Siyang Yi
UMIT: Unifying Medical Imaging Tasks via Vision-Language Models
Mar 20, 2025



Abstract:With the rapid advancement of deep learning, particularly in the field of medical image analysis, an increasing number of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) are being widely applied to solve complex health and biomedical challenges. However, existing research has primarily focused on specific tasks or single modalities, which limits their applicability and generalization across diverse medical scenarios. To address this challenge, we propose UMIT, a unified multi-modal, multi-task VLM designed specifically for medical imaging tasks. UMIT is able to solve various tasks, including visual question answering, disease detection, and medical report generation. In addition, it is applicable to multiple imaging modalities (e.g., X-ray, CT and PET), covering a wide range of applications from basic diagnostics to complex lesion analysis. Moreover, UMIT supports both English and Chinese, expanding its applicability globally and ensuring accessibility to healthcare services in different linguistic contexts. To enhance the model's adaptability and task-handling capability, we design a unique two-stage training strategy and fine-tune UMIT with designed instruction templates. Through extensive empirical evaluation, UMIT outperforms previous methods in five tasks across multiple datasets. The performance of UMIT indicates that it can significantly enhance diagnostic accuracy and workflow efficiency, thus providing effective solutions for medical imaging applications.
ChatReID: Open-ended Interactive Person Retrieval via Hierarchical Progressive Tuning for Vision Language Models
Feb 27, 2025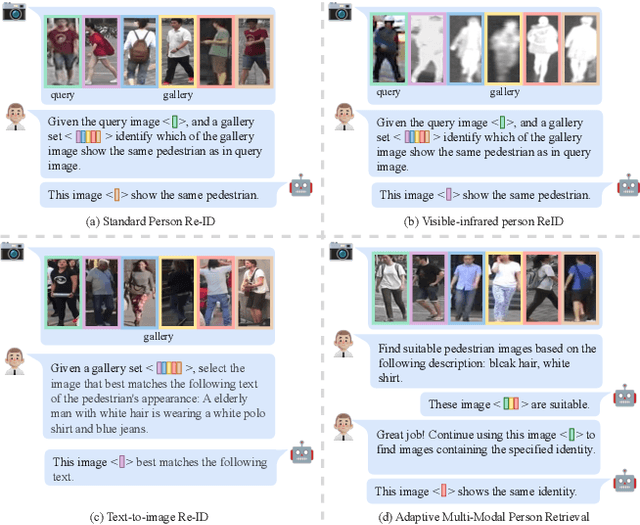
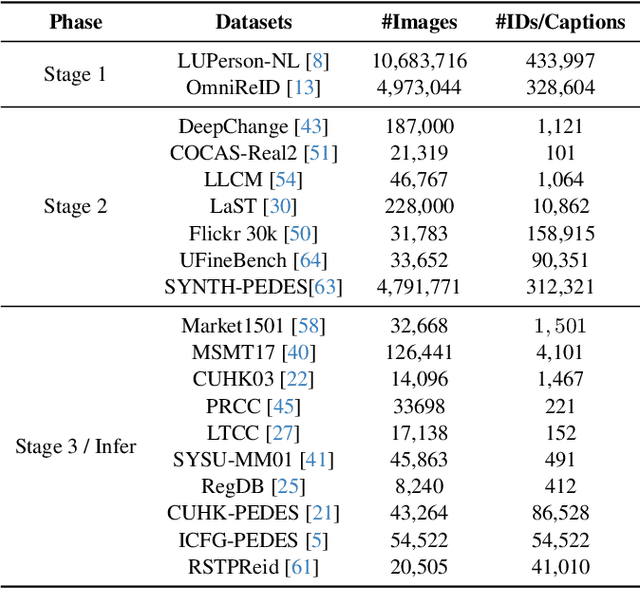
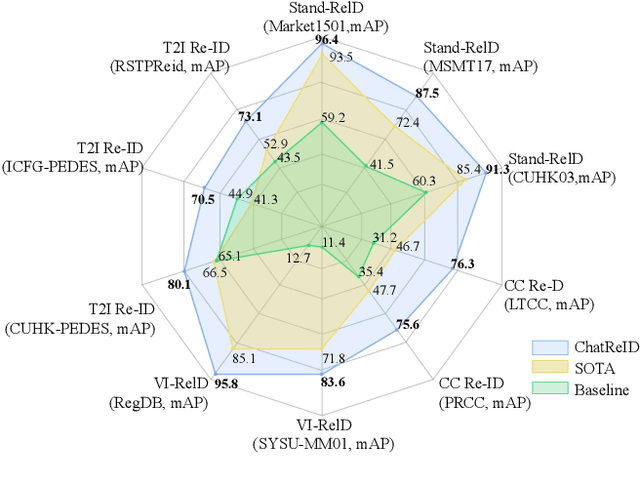
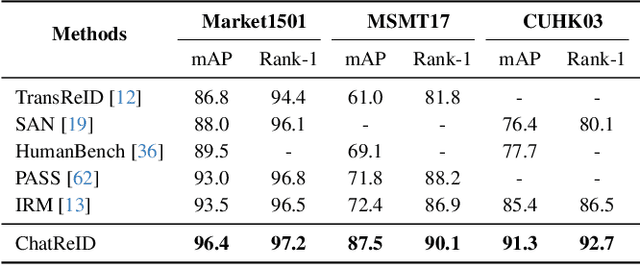
Abstract:Person re-identification (Re-ID) is a critical task in human-centric intelligent systems, enabling consistent identification of individuals across different camera views using multi-modal query information. Recent studies have successfully integrated LVLMs with person Re-ID, yielding promising results. However, existing LVLM-based methods face several limitations. They rely on extracting textual embeddings from fixed templates, which are used either as intermediate features for image representation or for prompt tuning in domain-specific tasks. Furthermore, they are unable to adopt the VQA inference format, significantly restricting their broader applicability. In this paper, we propose a novel, versatile, one-for-all person Re-ID framework, ChatReID. Our approach introduces a Hierarchical Progressive Tuning (HPT) strategy, which ensures fine-grained identity-level retrieval by progressively refining the model's ability to distinguish pedestrian identities. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach outperforms SOTA methods across ten benchmarks in four different Re-ID settings, offering enhanced flexibility and user-friendliness. ChatReID provides a scalable, practical solution for real-world person Re-ID applications, enabling effective multi-modal interaction and fine-grained identity discrimination.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge