Shuchen Meng
Enhancing Exchange Rate Forecasting with Explainable Deep Learning Models
Oct 25, 2024
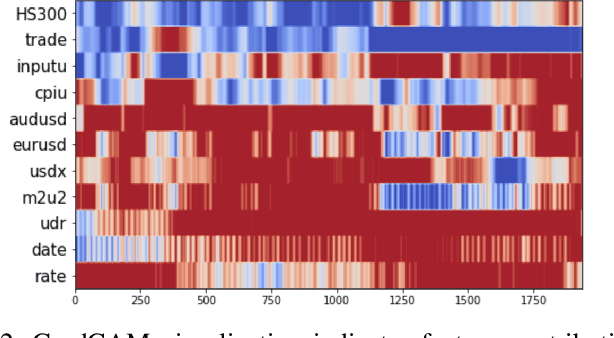

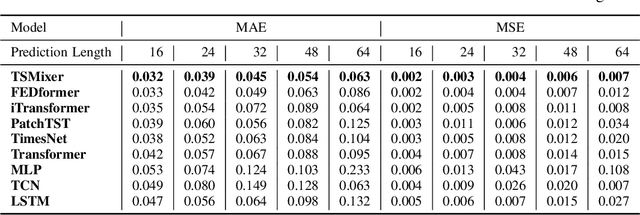
Abstract:Accurate exchange rate prediction is fundamental to financial stability and international trade, positioning it as a critical focus in economic and financial research. Traditional forecasting models often falter when addressing the inherent complexities and non-linearities of exchange rate data. This study explores the application of advanced deep learning models, including LSTM, CNN, and transformer-based architectures, to enhance the predictive accuracy of the RMB/USD exchange rate. Utilizing 40 features across 6 categories, the analysis identifies TSMixer as the most effective model for this task. A rigorous feature selection process emphasizes the inclusion of key economic indicators, such as China-U.S. trade volumes and exchange rates of other major currencies like the euro-RMB and yen-dollar pairs. The integration of grad-CAM visualization techniques further enhances model interpretability, allowing for clearer identification of the most influential features and bolstering the credibility of the predictions. These findings underscore the pivotal role of fundamental economic data in exchange rate forecasting and highlight the substantial potential of machine learning models to deliver more accurate and reliable predictions, thereby serving as a valuable tool for financial analysis and decision-making.
Harnessing Earnings Reports for Stock Predictions: A QLoRA-Enhanced LLM Approach
Aug 13, 2024


Abstract:Accurate stock market predictions following earnings reports are crucial for investors. Traditional methods, particularly classical machine learning models, struggle with these predictions because they cannot effectively process and interpret extensive textual data contained in earnings reports and often overlook nuances that influence market movements. This paper introduces an advanced approach by employing Large Language Models (LLMs) instruction fine-tuned with a novel combination of instruction-based techniques and quantized low-rank adaptation (QLoRA) compression. Our methodology integrates 'base factors', such as financial metric growth and earnings transcripts, with 'external factors', including recent market indices performances and analyst grades, to create a rich, supervised dataset. This comprehensive dataset enables our models to achieve superior predictive performance in terms of accuracy, weighted F1, and Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC), especially evident in the comparison with benchmarks such as GPT-4. We specifically highlight the efficacy of the llama-3-8b-Instruct-4bit model, which showcases significant improvements over baseline models. The paper also discusses the potential of expanding the output capabilities to include a 'Hold' option and extending the prediction horizon, aiming to accommodate various investment styles and time frames. This study not only demonstrates the power of integrating cutting-edge AI with fine-tuned financial data but also paves the way for future research in enhancing AI-driven financial analysis tools.
Advanced User Credit Risk Prediction Model using LightGBM, XGBoost and Tabnet with SMOTEENN
Aug 07, 2024Abstract:Bank credit risk is a significant challenge in modern financial transactions, and the ability to identify qualified credit card holders among a large number of applicants is crucial for the profitability of a bank'sbank's credit card business. In the past, screening applicants'applicants' conditions often required a significant amount of manual labor, which was time-consuming and labor-intensive. Although the accuracy and reliability of previously used ML models have been continuously improving, the pursuit of more reliable and powerful AI intelligent models is undoubtedly the unremitting pursuit by major banks in the financial industry. In this study, we used a dataset of over 40,000 records provided by a commercial bank as the research object. We compared various dimensionality reduction techniques such as PCA and T-SNE for preprocessing high-dimensional datasets and performed in-depth adaptation and tuning of distributed models such as LightGBM and XGBoost, as well as deep models like Tabnet. After a series of research and processing, we obtained excellent research results by combining SMOTEENN with these techniques. The experiments demonstrated that LightGBM combined with PCA and SMOTEENN techniques can assist banks in accurately predicting potential high-quality customers, showing relatively outstanding performance compared to other models.
Time Series Modeling for Heart Rate Prediction: From ARIMA to Transformers
Jun 18, 2024Abstract:Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a leading cause of death globally, necessitating precise forecasting models for monitoring vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, and ECG. Traditional models, such as ARIMA and Prophet, are limited by their need for manual parameter tuning and challenges in handling noisy, sparse, and highly variable medical data. This study investigates advanced deep learning models, including LSTM, and transformer-based architectures, for predicting heart rate time series from the MIT-BIH Database. Results demonstrate that deep learning models, particularly PatchTST, significantly outperform traditional models across multiple metrics, capturing complex patterns and dependencies more effectively. This research underscores the potential of deep learning to enhance patient monitoring and CVD management, suggesting substantial clinical benefits. Future work should extend these findings to larger, more diverse datasets and real-world clinical applications to further validate and optimize model performance.
RIS-Assisted Physical Layer Authentication for 6G Endogenous Security
Sep 14, 2023


Abstract:The physical layer authentication (PLA) is a promising technology which can enhance the access security of a massive number of devices in the near future. In this paper, we propose a reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-assisted PLA system, in which the legitimate transmitter can customize the channel fingerprints during PLA by controlling the ON-OFF state of the RIS. Without loss of generality, we use the received signal strength (RSS) based spoofing detection approach to analyze the feasibility of the proposed architecture. Specifically, based on the RSS, we derive the statistical properties of PLA and give some interesting insights, which showcase that the RIS-assisted PLA is theoretically feasible. Then, we derive the optimal detection threshold to maximize the performance in the context of the presented performance metrics. Next, the actual feasibility of the proposed system is verified via proof-of-concept experiments on a RIS-assisted PLA prototype platform. The experiment results show that there are 3.5% and 76% performance improvements when the transmission sources are at different locations and at the same location, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge