Shuiqiao Yang
ThreatModeling-LLM: Automating Threat Modeling using Large Language Models for Banking System
Nov 26, 2024Abstract:Threat modeling is a crucial component of cybersecurity, particularly for industries such as banking, where the security of financial data is paramount. Traditional threat modeling approaches require expert intervention and manual effort, often leading to inefficiencies and human error. The advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) offers a promising avenue for automating these processes, enhancing both efficiency and efficacy. However, this transition is not straightforward due to three main challenges: (1) the lack of publicly available, domain-specific datasets, (2) the need for tailored models to handle complex banking system architectures, and (3) the requirement for real-time, adaptive mitigation strategies that align with compliance standards like NIST 800-53. In this paper, we introduce ThreatModeling-LLM, a novel and adaptable framework that automates threat modeling for banking systems using LLMs. ThreatModeling-LLM operates in three stages: 1) dataset creation, 2) prompt engineering and 3) model fine-tuning. We first generate a benchmark dataset using Microsoft Threat Modeling Tool (TMT). Then, we apply Chain of Thought (CoT) and Optimization by PROmpting (OPRO) on the pre-trained LLMs to optimize the initial prompt. Lastly, we fine-tune the LLM using Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) based on the benchmark dataset and the optimized prompt to improve the threat identification and mitigation generation capabilities of pre-trained LLMs.
SS-shapelets: Semi-supervised Clustering of Time Series Using Representative Shapelets
Apr 06, 2023



Abstract:Shapelets that discriminate time series using local features (subsequences) are promising for time series clustering. Existing time series clustering methods may fail to capture representative shapelets because they discover shapelets from a large pool of uninformative subsequences, and thus result in low clustering accuracy. This paper proposes a Semi-supervised Clustering of Time Series Using Representative Shapelets (SS-Shapelets) method, which utilizes a small number of labeled and propagated pseudo-labeled time series to help discover representative shapelets, thereby improving the clustering accuracy. In SS-Shapelets, we propose two techniques to discover representative shapelets for the effective clustering of time series. 1) A \textit{salient subsequence chain} ($SSC$) that can extract salient subsequences (as candidate shapelets) of a labeled/pseudo-labeled time series, which helps remove massive uninformative subsequences from the pool. 2) A \textit{linear discriminant selection} ($LDS$) algorithm to identify shapelets that can capture representative local features of time series in different classes, for convenient clustering. Experiments on UCR time series datasets demonstrate that SS-shapelets discovers representative shapelets and achieves higher clustering accuracy than counterpart semi-supervised time series clustering methods.
Hybrid Variational Autoencoder for Time Series Forecasting
Mar 13, 2023
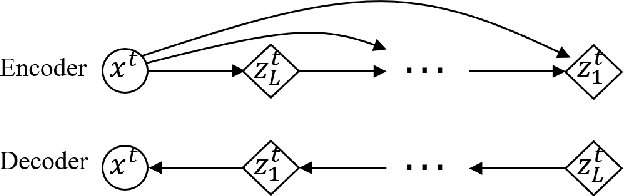
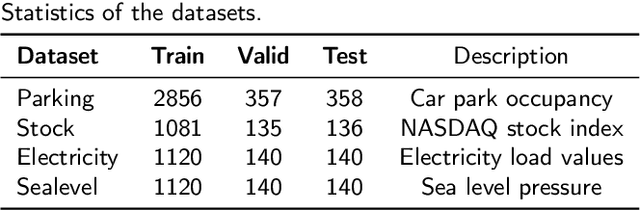
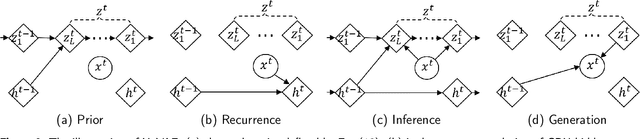
Abstract:Variational autoencoders (VAE) are powerful generative models that learn the latent representations of input data as random variables. Recent studies show that VAE can flexibly learn the complex temporal dynamics of time series and achieve more promising forecasting results than deterministic models. However, a major limitation of existing works is that they fail to jointly learn the local patterns (e.g., seasonality and trend) and temporal dynamics of time series for forecasting. Accordingly, we propose a novel hybrid variational autoencoder (HyVAE) to integrate the learning of local patterns and temporal dynamics by variational inference for time series forecasting. Experimental results on four real-world datasets show that the proposed HyVAE achieves better forecasting results than various counterpart methods, as well as two HyVAE variants that only learn the local patterns or temporal dynamics of time series, respectively.
Transferable Graph Backdoor Attack
Jul 05, 2022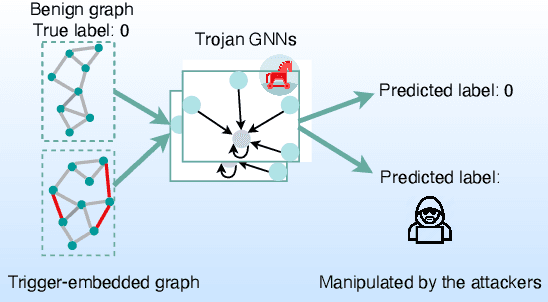
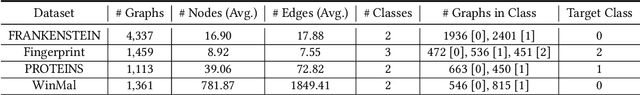
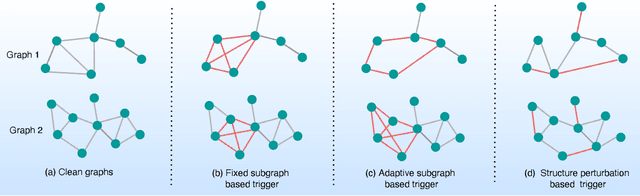
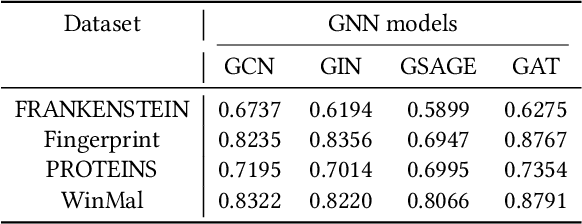
Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have achieved tremendous success in many graph mining tasks benefitting from the message passing strategy that fuses the local structure and node features for better graph representation learning. Despite the success of GNNs, and similar to other types of deep neural networks, GNNs are found to be vulnerable to unnoticeable perturbations on both graph structure and node features. Many adversarial attacks have been proposed to disclose the fragility of GNNs under different perturbation strategies to create adversarial examples. However, vulnerability of GNNs to successful backdoor attacks was only shown recently. In this paper, we disclose the TRAP attack, a Transferable GRAPh backdoor attack. The core attack principle is to poison the training dataset with perturbation-based triggers that can lead to an effective and transferable backdoor attack. The perturbation trigger for a graph is generated by performing the perturbation actions on the graph structure via a gradient based score matrix from a surrogate model. Compared with prior works, TRAP attack is different in several ways: i) it exploits a surrogate Graph Convolutional Network (GCN) model to generate perturbation triggers for a blackbox based backdoor attack; ii) it generates sample-specific perturbation triggers which do not have a fixed pattern; and iii) the attack transfers, for the first time in the context of GNNs, to different GNN models when trained with the forged poisoned training dataset. Through extensive evaluations on four real-world datasets, we demonstrate the effectiveness of the TRAP attack to build transferable backdoors in four different popular GNNs using four real-world datasets.
Fake News Quick Detection on Dynamic Heterogeneous Information Networks
May 14, 2022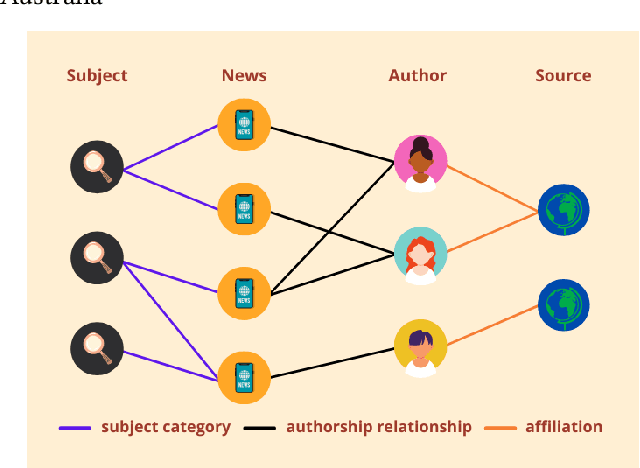
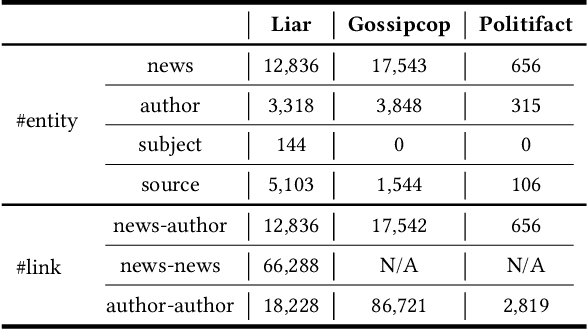
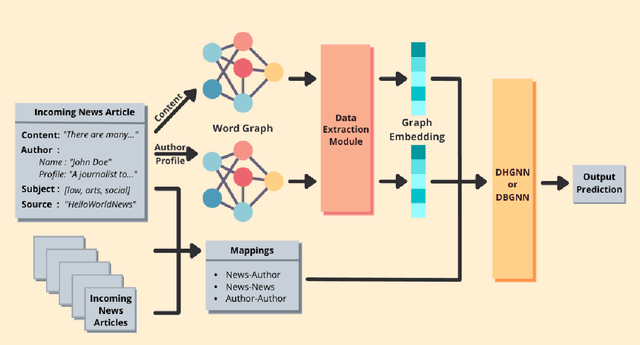
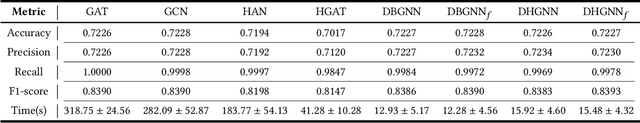
Abstract:The spread of fake news has caused great harm to society in recent years. So the quick detection of fake news has become an important task. Some current detection methods often model news articles and other related components as a static heterogeneous information network (HIN) and use expensive message-passing algorithms. However, in the real-world, quickly identifying fake news is of great significance and the network may vary over time in terms of dynamic nodes and edges. Therefore, in this paper, we propose a novel Dynamic Heterogeneous Graph Neural Network (DHGNN) for fake news quick detection. More specifically, we first implement BERT and fine-tuned BERT to get a semantic representation of the news article contents and author profiles and convert it into graph data. Then, we construct the heterogeneous news-author graph to reflect contextual information and relationships. Additionally, we adapt ideas from personalized PageRank propagation and dynamic propagation to heterogeneous networks in order to reduce the time complexity of back-propagating through many nodes during training. Experiments on three real-world fake news datasets show that DHGNN can outperform other GNN-based models in terms of both effectiveness and efficiency.
Representation Learning for Short Text Clustering
Sep 21, 2021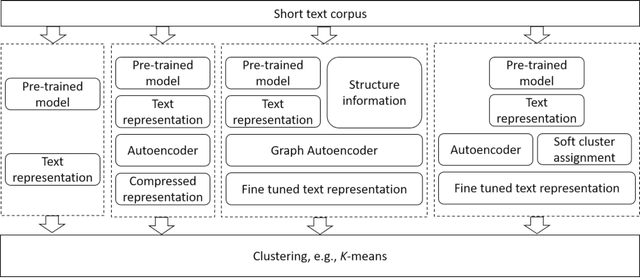
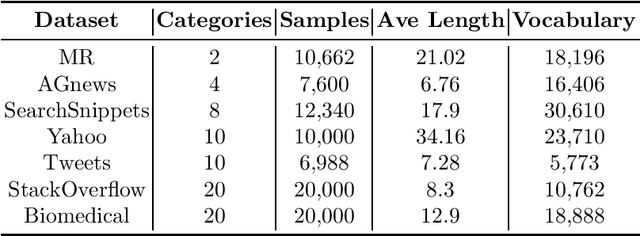
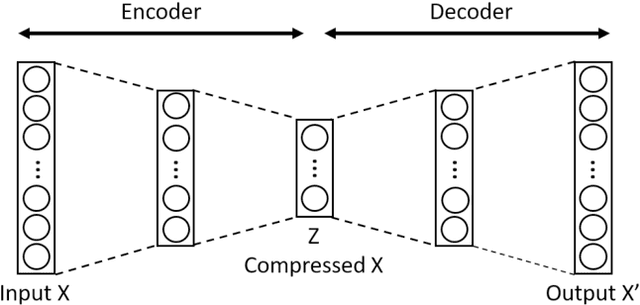
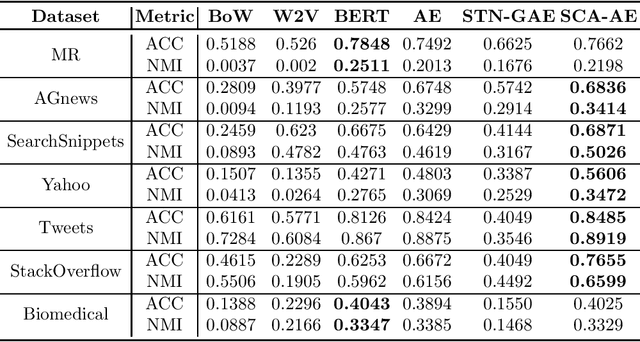
Abstract:Effective representation learning is critical for short text clustering due to the sparse, high-dimensional and noise attributes of short text corpus. Existing pre-trained models (e.g., Word2vec and BERT) have greatly improved the expressiveness for short text representations with more condensed, low-dimensional and continuous features compared to the traditional Bag-of-Words (BoW) model. However, these models are trained for general purposes and thus are suboptimal for the short text clustering task. In this paper, we propose two methods to exploit the unsupervised autoencoder (AE) framework to further tune the short text representations based on these pre-trained text models for optimal clustering performance. In our first method Structural Text Network Graph Autoencoder (STN-GAE), we exploit the structural text information among the corpus by constructing a text network, and then adopt graph convolutional network as encoder to fuse the structural features with the pre-trained text features for text representation learning. In our second method Soft Cluster Assignment Autoencoder (SCA-AE), we adopt an extra soft cluster assignment constraint on the latent space of autoencoder to encourage the learned text representations to be more clustering-friendly. We tested two methods on seven popular short text datasets, and the experimental results show that when only using the pre-trained model for short text clustering, BERT performs better than BoW and Word2vec. However, as long as we further tune the pre-trained representations, the proposed method like SCA-AE can greatly increase the clustering performance, and the accuracy improvement compared to use BERT alone could reach as much as 14\%.
Variational Co-embedding Learning for Attributed Network Clustering
Apr 15, 2021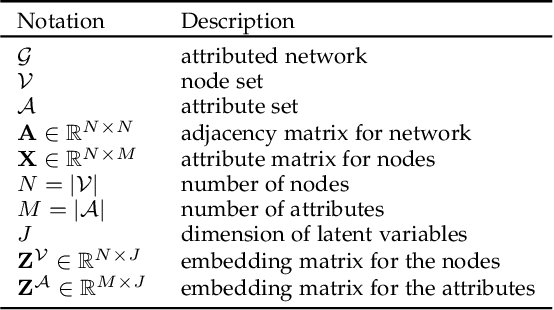
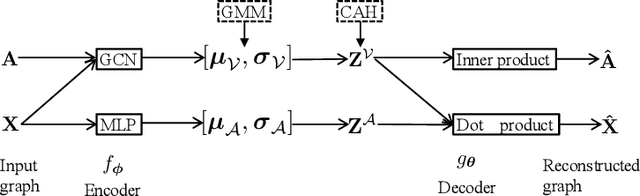
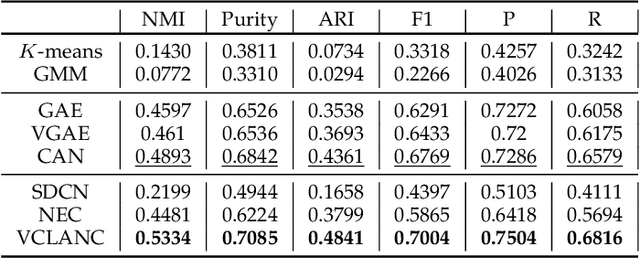
Abstract:Recent works for attributed network clustering utilize graph convolution to obtain node embeddings and simultaneously perform clustering assignments on the embedding space. It is effective since graph convolution combines the structural and attributive information for node embedding learning. However, a major limitation of such works is that the graph convolution only incorporates the attribute information from the local neighborhood of nodes but fails to exploit the mutual affinities between nodes and attributes. In this regard, we propose a variational co-embedding learning model for attributed network clustering (VCLANC). VCLANC is composed of dual variational auto-encoders to simultaneously embed nodes and attributes. Relying on this, the mutual affinity information between nodes and attributes could be reconstructed from the embedding space and served as extra self-supervised knowledge for representation learning. At the same time, trainable Gaussian mixture model is used as priors to infer the node clustering assignments. To strengthen the performance of the inferred clusters, we use a mutual distance loss on the centers of the Gaussian priors and a clustering assignment hardening loss on the node embeddings. Experimental results on four real-world attributed network datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed VCLANC for attributed network clustering.
Examination of community sentiment dynamics due to covid-19 pandemic: a case study from Australia
Jun 22, 2020

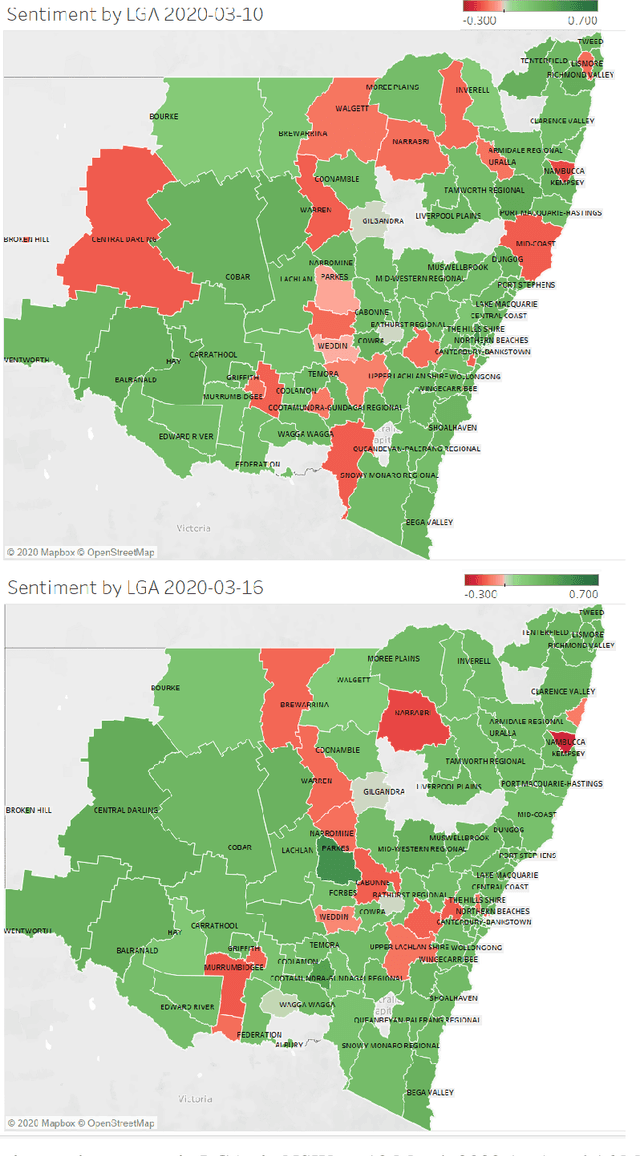
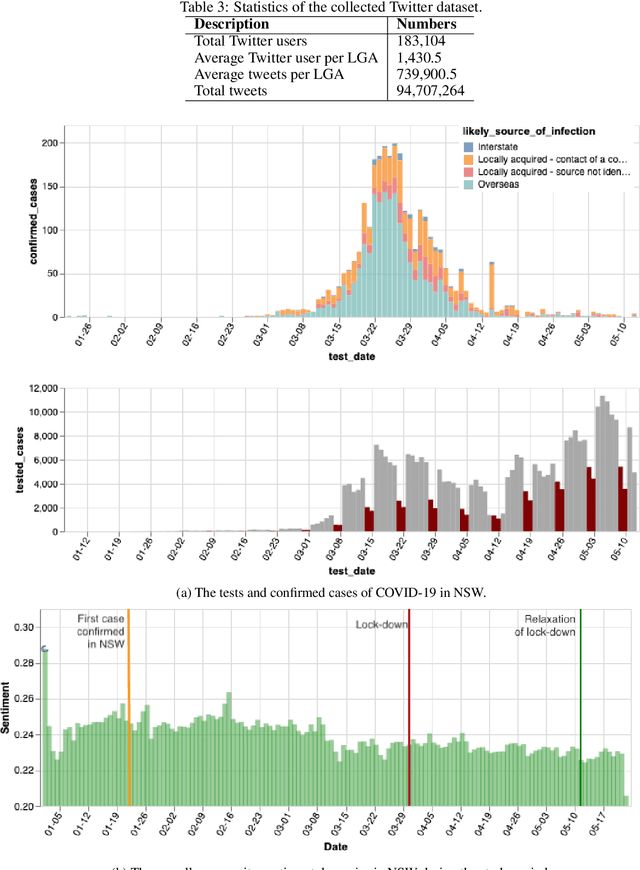
Abstract:The outbreak of the novel Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) has caused unprecedented impacts to people's daily life around the world. Various measures and policies such as lock-down and social-distancing are implemented by governments to combat the disease during the pandemic period. These measures and policies as well as virus itself may cause different mental health issues to people such as depression, anxiety, sadness, etc. In this paper, we exploit the massive text data posted by Twitter users to analyse the sentiment dynamics of people living in the state of New South Wales (NSW) in Australia during the pandemic period. Different from the existing work that mostly focuses the country-level and static sentiment analysis, we analyse the sentiment dynamics at the fine-grained local government areas (LGAs). Based on the analysis of around 94 million tweets that posted by around 183 thousand users located at different LGAs in NSW in five months, we found that people in NSW showed an overall positive sentimental polarity and the COVID-19 pandemic decreased the overall positive sentimental polarity during the pandemic period. The fine-grained analysis of sentiment in LGAs found that despite the dominant positive sentiment most of days during the study period, some LGAs experienced significant sentiment changes from positive to negative. This study also analysed the sentimental dynamics delivered by the hot topics in Twitter such as government policies (e.g. the Australia's JobKeeper program, lock-down, social-distancing) as well as the focused social events (e.g. the Ruby Princess Cruise). The results showed that the policies and events did affect people's overall sentiment, and they affected people's overall sentiment differently at different stages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge