Chun Xiao
A Non-Uniform Low-Light Image Enhancement Method with Multi-Scale Attention Transformer and Luminance Consistency Loss
Dec 27, 2023Abstract:Low-light image enhancement aims to improve the perception of images collected in dim environments and provide high-quality data support for image recognition tasks. When dealing with photos captured under non-uniform illumination, existing methods cannot adaptively extract the differentiated luminance information, which will easily cause over-exposure and under-exposure. From the perspective of unsupervised learning, we propose a multi-scale attention Transformer named MSATr, which sufficiently extracts local and global features for light balance to improve the visual quality. Specifically, we present a multi-scale window division scheme, which uses exponential sequences to adjust the window size of each layer. Within different-sized windows, the self-attention computation can be refined, ensuring the pixel-level feature processing capability of the model. For feature interaction across windows, a global transformer branch is constructed to provide comprehensive brightness perception and alleviate exposure problems. Furthermore, we propose a loop training strategy, using the diverse images generated by weighted mixing and a luminance consistency loss to improve the model's generalization ability effectively. Extensive experiments on several benchmark datasets quantitatively and qualitatively prove that our MSATr is superior to state-of-the-art low-light image enhancement methods, and the enhanced images have more natural brightness and outstanding details. The code is released at https://github.com/fang001021/MSATr.
Examination of community sentiment dynamics due to covid-19 pandemic: a case study from Australia
Jun 22, 2020

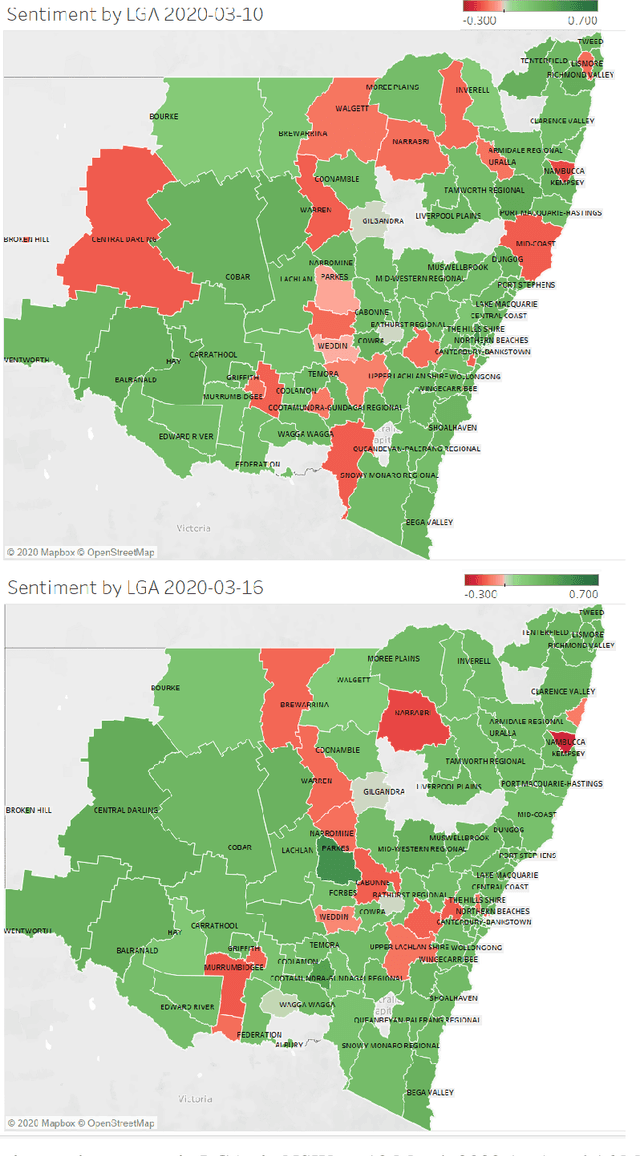
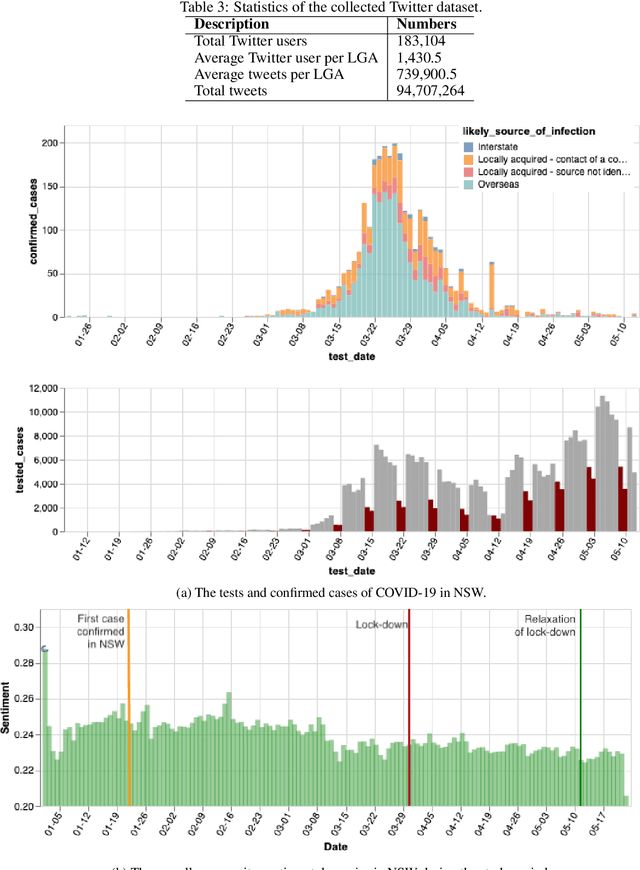
Abstract:The outbreak of the novel Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) has caused unprecedented impacts to people's daily life around the world. Various measures and policies such as lock-down and social-distancing are implemented by governments to combat the disease during the pandemic period. These measures and policies as well as virus itself may cause different mental health issues to people such as depression, anxiety, sadness, etc. In this paper, we exploit the massive text data posted by Twitter users to analyse the sentiment dynamics of people living in the state of New South Wales (NSW) in Australia during the pandemic period. Different from the existing work that mostly focuses the country-level and static sentiment analysis, we analyse the sentiment dynamics at the fine-grained local government areas (LGAs). Based on the analysis of around 94 million tweets that posted by around 183 thousand users located at different LGAs in NSW in five months, we found that people in NSW showed an overall positive sentimental polarity and the COVID-19 pandemic decreased the overall positive sentimental polarity during the pandemic period. The fine-grained analysis of sentiment in LGAs found that despite the dominant positive sentiment most of days during the study period, some LGAs experienced significant sentiment changes from positive to negative. This study also analysed the sentimental dynamics delivered by the hot topics in Twitter such as government policies (e.g. the Australia's JobKeeper program, lock-down, social-distancing) as well as the focused social events (e.g. the Ruby Princess Cruise). The results showed that the policies and events did affect people's overall sentiment, and they affected people's overall sentiment differently at different stages.
An Approach for Resource Sharing in Multilingual NLP
Apr 23, 2003

Abstract:In this paper we describe an approach for the analysis of documents in German and English with a shared pool of resources. For the analysis of German documents we use a document suite, which supports the user in tasks like information retrieval and information extraction. The core of the document suite is based on our tool XDOC. Now we want to exploit these methods for the analysis of English documents as well. For this aim we need a multilingual presentation format of the resources. These resources must be transformed into an unified format, in which we can set additional information about linguistic characteristics of the language depending on the analyzed documents. In this paper we describe our approach for such an exchange model for multilingual resources based on XML.
* poster
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge