Senyan Xu
CompEvent: Complex-valued Event-RGB Fusion for Low-light Video Enhancement and Deblurring
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Low-light video deblurring poses significant challenges in applications like nighttime surveillance and autonomous driving due to dim lighting and long exposures. While event cameras offer potential solutions with superior low-light sensitivity and high temporal resolution, existing fusion methods typically employ staged strategies, limiting their effectiveness against combined low-light and motion blur degradations. To overcome this, we propose CompEvent, a complex neural network framework enabling holistic full-process fusion of event data and RGB frames for enhanced joint restoration. CompEvent features two core components: 1) Complex Temporal Alignment GRU, which utilizes complex-valued convolutions and processes video and event streams iteratively via GRU to achieve temporal alignment and continuous fusion; and 2) Complex Space-Frequency Learning module, which performs unified complex-valued signal processing in both spatial and frequency domains, facilitating deep fusion through spatial structures and system-level characteristics. By leveraging the holistic representation capability of complex-valued neural networks, CompEvent achieves full-process spatiotemporal fusion, maximizes complementary learning between modalities, and significantly strengthens low-light video deblurring capability. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CompEvent outperforms SOTA methods in addressing this challenging task. The code is available at https://github.com/YuXie1/CompEvent.
NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Efficient Burst HDR and Restoration: Datasets, Methods, and Results
May 17, 2025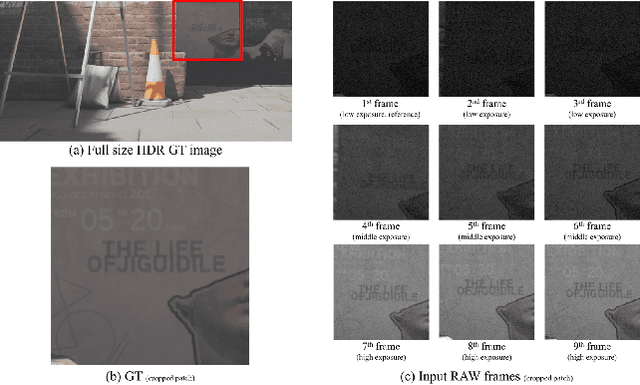
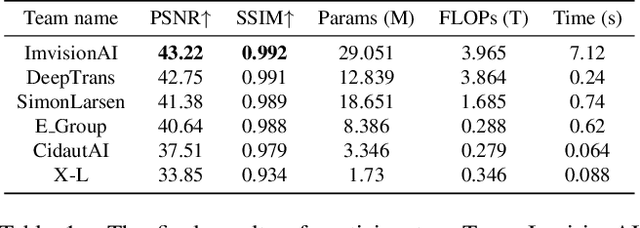

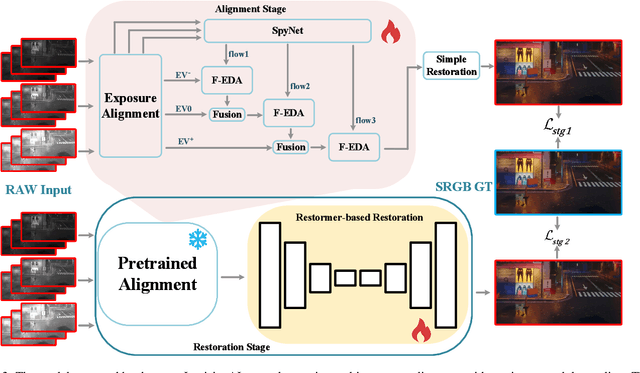
Abstract:This paper reviews the NTIRE 2025 Efficient Burst HDR and Restoration Challenge, which aims to advance efficient multi-frame high dynamic range (HDR) and restoration techniques. The challenge is based on a novel RAW multi-frame fusion dataset, comprising nine noisy and misaligned RAW frames with various exposure levels per scene. Participants were tasked with developing solutions capable of effectively fusing these frames while adhering to strict efficiency constraints: fewer than 30 million model parameters and a computational budget under 4.0 trillion FLOPs. A total of 217 participants registered, with six teams finally submitting valid solutions. The top-performing approach achieved a PSNR of 43.22 dB, showcasing the potential of novel methods in this domain. This paper provides a comprehensive overview of the challenge, compares the proposed solutions, and serves as a valuable reference for researchers and practitioners in efficient burst HDR and restoration.
NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Event-Based Image Deblurring: Methods and Results
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:This paper presents an overview of NTIRE 2025 the First Challenge on Event-Based Image Deblurring, detailing the proposed methodologies and corresponding results. The primary goal of the challenge is to design an event-based method that achieves high-quality image deblurring, with performance quantitatively assessed using Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR). Notably, there are no restrictions on computational complexity or model size. The task focuses on leveraging both events and images as inputs for single-image deblurring. A total of 199 participants registered, among whom 15 teams successfully submitted valid results, offering valuable insights into the current state of event-based image deblurring. We anticipate that this challenge will drive further advancements in event-based vision research.
Technique Report of CVPR 2024 PBDL Challenges
Jun 15, 2024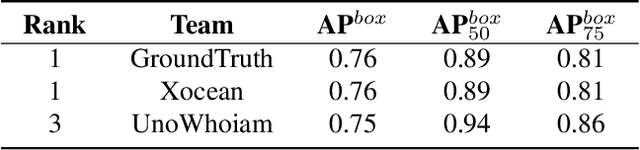

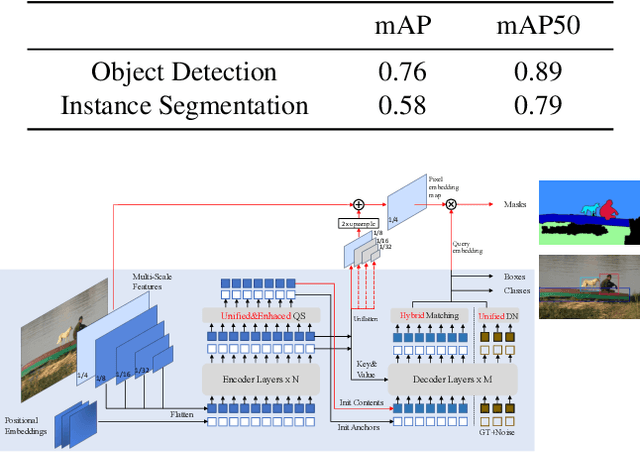
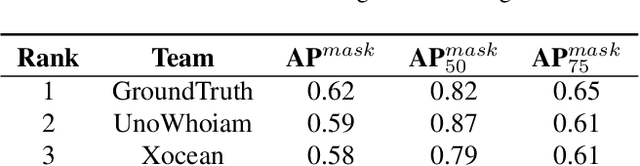
Abstract:The intersection of physics-based vision and deep learning presents an exciting frontier for advancing computer vision technologies. By leveraging the principles of physics to inform and enhance deep learning models, we can develop more robust and accurate vision systems. Physics-based vision aims to invert the processes to recover scene properties such as shape, reflectance, light distribution, and medium properties from images. In recent years, deep learning has shown promising improvements for various vision tasks, and when combined with physics-based vision, these approaches can enhance the robustness and accuracy of vision systems. This technical report summarizes the outcomes of the Physics-Based Vision Meets Deep Learning (PBDL) 2024 challenge, held in CVPR 2024 workshop. The challenge consisted of eight tracks, focusing on Low-Light Enhancement and Detection as well as High Dynamic Range (HDR) Imaging. This report details the objectives, methodologies, and results of each track, highlighting the top-performing solutions and their innovative approaches.
DemosaicFormer: Coarse-to-Fine Demosaicing Network for HybridEVS Camera
Jun 12, 2024



Abstract:Hybrid Event-Based Vision Sensor (HybridEVS) is a novel sensor integrating traditional frame-based and event-based sensors, offering substantial benefits for applications requiring low-light, high dynamic range, and low-latency environments, such as smartphones and wearable devices. Despite its potential, the lack of Image signal processing (ISP) pipeline specifically designed for HybridEVS poses a significant challenge. To address this challenge, in this study, we propose a coarse-to-fine framework named DemosaicFormer which comprises coarse demosaicing and pixel correction. Coarse demosaicing network is designed to produce a preliminary high-quality estimate of the RGB image from the HybridEVS raw data while the pixel correction network enhances the performance of image restoration and mitigates the impact of defective pixels. Our key innovation is the design of a Multi-Scale Gating Module (MSGM) applying the integration of cross-scale features, which allows feature information to flow between different scales. Additionally, the adoption of progressive training and data augmentation strategies further improves model's robustness and effectiveness. Experimental results show superior performance against the existing methods both qualitatively and visually, and our DemosaicFormer achieves the best performance in terms of all the evaluation metrics in the MIPI 2024 challenge on Demosaic for Hybridevs Camera. The code is available at https://github.com/QUEAHREN/DemosaicFormer.
FourierMamba: Fourier Learning Integration with State Space Models for Image Deraining
May 29, 2024



Abstract:Image deraining aims to remove rain streaks from rainy images and restore clear backgrounds. Currently, some research that employs the Fourier transform has proved to be effective for image deraining, due to it acting as an effective frequency prior for capturing rain streaks. However, despite there exists dependency of low frequency and high frequency in images, these Fourier-based methods rarely exploit the correlation of different frequencies for conjuncting their learning procedures, limiting the full utilization of frequency information for image deraining. Alternatively, the recently emerged Mamba technique depicts its effectiveness and efficiency for modeling correlation in various domains (e.g., spatial, temporal), and we argue that introducing Mamba into its unexplored Fourier spaces to correlate different frequencies would help improve image deraining. This motivates us to propose a new framework termed FourierMamba, which performs image deraining with Mamba in the Fourier space. Owning to the unique arrangement of frequency orders in Fourier space, the core of FourierMamba lies in the scanning encoding of different frequencies, where the low-high frequency order formats exhibit differently in the spatial dimension (unarranged in axis) and channel dimension (arranged in axis). Therefore, we design FourierMamba that correlates Fourier space information in the spatial and channel dimensions with distinct designs. Specifically, in the spatial dimension Fourier space, we introduce the zigzag coding to scan the frequencies to rearrange the orders from low to high frequencies, thereby orderly correlating the connections between frequencies; in the channel dimension Fourier space with arranged orders of frequencies in axis, we can directly use Mamba to perform frequency correlation and improve the channel information representation.
MIPI 2024 Challenge on Demosaic for HybridEVS Camera: Methods and Results
May 08, 2024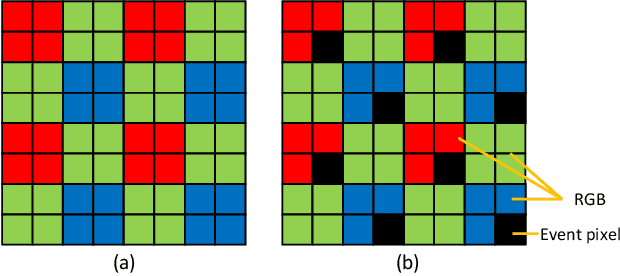
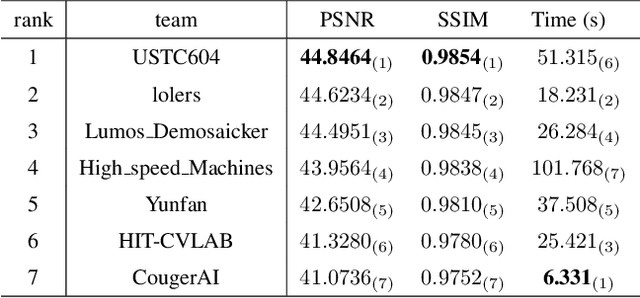
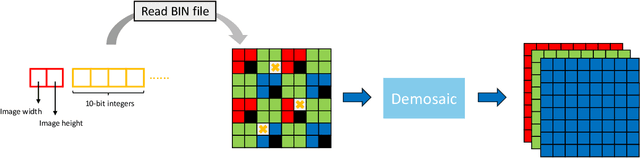

Abstract:The increasing demand for computational photography and imaging on mobile platforms has led to the widespread development and integration of advanced image sensors with novel algorithms in camera systems. However, the scarcity of high-quality data for research and the rare opportunity for in-depth exchange of views from industry and academia constrain the development of mobile intelligent photography and imaging (MIPI). Building on the achievements of the previous MIPI Workshops held at ECCV 2022 and CVPR 2023, we introduce our third MIPI challenge including three tracks focusing on novel image sensors and imaging algorithms. In this paper, we summarize and review the Nighttime Flare Removal track on MIPI 2024. In total, 170 participants were successfully registered, and 14 teams submitted results in the final testing phase. The developed solutions in this challenge achieved state-of-the-art performance on Nighttime Flare Removal. More details of this challenge and the link to the dataset can be found at https://mipi-challenge.org/MIPI2024/.
Deep RAW Image Super-Resolution. A NTIRE 2024 Challenge Survey
Apr 24, 2024
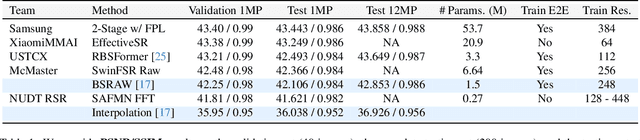
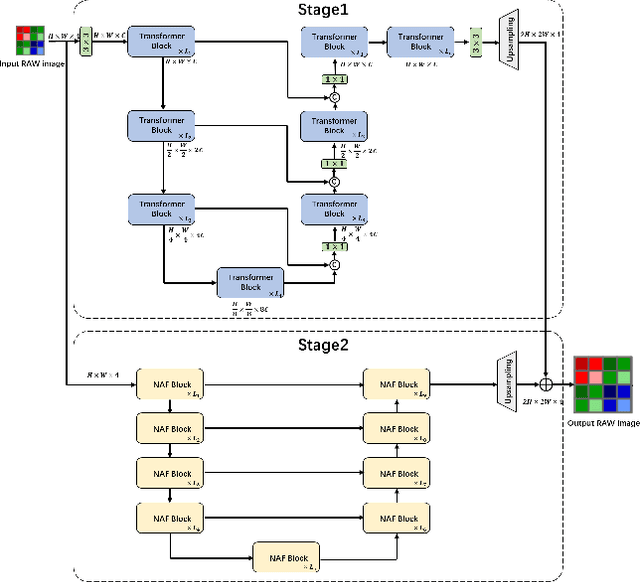
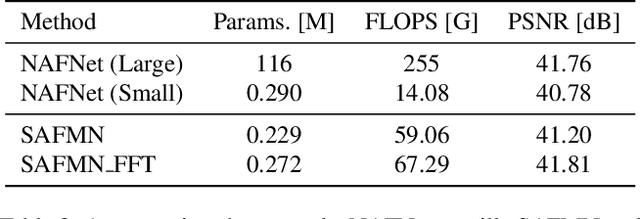
Abstract:This paper reviews the NTIRE 2024 RAW Image Super-Resolution Challenge, highlighting the proposed solutions and results. New methods for RAW Super-Resolution could be essential in modern Image Signal Processing (ISP) pipelines, however, this problem is not as explored as in the RGB domain. Th goal of this challenge is to upscale RAW Bayer images by 2x, considering unknown degradations such as noise and blur. In the challenge, a total of 230 participants registered, and 45 submitted results during thee challenge period. The performance of the top-5 submissions is reviewed and provided here as a gauge for the current state-of-the-art in RAW Image Super-Resolution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge