Savvas Damaskinos
HistoKT: Cross Knowledge Transfer in Computational Pathology
Jan 27, 2022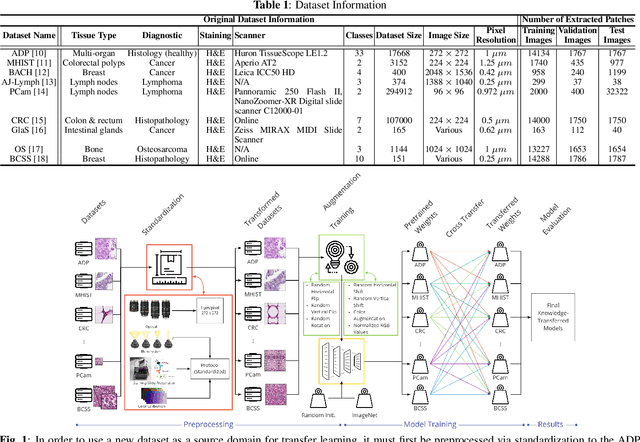



Abstract:The lack of well-annotated datasets in computational pathology (CPath) obstructs the application of deep learning techniques for classifying medical images. %Since pathologist time is expensive, dataset curation is intrinsically difficult. Many CPath workflows involve transferring learned knowledge between various image domains through transfer learning. Currently, most transfer learning research follows a model-centric approach, tuning network parameters to improve transfer results over few datasets. In this paper, we take a data-centric approach to the transfer learning problem and examine the existence of generalizable knowledge between histopathological datasets. First, we create a standardization workflow for aggregating existing histopathological data. We then measure inter-domain knowledge by training ResNet18 models across multiple histopathological datasets, and cross-transferring between them to determine the quantity and quality of innate shared knowledge. Additionally, we use weight distillation to share knowledge between models without additional training. We find that hard to learn, multi-class datasets benefit most from pretraining, and a two stage learning framework incorporating a large source domain such as ImageNet allows for better utilization of smaller datasets. Furthermore, we find that weight distillation enables models trained on purely histopathological features to outperform models using external natural image data.
Probeable DARTS with Application to Computational Pathology
Aug 16, 2021



Abstract:AI technology has made remarkable achievements in computational pathology (CPath), especially with the help of deep neural networks. However, the network performance is highly related to architecture design, which commonly requires human experts with domain knowledge. In this paper, we combat this challenge with the recent advance in neural architecture search (NAS) to find an optimal network for CPath applications. In particular, we use differentiable architecture search (DARTS) for its efficiency. We first adopt a probing metric to show that the original DARTS lacks proper hyperparameter tuning on the CIFAR dataset, and how the generalization issue can be addressed using an adaptive optimization strategy. We then apply our searching framework on CPath applications by searching for the optimum network architecture on a histological tissue type dataset (ADP). Results show that the searched network outperforms state-of-the-art networks in terms of prediction accuracy and computation complexity. We further conduct extensive experiments to demonstrate the transferability of the searched network to new CPath applications, the robustness against downscaled inputs, as well as the reliability of predictions.
Fine-Tuning and Training of DenseNet for Histopathology Image Representation Using TCGA Diagnostic Slides
Jan 20, 2021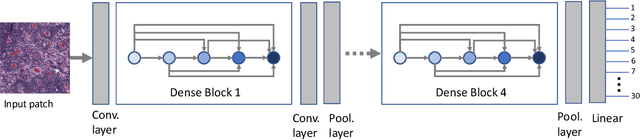
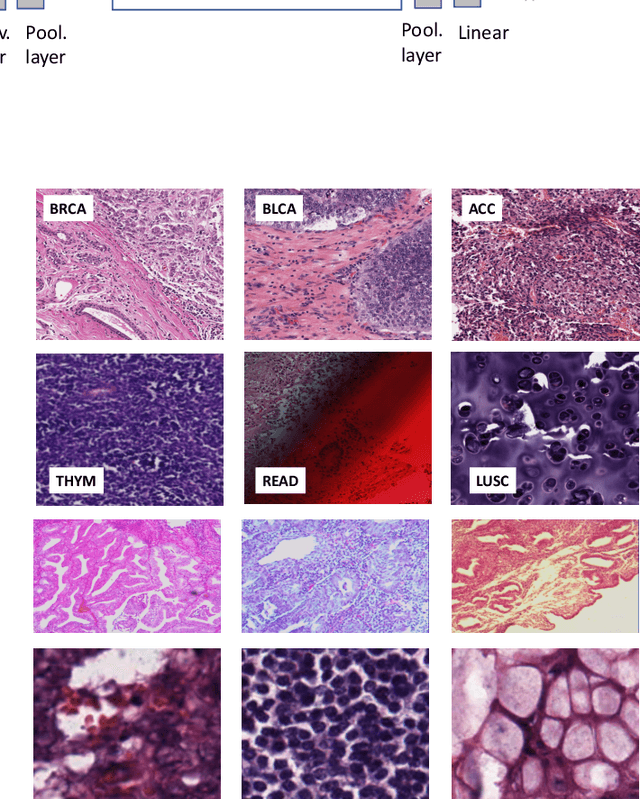
Abstract:Feature vectors provided by pre-trained deep artificial neural networks have become a dominant source for image representation in recent literature. Their contribution to the performance of image analysis can be improved through finetuning. As an ultimate solution, one might even train a deep network from scratch with the domain-relevant images, a highly desirable option which is generally impeded in pathology by lack of labeled images and the computational expense. In this study, we propose a new network, namely KimiaNet, that employs the topology of the DenseNet with four dense blocks, fine-tuned and trained with histopathology images in different configurations. We used more than 240,000 image patches with 1000x1000 pixels acquired at 20x magnification through our proposed "highcellularity mosaic" approach to enable the usage of weak labels of 7,126 whole slide images of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded human pathology samples publicly available through the The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) repository. We tested KimiaNet using three public datasets, namely TCGA, endometrial cancer images, and colorectal cancer images by evaluating the performance of search and classification when corresponding features of different networks are used for image representation. As well, we designed and trained multiple convolutional batch-normalized ReLU (CBR) networks. The results show that KimiaNet provides superior results compared to the original DenseNet and smaller CBR networks when used as feature extractor to represent histopathology images.
Pan-Cancer Diagnostic Consensus Through Searching Archival Histopathology Images Using Artificial Intelligence
Nov 20, 2019



Abstract:The emergence of digital pathology has opened new horizons for histopathology and cytology. Artificial-intelligence algorithms are able to operate on digitized slides to assist pathologists with diagnostic tasks. Whereas machine learning involving classification and segmentation methods have obvious benefits for image analysis in pathology, image search represents a fundamental shift in computational pathology. Matching the pathology of new patients with already diagnosed and curated cases offers pathologist a novel approach to improve diagnostic accuracy through visual inspection of similar cases and computational majority vote for consensus building. In this study, we report the results from searching the largest public repository (The Cancer Genome Atlas [TCGA] program by National Cancer Institute, USA) of whole slide images from almost 11,000 patients depicting different types of malignancies. For the first time, we successfully indexed and searched almost 30,000 high-resolution digitized slides constituting 16 terabytes of data comprised of 20 million 1000x1000 pixels image patches. The TCGA image database covers 25 anatomic sites and contains 32 cancer subtypes. High-performance storage and GPU power were employed for experimentation. The results were assessed with conservative "majority voting" to build consensus for subtype diagnosis through vertical search and demonstrated high accuracy values for both frozen sections slides (e.g., bladder urothelial carcinoma 93%, kidney renal clear cell carcinoma 97%, and ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma 99%) and permanent histopathology slides (e.g., prostate adenocarcinoma 98%, skin cutaneous melanoma 99%, and thymoma 100%). The key finding of this validation study was that computational consensus appears to be possible for rendering diagnoses if a sufficiently large number of searchable cases are available for each cancer subtype.
Focus Quality Assessment of High-Throughput Whole Slide Imaging in Digital Pathology
Nov 14, 2018



Abstract:One of the challenges facing the adoption of digital pathology workflows for clinical use is the need for automated quality control. As the scanners sometimes determine focus inaccurately, the resultant image blur deteriorates the scanned slide to the point of being unusable. Also, the scanned slide images tend to be extremely large when scanned at greater or equal 20X image resolution. Hence, for digital pathology to be clinically useful, it is necessary to use computational tools to quickly and accurately quantify the image focus quality and determine whether an image needs to be re-scanned. We propose a no-reference focus quality assessment metric specifically for digital pathology images, that operates by using a sum of even-derivative filter bases to synthesize a human visual system-like kernel, which is modeled as the inverse of the lens' point spread function. This kernel is then applied to a digital pathology image to modify high-frequency image information deteriorated by the scanner's optics and quantify the focus quality at the patch level. We show in several experiments that our method correlates better with ground-truth $z$-level data than other methods, and is more computationally efficient. We also extend our method to generate a local slide-level focus quality heatmap, which can be used for automated slide quality control, and demonstrate the utility of our method for clinical scan quality control by comparison with subjective slide quality scores.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge