Ke Niu
CME-CAD: Heterogeneous Collaborative Multi-Expert Reinforcement Learning for CAD Code Generation
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Computer-Aided Design (CAD) is essential in industrial design, but the complexity of traditional CAD modeling and workflows presents significant challenges for automating the generation of high-precision, editable CAD models. Existing methods that reconstruct 3D models from sketches often produce non-editable and approximate models that fall short of meeting the stringent requirements for precision and editability in industrial design. Moreover, the reliance on text or image-based inputs often requires significant manual annotation, limiting their scalability and applicability in industrial settings. To overcome these challenges, we propose the Heterogeneous Collaborative Multi-Expert Reinforcement Learning (CME-CAD) paradigm, a novel training paradigm for CAD code generation. Our approach integrates the complementary strengths of these models, facilitating collaborative learning and improving the model's ability to generate accurate, constraint-compatible, and fully editable CAD models. We introduce a two-stage training process: Multi-Expert Fine-Tuning (MEFT), and Multi-Expert Reinforcement Learning (MERL). Additionally, we present CADExpert, an open-source benchmark consisting of 17,299 instances, including orthographic projections with precise dimension annotations, expert-generated Chain-of-Thought (CoT) processes, executable CADQuery code, and rendered 3D models.
From Intent to Execution: Multimodal Chain-of-Thought Reinforcement Learning for Precise CAD Code Generation
Aug 13, 2025Abstract:Computer-Aided Design (CAD) plays a vital role in engineering and manufacturing, yet current CAD workflows require extensive domain expertise and manual modeling effort. Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have made it possible to generate code from natural language, opening new opportunities for automating parametric 3D modeling. However, directly translating human design intent into executable CAD code remains highly challenging, due to the need for logical reasoning, syntactic correctness, and numerical precision. In this work, we propose CAD-RL, a multimodal Chain-of-Thought (CoT) guided reinforcement learning post training framework for CAD modeling code generation. Our method combines CoT-based Cold Start with goal-driven reinforcement learning post training using three task-specific rewards: executability reward, geometric accuracy reward, and external evaluation reward. To ensure stable policy learning under sparse and high-variance reward conditions, we introduce three targeted optimization strategies: Trust Region Stretch for improved exploration, Precision Token Loss for enhanced dimensions parameter accuracy, and Overlong Filtering to reduce noisy supervision. To support training and benchmarking, we release ExeCAD, a noval dataset comprising 16,540 real-world CAD examples with paired natural language and structured design language descriptions, executable CADQuery scripts, and rendered 3D models. Experiments demonstrate that CAD-RL achieves significant improvements in reasoning quality, output precision, and code executability over existing VLMs.
Endoscopic Depth Estimation Based on Deep Learning: A Survey
Jul 28, 2025Abstract:Endoscopic depth estimation is a critical technology for improving the safety and precision of minimally invasive surgery. It has attracted considerable attention from researchers in medical imaging, computer vision, and robotics. Over the past decade, a large number of methods have been developed. Despite the existence of several related surveys, a comprehensive overview focusing on recent deep learning-based techniques is still limited. This paper endeavors to bridge this gap by systematically reviewing the state-of-the-art literature. Specifically, we provide a thorough survey of the field from three key perspectives: data, methods, and applications, covering a range of methods including both monocular and stereo approaches. We describe common performance evaluation metrics and summarize publicly available datasets. Furthermore, this review analyzes the specific challenges of endoscopic scenes and categorizes representative techniques based on their supervision strategies and network architectures. The application of endoscopic depth estimation in the important area of robot-assisted surgery is also reviewed. Finally, we outline potential directions for future research, such as domain adaptation, real-time implementation, and enhanced model generalization, thereby providing a valuable starting point for researchers to engage with and advance the field.
UMIT: Unifying Medical Imaging Tasks via Vision-Language Models
Mar 20, 2025



Abstract:With the rapid advancement of deep learning, particularly in the field of medical image analysis, an increasing number of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) are being widely applied to solve complex health and biomedical challenges. However, existing research has primarily focused on specific tasks or single modalities, which limits their applicability and generalization across diverse medical scenarios. To address this challenge, we propose UMIT, a unified multi-modal, multi-task VLM designed specifically for medical imaging tasks. UMIT is able to solve various tasks, including visual question answering, disease detection, and medical report generation. In addition, it is applicable to multiple imaging modalities (e.g., X-ray, CT and PET), covering a wide range of applications from basic diagnostics to complex lesion analysis. Moreover, UMIT supports both English and Chinese, expanding its applicability globally and ensuring accessibility to healthcare services in different linguistic contexts. To enhance the model's adaptability and task-handling capability, we design a unique two-stage training strategy and fine-tune UMIT with designed instruction templates. Through extensive empirical evaluation, UMIT outperforms previous methods in five tasks across multiple datasets. The performance of UMIT indicates that it can significantly enhance diagnostic accuracy and workflow efficiency, thus providing effective solutions for medical imaging applications.
ChatReID: Open-ended Interactive Person Retrieval via Hierarchical Progressive Tuning for Vision Language Models
Feb 27, 2025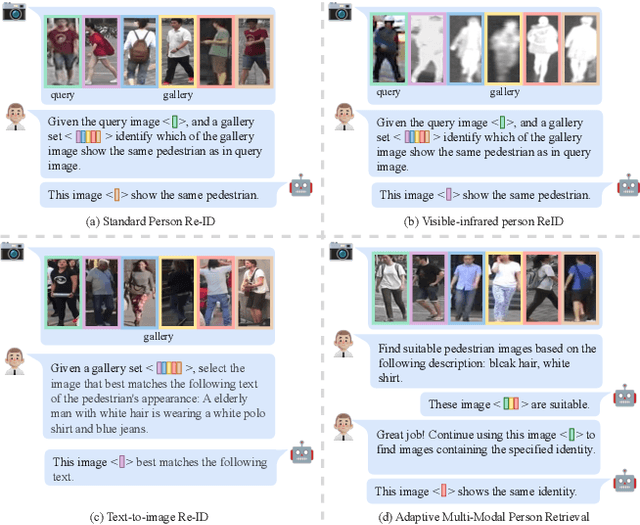
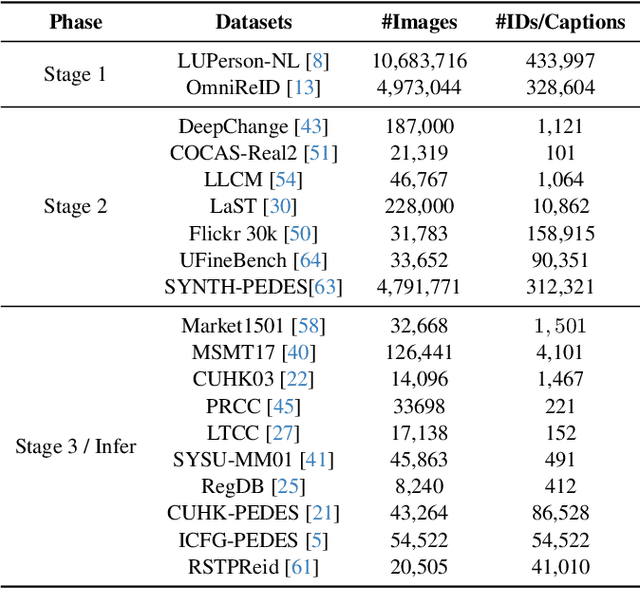
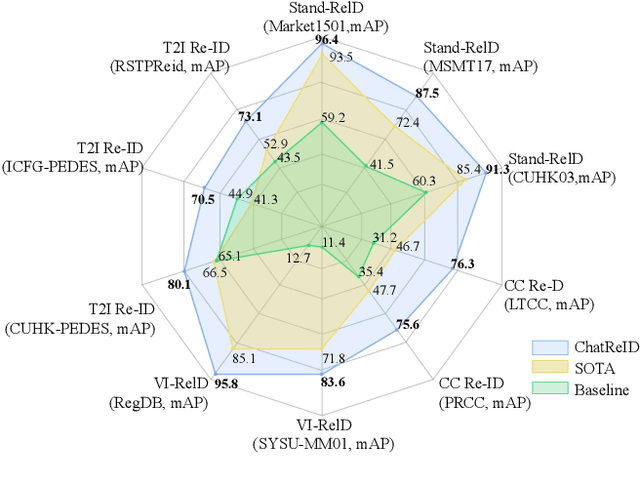
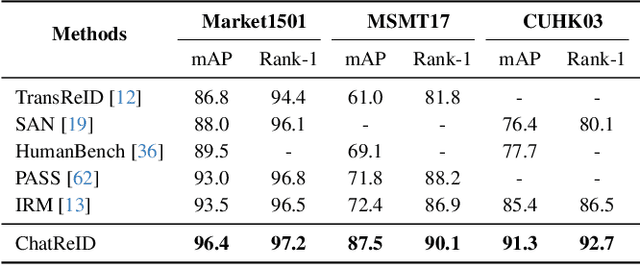
Abstract:Person re-identification (Re-ID) is a critical task in human-centric intelligent systems, enabling consistent identification of individuals across different camera views using multi-modal query information. Recent studies have successfully integrated LVLMs with person Re-ID, yielding promising results. However, existing LVLM-based methods face several limitations. They rely on extracting textual embeddings from fixed templates, which are used either as intermediate features for image representation or for prompt tuning in domain-specific tasks. Furthermore, they are unable to adopt the VQA inference format, significantly restricting their broader applicability. In this paper, we propose a novel, versatile, one-for-all person Re-ID framework, ChatReID. Our approach introduces a Hierarchical Progressive Tuning (HPT) strategy, which ensures fine-grained identity-level retrieval by progressively refining the model's ability to distinguish pedestrian identities. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach outperforms SOTA methods across ten benchmarks in four different Re-ID settings, offering enhanced flexibility and user-friendliness. ChatReID provides a scalable, practical solution for real-world person Re-ID applications, enabling effective multi-modal interaction and fine-grained identity discrimination.
Fundus Image Quality Assessment and Enhancement: a Systematic Review
Jan 20, 2025Abstract:As an affordable and convenient eye scan, fundus photography holds the potential for preventing vision impairment, especially in resource-limited regions. However, fundus image degradation is common under intricate imaging environments, impacting following diagnosis and treatment. Consequently, image quality assessment (IQA) and enhancement (IQE) are essential for ensuring the clinical value and reliability of fundus images. While existing reviews offer some overview of this field, a comprehensive analysis of the interplay between IQA and IQE, along with their clinical deployment challenges, is lacking. This paper addresses this gap by providing a thorough review of fundus IQA and IQE algorithms, research advancements, and practical applications. We outline the fundamentals of the fundus photography imaging system and the associated interferences, and then systematically summarize the paradigms in fundus IQA and IQE. Furthermore, we discuss the practical challenges and solutions in deploying IQA and IQE, as well as offer insights into potential future research directions.
AIF-SFDA: Autonomous Information Filter-driven Source-Free Domain Adaptation for Medical Image Segmentation
Jan 06, 2025



Abstract:Decoupling domain-variant information (DVI) from domain-invariant information (DII) serves as a prominent strategy for mitigating domain shifts in the practical implementation of deep learning algorithms. However, in medical settings, concerns surrounding data collection and privacy often restrict access to both training and test data, hindering the empirical decoupling of information by existing methods. To tackle this issue, we propose an Autonomous Information Filter-driven Source-free Domain Adaptation (AIF-SFDA) algorithm, which leverages a frequency-based learnable information filter to autonomously decouple DVI and DII. Information Bottleneck (IB) and Self-supervision (SS) are incorporated to optimize the learnable frequency filter. The IB governs the information flow within the filter to diminish redundant DVI, while SS preserves DII in alignment with the specific task and image modality. Thus, the autonomous information filter can overcome domain shifts relying solely on target data. A series of experiments covering various medical image modalities and segmentation tasks were conducted to demonstrate the benefits of AIF-SFDA through comparisons with leading algorithms and ablation studies. The code is available at https://github.com/JingHuaMan/AIF-SFDA.
Synthesizing Efficient Data with Diffusion Models for Person Re-Identification Pre-Training
Jun 10, 2024
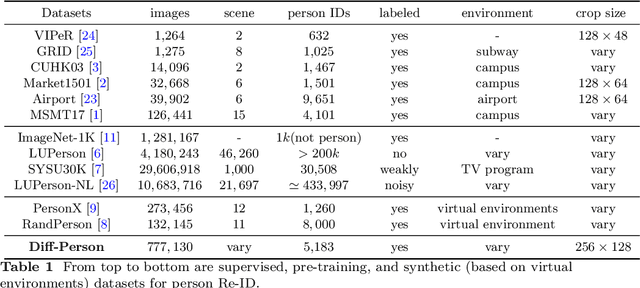
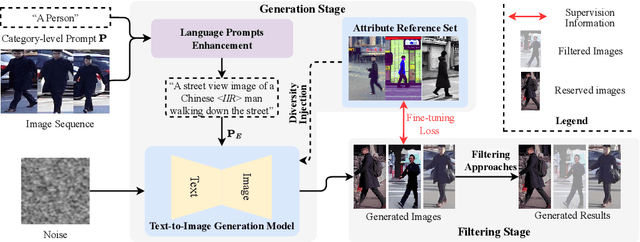
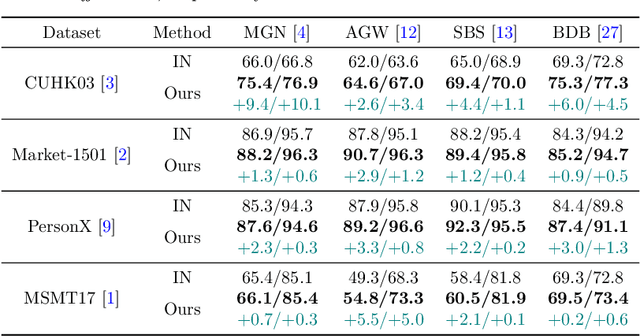
Abstract:Existing person re-identification (Re-ID) methods principally deploy the ImageNet-1K dataset for model initialization, which inevitably results in sub-optimal situations due to the large domain gap. One of the key challenges is that building large-scale person Re-ID datasets is time-consuming. Some previous efforts address this problem by collecting person images from the internet e.g., LUPerson, but it struggles to learn from unlabeled, uncontrollable, and noisy data. In this paper, we present a novel paradigm Diffusion-ReID to efficiently augment and generate diverse images based on known identities without requiring any cost of data collection and annotation. Technically, this paradigm unfolds in two stages: generation and filtering. During the generation stage, we propose Language Prompts Enhancement (LPE) to ensure the ID consistency between the input image sequence and the generated images. In the diffusion process, we propose a Diversity Injection (DI) module to increase attribute diversity. In order to make the generated data have higher quality, we apply a Re-ID confidence threshold filter to further remove the low-quality images. Benefiting from our proposed paradigm, we first create a new large-scale person Re-ID dataset Diff-Person, which consists of over 777K images from 5,183 identities. Next, we build a stronger person Re-ID backbone pre-trained on our Diff-Person. Extensive experiments are conducted on four person Re-ID benchmarks in six widely used settings. Compared with other pre-training and self-supervised competitors, our approach shows significant superiority.
DeNoising-MOT: Towards Multiple Object Tracking with Severe Occlusions
Sep 09, 2023Abstract:Multiple object tracking (MOT) tends to become more challenging when severe occlusions occur. In this paper, we analyze the limitations of traditional Convolutional Neural Network-based methods and Transformer-based methods in handling occlusions and propose DNMOT, an end-to-end trainable DeNoising Transformer for MOT. To address the challenge of occlusions, we explicitly simulate the scenarios when occlusions occur. Specifically, we augment the trajectory with noises during training and make our model learn the denoising process in an encoder-decoder architecture, so that our model can exhibit strong robustness and perform well under crowded scenes. Additionally, we propose a Cascaded Mask strategy to better coordinate the interaction between different types of queries in the decoder to prevent the mutual suppression between neighboring trajectories under crowded scenes. Notably, the proposed method requires no additional modules like matching strategy and motion state estimation in inference. We conduct extensive experiments on the MOT17, MOT20, and DanceTrack datasets, and the experimental results show that our method outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods by a clear margin.
A Generic Fundus Image Enhancement Network Boosted by Frequency Self-supervised Representation Learning
Sep 02, 2023



Abstract:Fundus photography is prone to suffer from image quality degradation that impacts clinical examination performed by ophthalmologists or intelligent systems. Though enhancement algorithms have been developed to promote fundus observation on degraded images, high data demands and limited applicability hinder their clinical deployment. To circumvent this bottleneck, a generic fundus image enhancement network (GFE-Net) is developed in this study to robustly correct unknown fundus images without supervised or extra data. Levering image frequency information, self-supervised representation learning is conducted to learn robust structure-aware representations from degraded images. Then with a seamless architecture that couples representation learning and image enhancement, GFE-Net can accurately correct fundus images and meanwhile preserve retinal structures. Comprehensive experiments are implemented to demonstrate the effectiveness and advantages of GFE-Net. Compared with state-of-the-art algorithms, GFE-Net achieves superior performance in data dependency, enhancement performance, deployment efficiency, and scale generalizability. Follow-up fundus image analysis is also facilitated by GFE-Net, whose modules are respectively verified to be effective for image enhancement.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge