TianQi Hou
Diving into Kronecker Adapters: Component Design Matters
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Kronecker adapters have emerged as a promising approach for fine-tuning large-scale models, enabling high-rank updates through tunable component structures. However, existing work largely treats the component structure as a fixed or heuristic design choice, leaving the dimensions and number of Kronecker components underexplored. In this paper, we identify component structure as a key factor governing the capacity of Kronecker adapters. We perform a fine-grained analysis of both the dimensions and number of Kronecker components. In particular, we show that the alignment between Kronecker adapters and full fine-tuning depends on component configurations. Guided by these insights, we propose Component Designed Kronecker Adapters (CDKA). We further provide parameter-budget-aware configuration guidelines and a tailored training stabilization strategy for practical deployment. Experiments across various natural language processing tasks demonstrate the effectiveness of CDKA. Code is available at https://github.com/rainstonee/CDKA.
Mismatched estimation of non-symmetric rank-one matrices corrupted by structured noise
Feb 08, 2023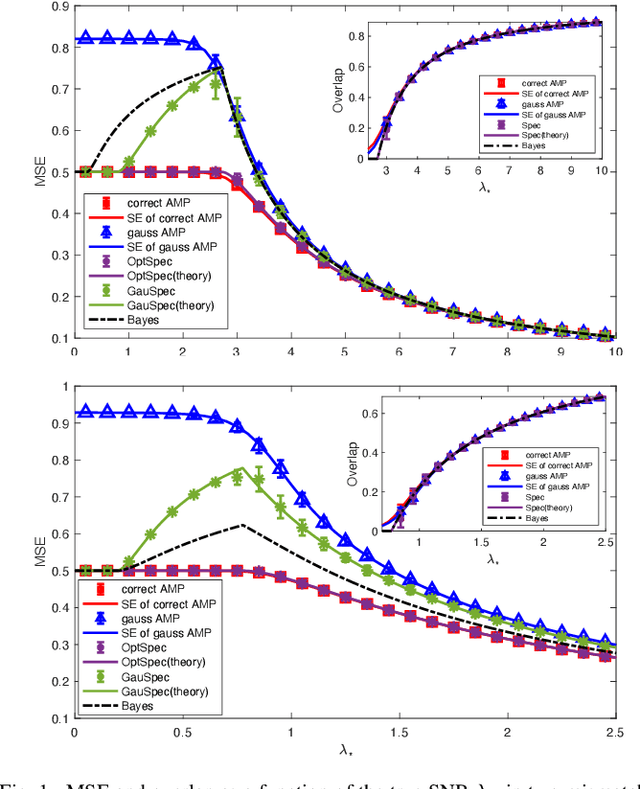
Abstract:We study the performance of a Bayesian statistician who estimates a rank-one signal corrupted by non-symmetric rotationally invariant noise with a generic distribution of singular values. As the signal-to-noise ratio and the noise structure are unknown, a Gaussian setup is incorrectly assumed. We derive the exact analytic expression for the error of the mismatched Bayes estimator and also provide the analysis of an approximate message passing (AMP) algorithm. The first result exploits the asymptotic behavior of spherical integrals for rectangular matrices and of low-rank matrix perturbations; the second one relies on the design and analysis of an auxiliary AMP. The numerical experiments show that there is a performance gap between the AMP and Bayes estimators, which is due to the incorrect estimation of the signal norm.
Approximate Message Passing for Multi-Layer Estimation in Rotationally Invariant Models
Dec 03, 2022Abstract:We consider the problem of reconstructing the signal and the hidden variables from observations coming from a multi-layer network with rotationally invariant weight matrices. The multi-layer structure models inference from deep generative priors, and the rotational invariance imposed on the weights generalizes the i.i.d.\ Gaussian assumption by allowing for a complex correlation structure, which is typical in applications. In this work, we present a new class of approximate message passing (AMP) algorithms and give a state evolution recursion which precisely characterizes their performance in the large system limit. In contrast with the existing multi-layer VAMP (ML-VAMP) approach, our proposed AMP -- dubbed multi-layer rotationally invariant generalized AMP (ML-RI-GAMP) -- provides a natural generalization beyond Gaussian designs, in the sense that it recovers the existing Gaussian AMP as a special case. Furthermore, ML-RI-GAMP exhibits a significantly lower complexity than ML-VAMP, as the computationally intensive singular value decomposition is replaced by an estimation of the moments of the design matrices. Finally, our numerical results show that this complexity gain comes at little to no cost in the performance of the algorithm.
The price of ignorance: how much does it cost to forget noise structure in low-rank matrix estimation?
May 20, 2022

Abstract:We consider the problem of estimating a rank-1 signal corrupted by structured rotationally invariant noise, and address the following question: how well do inference algorithms perform when the noise statistics is unknown and hence Gaussian noise is assumed? While the matched Bayes-optimal setting with unstructured noise is well understood, the analysis of this mismatched problem is only at its premises. In this paper, we make a step towards understanding the effect of the strong source of mismatch which is the noise statistics. Our main technical contribution is the rigorous analysis of a Bayes estimator and of an approximate message passing (AMP) algorithm, both of which incorrectly assume a Gaussian setup. The first result exploits the theory of spherical integrals and of low-rank matrix perturbations; the idea behind the second one is to design and analyze an artificial AMP which, by taking advantage of the flexibility in the denoisers, is able to "correct" the mismatch. Armed with these sharp asymptotic characterizations, we unveil a rich and often unexpected phenomenology. For example, despite AMP is in principle designed to efficiently compute the Bayes estimator, the former is outperformed by the latter in terms of mean-square error. We show that this performance gap is due to an incorrect estimation of the signal norm. In fact, when the SNR is large enough, the overlaps of the AMP and the Bayes estimator coincide, and they even match those of optimal estimators taking into account the structure of the noise.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge