Shiyao Zhang
Failure-Aware Bimanual Teleoperation via Conservative Value Guided Assistance
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Teleoperation of high-precision manipulation is con-strained by tight success tolerances and complex contact dy-namics, which make impending failures difficult for human operators to anticipate under partial observability. This paper proposes a value-guided, failure-aware framework for bimanual teleoperation that provides compliant haptic assistance while pre-serving continuous human authority. The framework is trained entirely from heterogeneous offline teleoperation data containing both successful and failed executions. Task feasibility is mod-eled as a conservative success score learned via Conservative Value Learning, yielding a risk-sensitive estimate that remains reliable under distribution shift. During online operation, the learned success score regulates the level of assistance, while a learned actor provides a corrective motion direction. Both are integrated through a joint-space impedance interface on the master side, yielding continuous guidance that steers the operator away from failure-prone actions without overriding intent. Experimental results on contact-rich manipulation tasks demonstrate improved task success rates and reduced operator workload compared to conventional teleoperation and shared-autonomy baselines, indicating that conservative value learning provides an effective mechanism for embedding failure awareness into bilateral teleoperation. Experimental videos are available at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XDTsvzEkDRE
Breathe with Me: Synchronizing Biosignals for User Embodiment in Robots
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:Embodiment of users within robotic systems has been explored in human-robot interaction, most often in telepresence and teleoperation. In these applications, synchronized visuomotor feedback can evoke a sense of body ownership and agency, contributing to the experience of embodiment. We extend this work by employing embreathment, the representation of the user's own breath in real time, as a means for enhancing user embodiment experience in robots. In a within-subjects experiment, participants controlled a robotic arm, while its movements were either synchronized or non-synchronized with their own breath. Synchrony was shown to significantly increase body ownership, and was preferred by most participants. We propose the representation of physiological signals as a novel interoceptive pathway for human-robot interaction, and discuss implications for telepresence, prosthetics, collaboration with robots, and shared autonomy.
Multi-Uncertainty Aware Autonomous Cooperative Planning
Nov 01, 2024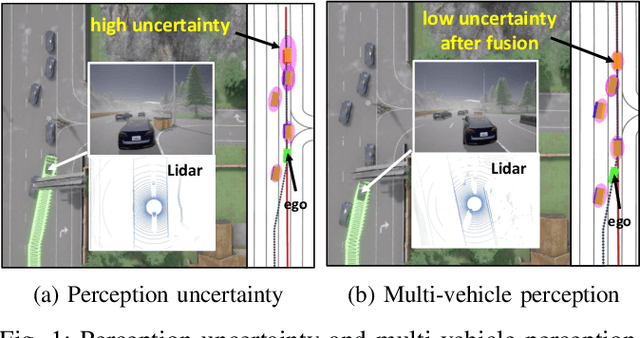
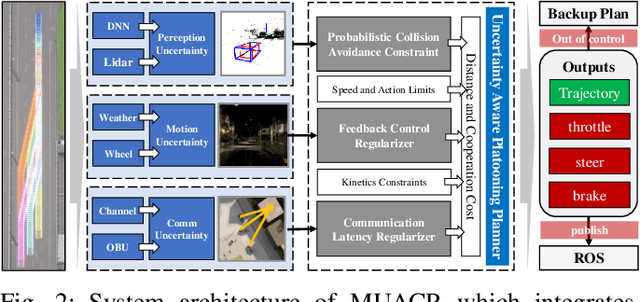
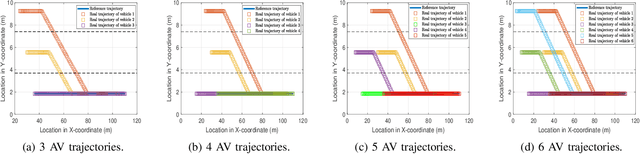
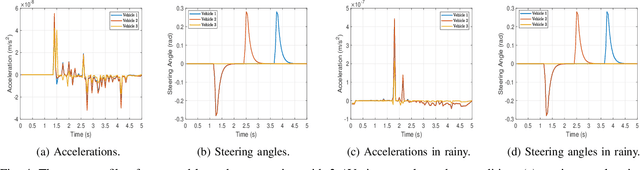
Abstract:Autonomous cooperative planning (ACP) is a promising technique to improve the efficiency and safety of multi-vehicle interactions for future intelligent transportation systems. However, realizing robust ACP is a challenge due to the aggregation of perception, motion, and communication uncertainties. This paper proposes a novel multi-uncertainty aware ACP (MUACP) framework that simultaneously accounts for multiple types of uncertainties via regularized cooperative model predictive control (RC-MPC). The regularizers and constraints for perception, motion, and communication are constructed according to the confidence levels, weather conditions, and outage probabilities, respectively. The effectiveness of the proposed method is evaluated in the Car Learning to Act (CARLA) simulation platform. Results demonstrate that the proposed MUACP efficiently performs cooperative formation in real time and outperforms other benchmark approaches in various scenarios under imperfect knowledge of the environment.
Siamese Multiple Attention Temporal Convolution Networks for Human Mobility Signature Identification
Aug 17, 2024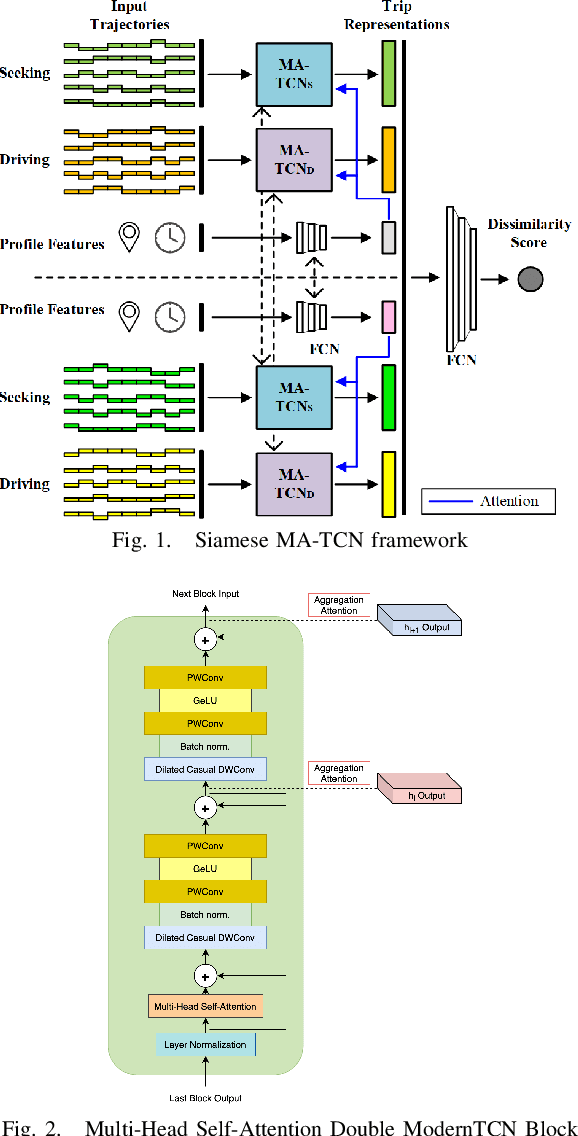
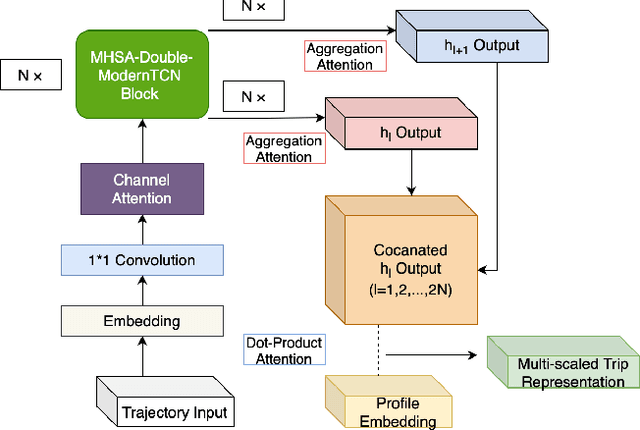
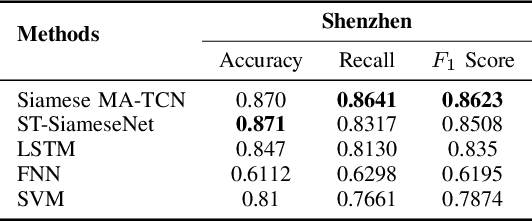
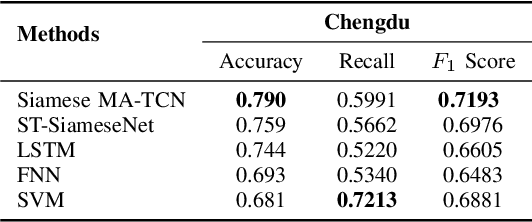
Abstract:The Human Mobility Signature Identification (HuMID) problem stands as a fundamental task within the realm of driving style representation, dedicated to discerning latent driving behaviors and preferences from diverse driver trajectories for driver identification. Its solutions hold significant implications across various domains (e.g., ride-hailing, insurance), wherein their application serves to safeguard users and mitigate potential fraudulent activities. Present HuMID solutions often exhibit limitations in adaptability when confronted with lengthy trajectories, consequently incurring substantial computational overhead. Furthermore, their inability to effectively extract crucial local information further impedes their performance. To address this problem, we propose a Siamese Multiple Attention Temporal Convolutional Network (Siamese MA-TCN) to capitalize on the strengths of both TCN architecture and multi-head self-attention, enabling the proficient extraction of both local and long-term dependencies. Additionally, we devise a novel attention mechanism tailored for the efficient aggregation of multi-scale representations derived from our model. Experimental evaluations conducted on two real-world taxi trajectory datasets reveal that our proposed model effectively extracts both local key information and long-term dependencies. These findings highlight the model's outstanding generalization capabilities, demonstrating its robustness and adaptability across datasets of varying sizes.
Harnessing Earnings Reports for Stock Predictions: A QLoRA-Enhanced LLM Approach
Aug 13, 2024


Abstract:Accurate stock market predictions following earnings reports are crucial for investors. Traditional methods, particularly classical machine learning models, struggle with these predictions because they cannot effectively process and interpret extensive textual data contained in earnings reports and often overlook nuances that influence market movements. This paper introduces an advanced approach by employing Large Language Models (LLMs) instruction fine-tuned with a novel combination of instruction-based techniques and quantized low-rank adaptation (QLoRA) compression. Our methodology integrates 'base factors', such as financial metric growth and earnings transcripts, with 'external factors', including recent market indices performances and analyst grades, to create a rich, supervised dataset. This comprehensive dataset enables our models to achieve superior predictive performance in terms of accuracy, weighted F1, and Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC), especially evident in the comparison with benchmarks such as GPT-4. We specifically highlight the efficacy of the llama-3-8b-Instruct-4bit model, which showcases significant improvements over baseline models. The paper also discusses the potential of expanding the output capabilities to include a 'Hold' option and extending the prediction horizon, aiming to accommodate various investment styles and time frames. This study not only demonstrates the power of integrating cutting-edge AI with fine-tuned financial data but also paves the way for future research in enhancing AI-driven financial analysis tools.
Evaluating Modern Approaches in 3D Scene Reconstruction: NeRF vs Gaussian-Based Methods
Aug 08, 2024Abstract:Exploring the capabilities of Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and Gaussian-based methods in the context of 3D scene reconstruction, this study contrasts these modern approaches with traditional Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) systems. Utilizing datasets such as Replica and ScanNet, we assess performance based on tracking accuracy, mapping fidelity, and view synthesis. Findings reveal that NeRF excels in view synthesis, offering unique capabilities in generating new perspectives from existing data, albeit at slower processing speeds. Conversely, Gaussian-based methods provide rapid processing and significant expressiveness but lack comprehensive scene completion. Enhanced by global optimization and loop closure techniques, newer methods like NICE-SLAM and SplaTAM not only surpass older frameworks such as ORB-SLAM2 in terms of robustness but also demonstrate superior performance in dynamic and complex environments. This comparative analysis bridges theoretical research with practical implications, shedding light on future developments in robust 3D scene reconstruction across various real-world applications.
FedVAE: Trajectory privacy preserving based on Federated Variational AutoEncoder
Jul 12, 2024



Abstract:The use of trajectory data with abundant spatial-temporal information is pivotal in Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS) and various traffic system tasks. Location-Based Services (LBS) capitalize on this trajectory data to offer users personalized services tailored to their location information. However, this trajectory data contains sensitive information about users' movement patterns and habits, necessitating confidentiality and protection from unknown collectors. To address this challenge, privacy-preserving methods like K-anonymity and Differential Privacy have been proposed to safeguard private information in the dataset. Despite their effectiveness, these methods can impact the original features by introducing perturbations or generating unrealistic trajectory data, leading to suboptimal performance in downstream tasks. To overcome these limitations, we propose a Federated Variational AutoEncoder (FedVAE) approach, which effectively generates a new trajectory dataset while preserving the confidentiality of private information and retaining the structure of the original features. In addition, FedVAE leverages Variational AutoEncoder (VAE) to maintain the original feature space and generate new trajectory data, and incorporates Federated Learning (FL) during the training stage, ensuring that users' data remains locally stored to protect their personal information. The results demonstrate its superior performance compared to other existing methods, affirming FedVAE as a promising solution for enhancing data privacy and utility in location-based applications.
Time Series Modeling for Heart Rate Prediction: From ARIMA to Transformers
Jun 18, 2024Abstract:Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a leading cause of death globally, necessitating precise forecasting models for monitoring vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, and ECG. Traditional models, such as ARIMA and Prophet, are limited by their need for manual parameter tuning and challenges in handling noisy, sparse, and highly variable medical data. This study investigates advanced deep learning models, including LSTM, and transformer-based architectures, for predicting heart rate time series from the MIT-BIH Database. Results demonstrate that deep learning models, particularly PatchTST, significantly outperform traditional models across multiple metrics, capturing complex patterns and dependencies more effectively. This research underscores the potential of deep learning to enhance patient monitoring and CVD management, suggesting substantial clinical benefits. Future work should extend these findings to larger, more diverse datasets and real-world clinical applications to further validate and optimize model performance.
Achieving Resolution-Agnostic DNN-based Image Watermarking:A Novel Perspective of Implicit Neural Representation
May 14, 2024



Abstract:DNN-based watermarking methods are rapidly developing and delivering impressive performances. Recent advances achieve resolution-agnostic image watermarking by reducing the variant resolution watermarking problem to a fixed resolution watermarking problem. However, such a reduction process can potentially introduce artifacts and low robustness. To address this issue, we propose the first, to the best of our knowledge, Resolution-Agnostic Image WaterMarking (RAIMark) framework by watermarking the implicit neural representation (INR) of image. Unlike previous methods, our method does not rely on the previous reduction process by directly watermarking the continuous signal instead of image pixels, thus achieving resolution-agnostic watermarking. Precisely, given an arbitrary-resolution image, we fit an INR for the target image. As a continuous signal, such an INR can be sampled to obtain images with variant resolutions. Then, we quickly fine-tune the fitted INR to get a watermarked INR conditioned on a binary secret message. A pre-trained watermark decoder extracts the hidden message from any sampled images with arbitrary resolutions. By directly watermarking INR, we achieve resolution-agnostic watermarking with increased robustness. Extensive experiments show that our method outperforms previous methods with significant improvements: averagely improved bit accuracy by 7%$\sim$29%. Notably, we observe that previous methods are vulnerable to at least one watermarking attack (e.g. JPEG, crop, resize), while ours are robust against all watermarking attacks.
Meta Attentive Graph Convolutional Recurrent Network for Traffic Forecasting
Aug 28, 2023Abstract:Traffic forecasting is a fundamental problem in intelligent transportation systems. Existing traffic predictors are limited by their expressive power to model the complex spatial-temporal dependencies in traffic data, mainly due to the following limitations. Firstly, most approaches are primarily designed to model the local shared patterns, which makes them insufficient to capture the specific patterns associated with each node globally. Hence, they fail to learn each node's unique properties and diversified patterns. Secondly, most existing approaches struggle to accurately model both short- and long-term dependencies simultaneously. In this paper, we propose a novel traffic predictor, named Meta Attentive Graph Convolutional Recurrent Network (MAGCRN). MAGCRN utilizes a Graph Convolutional Recurrent Network (GCRN) as a core module to model local dependencies and improves its operation with two novel modules: 1) a Node-Specific Meta Pattern Learning (NMPL) module to capture node-specific patterns globally and 2) a Node Attention Weight Generation Module (NAWG) module to capture short- and long-term dependencies by connecting the node-specific features with the ones learned initially at each time step during GCRN operation. Experiments on six real-world traffic datasets demonstrate that NMPL and NAWG together enable MAGCRN to outperform state-of-the-art baselines on both short- and long-term predictions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge