale person Re-ID datasets is time-consuming. Some previous efforts address this problem by collecting person images from the internet e.g., LUPerson, but it struggles to learn from unlabeled, uncontrollable, and noisy data. In this paper, we present a novel paradigm Diffusion-ReID to efficiently augment and generate diverse images based on known identities without requiring any cost of data collection and annotation. Technically, this paradigm unfolds in two stages: generation and filtering. During the generation stage, we propose Language Prompts Enhancement (LPE) to ensure the ID consistency between the input image sequence and the generated images. In the diffusion process, we propose a Diversity Injection (DI) module to increase attribute diversity. In order to make the generated data have higher quality, we apply a Re-ID confidence threshold filter to further remove the low-quality images. Benefiting from our proposed paradigm, we first create a new large-scale person Re-ID dataset Diff-Person, which consists of over 777K images from 5,183 identities. Next, we build a stronger person Re-ID backbone pre-trained on our Diff-Person. Extensive experiments are conducted on four person Re-ID benchmarks in six widely used settings. Compared with other pre-training and self-supervised competitors, our approach shows significant superiority.
DeNoising-MOT: Towards Multiple Object Tracking with Severe Occlusions
Sep 09, 2023Abstract:Multiple object tracking (MOT) tends to become more challenging when severe occlusions occur. In this paper, we analyze the limitations of traditional Convolutional Neural Network-based methods and Transformer-based methods in handling occlusions and propose DNMOT, an end-to-end trainable DeNoising Transformer for MOT. To address the challenge of occlusions, we explicitly simulate the scenarios when occlusions occur. Specifically, we augment the trajectory with noises during training and make our model learn the denoising process in an encoder-decoder architecture, so that our model can exhibit strong robustness and perform well under crowded scenes. Additionally, we propose a Cascaded Mask strategy to better coordinate the interaction between different types of queries in the decoder to prevent the mutual suppression between neighboring trajectories under crowded scenes. Notably, the proposed method requires no additional modules like matching strategy and motion state estimation in inference. We conduct extensive experiments on the MOT17, MOT20, and DanceTrack datasets, and the experimental results show that our method outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods by a clear margin.
Mismatched estimation of non-symmetric rank-one matrices corrupted by structured noise
Feb 08, 2023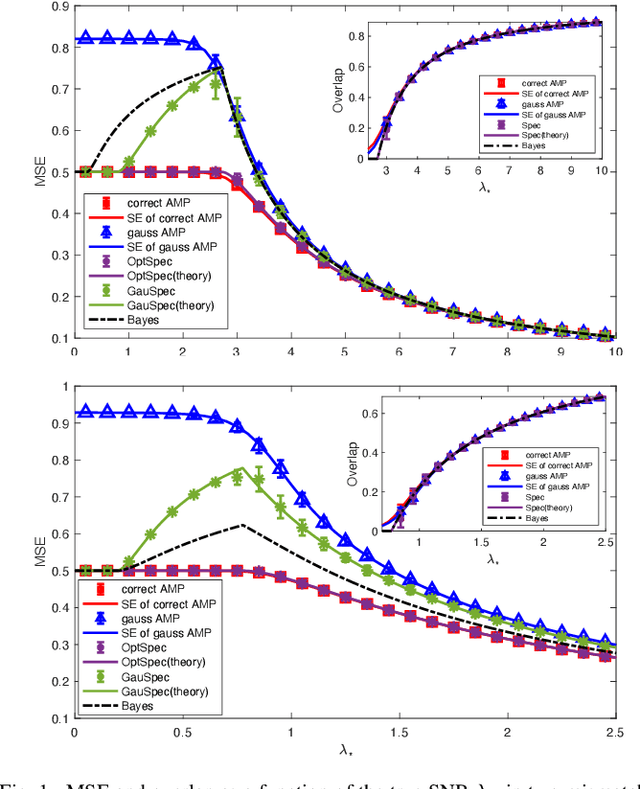
Abstract:We study the performance of a Bayesian statistician who estimates a rank-one signal corrupted by non-symmetric rotationally invariant noise with a generic distribution of singular values. As the signal-to-noise ratio and the noise structure are unknown, a Gaussian setup is incorrectly assumed. We derive the exact analytic expression for the error of the mismatched Bayes estimator and also provide the analysis of an approximate message passing (AMP) algorithm. The first result exploits the asymptotic behavior of spherical integrals for rectangular matrices and of low-rank matrix perturbations; the second one relies on the design and analysis of an auxiliary AMP. The numerical experiments show that there is a performance gap between the AMP and Bayes estimators, which is due to the incorrect estimation of the signal norm.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge