Mojtaba Valipour
S2D: Sorted Speculative Decoding For More Efficient Deployment of Nested Large Language Models
Jul 02, 2024



Abstract:Deployment of autoregressive large language models (LLMs) is costly, and as these models increase in size, the associated costs will become even more considerable. Consequently, different methods have been proposed to accelerate the token generation process and reduce costs. Speculative decoding (SD) is among the most promising approaches to speed up the LLM decoding process by verifying multiple tokens in parallel and using an auxiliary smaller draft model to generate the possible tokens. In SD, usually, one draft model is used to serve a specific target model; however, in practice, LLMs are diverse, and we might need to deal with many target models or more than one target model simultaneously. In this scenario, it is not clear which draft model should be used for which target model, and searching among different draft models or training customized draft models can further increase deployment costs. In this paper, we first introduce a novel multi-target scenario for the deployment of draft models for faster inference. Then, we present a novel, more efficient sorted speculative decoding mechanism that outperforms regular baselines in multi-target settings. We evaluated our method on Spec-Bench in different settings, including base models such as Vicuna 7B, 13B, and LLama Chat 70B. Our results suggest that our draft models perform better than baselines for multiple target models at the same time.
SeeFar: Satellite Agnostic Multi-Resolution Dataset for Geospatial Foundation Models
Jun 10, 2024


Abstract:SeeFar is an evolving collection of multi-resolution satellite images from public and commercial satellites. We specifically curated this dataset for training geospatial foundation models, unconstrained by satellite type. In recent years, advances in technology have made satellite imagery more accessible than ever. More earth-observing satellites have been launched in the last five years than in the previous fifty. Modern commercial satellites now offer up to 100 times the spatial resolution of public access satellites. However, the high cost and limited historical availability of commercial satellite imagery is a barrier to the training of foundational models, impacting what images can be used during inference. The SeeFar dataset represents a step towards training models that are satellite-agnostic by combining multi-resolution commercial and public access pre-processed images. This will enable users to utilize historical data alongside higher-resolution, more expensive satellite imagery, offering greater flexibility during inference. To achieve this, we describe a process for standardizing data from diverse satellite sources, normalizing different data formats, and aligning spectral bands to enhance interoperability. The SeeFar dataset includes images at a resolution of 384x384 pixels, spanning four spectral bands (Blue, Green, Red, and Near-Infrared) and expanding spatial resolutions (starting with 30, 10, 1.5, and 1.0 meters), all in cloud-optimized GeoTIFF format. It also provides consistent and comprehensive metadata to enhance data transparency and reliability. By aggregating data from multiple sources, SeeFar makes processed and consistent satellite data accessible to a wider range of users - from researchers to policymakers - fostering competition and innovation in satellite imagery analysis. The dataset is available at \url{coastalcarbon.ai/seefar}.
QDyLoRA: Quantized Dynamic Low-Rank Adaptation for Efficient Large Language Model Tuning
Feb 16, 2024



Abstract:Finetuning large language models requires huge GPU memory, restricting the choice to acquire Larger models. While the quantized version of the Low-Rank Adaptation technique, named QLoRA, significantly alleviates this issue, finding the efficient LoRA rank is still challenging. Moreover, QLoRA is trained on a pre-defined rank and, therefore, cannot be reconfigured for its lower ranks without requiring further fine-tuning steps. This paper proposes QDyLoRA -Quantized Dynamic Low-Rank Adaptation-, as an efficient quantization approach for dynamic low-rank adaptation. Motivated by Dynamic LoRA, QDyLoRA is able to efficiently finetune LLMs on a set of pre-defined LoRA ranks. QDyLoRA enables fine-tuning Falcon-40b for ranks 1 to 64 on a single 32 GB V100-GPU through one round of fine-tuning. Experimental results show that QDyLoRA is competitive to QLoRA and outperforms when employing its optimal rank.
Sorted LLaMA: Unlocking the Potential of Intermediate Layers of Large Language Models for Dynamic Inference Using Sorted Fine-Tuning (SoFT)
Sep 16, 2023



Abstract:The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) has revolutionized natural language processing (NLP). While these models excel at understanding and generating human-like text, their widespread deployment can be prohibitively expensive. SortedNet is a recent training technique for enabling dynamic inference for deep neural networks. It leverages network modularity to create sub-models with varying computational loads, sorting them based on computation/accuracy characteristics in a nested manner. We extend SortedNet to generative NLP tasks, making large language models dynamic without any pretraining and by only replacing standard Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) with Sorted Fine-Tuning (SoFT) at the same costs. Our approach boosts model efficiency, eliminating the need for multiple models for various scenarios during inference. We show that using this approach, we are able to unlock the potential of intermediate layers of transformers in generating the target output. Our sub-models remain integral components of the original model, minimizing storage requirements and transition costs between different computational/latency budgets. By applying this approach on LLaMa 2 13B for tuning on the Stanford Alpaca dataset and comparing it to normal tuning and early exit via PandaLM benchmark, we show that Sorted Fine-Tuning can deliver models twice as fast as the original model while maintaining or exceeding performance.
SortedNet, a Place for Every Network and Every Network in its Place: Towards a Generalized Solution for Training Many-in-One Neural Networks
Sep 01, 2023Abstract:As the size of deep learning models continues to grow, finding optimal models under memory and computation constraints becomes increasingly more important. Although usually the architecture and constituent building blocks of neural networks allow them to be used in a modular way, their training process is not aware of this modularity. Consequently, conventional neural network training lacks the flexibility to adapt the computational load of the model during inference. This paper proposes SortedNet, a generalized and scalable solution to harness the inherent modularity of deep neural networks across various dimensions for efficient dynamic inference. Our training considers a nested architecture for the sub-models with shared parameters and trains them together with the main model in a sorted and probabilistic manner. This sorted training of sub-networks enables us to scale the number of sub-networks to hundreds using a single round of training. We utilize a novel updating scheme during training that combines random sampling of sub-networks with gradient accumulation to improve training efficiency. Furthermore, the sorted nature of our training leads to a search-free sub-network selection at inference time; and the nested architecture of the resulting sub-networks leads to minimal storage requirement and efficient switching between sub-networks at inference. Our general dynamic training approach is demonstrated across various architectures and tasks, including large language models and pre-trained vision models. Experimental results show the efficacy of the proposed approach in achieving efficient sub-networks while outperforming state-of-the-art dynamic training approaches. Our findings demonstrate the feasibility of training up to 160 different sub-models simultaneously, showcasing the extensive scalability of our proposed method while maintaining 96% of the model performance.
DyLoRA: Parameter Efficient Tuning of Pre-trained Models using Dynamic Search-Free Low-Rank Adaptation
Oct 14, 2022



Abstract:With the ever-growing size of pre-trained models (PMs), fine-tuning them has become more expensive and resource-hungry. As a remedy, low-rank adapters (LoRA) keep the main pre-trained weights of the model frozen and just introduce some learnable truncated SVD modules (so-called LoRA blocks) to the model. While LoRA blocks are parameter efficient, they suffer from two major problems: first, the size of these blocks is fixed and cannot be modified after training (for example, if we need to change the rank of LoRA blocks, then we need to re-train them from scratch); second, optimizing their rank requires an exhaustive search and effort. In this work, we introduce a dynamic low-rank adaptation (DyLoRA) technique to address these two problems together. Our DyLoRA method trains LoRA blocks for a range of ranks instead of a single rank by sorting out the representation learned by the adapter module at different ranks during training. We evaluate our solution on different tasks of the GLUE benchmark using the RoBERTa model. Our results show that we can train dynamic search-free models with DyLoRA at least $7\times$ faster than LoRA without significantly compromising performance. Moreover, our models can perform consistently well on a much larger range of ranks compared to LoRA.
SymbolicGPT: A Generative Transformer Model for Symbolic Regression
Jun 27, 2021



Abstract:Symbolic regression is the task of identifying a mathematical expression that best fits a provided dataset of input and output values. Due to the richness of the space of mathematical expressions, symbolic regression is generally a challenging problem. While conventional approaches based on genetic evolution algorithms have been used for decades, deep learning-based methods are relatively new and an active research area. In this work, we present SymbolicGPT, a novel transformer-based language model for symbolic regression. This model exploits the advantages of probabilistic language models like GPT, including strength in performance and flexibility. Through comprehensive experiments, we show that our model performs strongly compared to competing models with respect to the accuracy, running time, and data efficiency.
Fine-Tuning and Training of DenseNet for Histopathology Image Representation Using TCGA Diagnostic Slides
Jan 20, 2021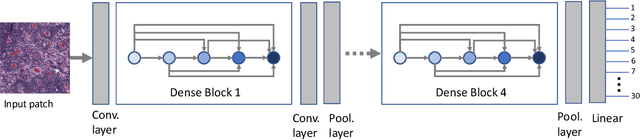
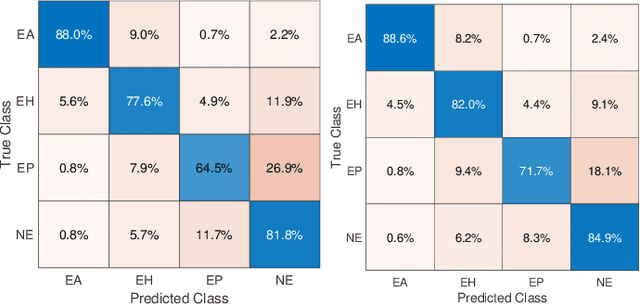
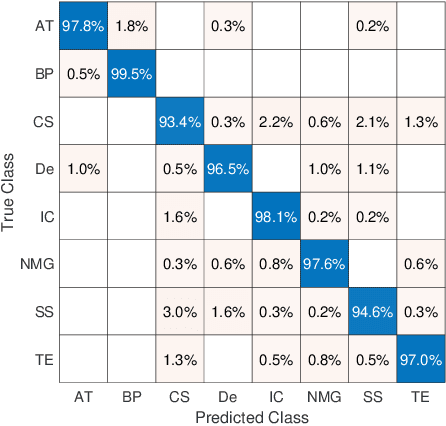
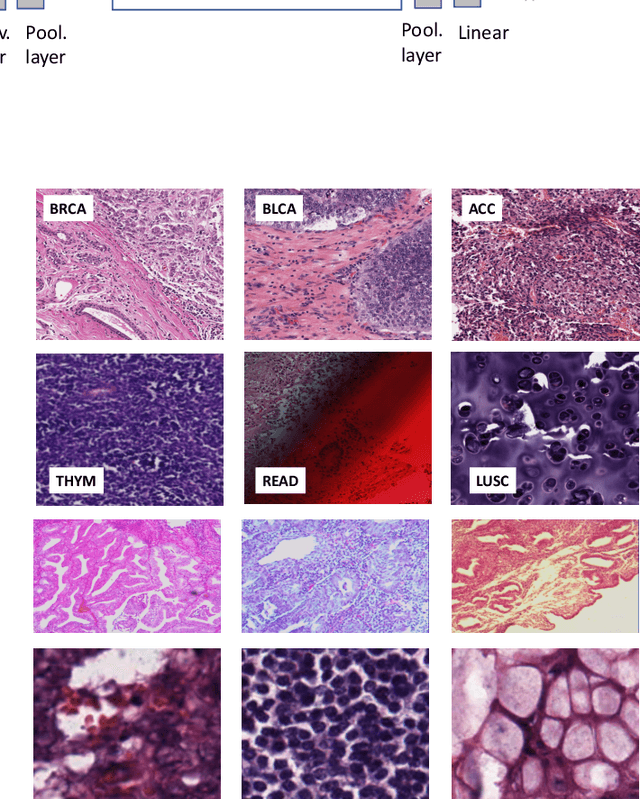
Abstract:Feature vectors provided by pre-trained deep artificial neural networks have become a dominant source for image representation in recent literature. Their contribution to the performance of image analysis can be improved through finetuning. As an ultimate solution, one might even train a deep network from scratch with the domain-relevant images, a highly desirable option which is generally impeded in pathology by lack of labeled images and the computational expense. In this study, we propose a new network, namely KimiaNet, that employs the topology of the DenseNet with four dense blocks, fine-tuned and trained with histopathology images in different configurations. We used more than 240,000 image patches with 1000x1000 pixels acquired at 20x magnification through our proposed "highcellularity mosaic" approach to enable the usage of weak labels of 7,126 whole slide images of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded human pathology samples publicly available through the The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) repository. We tested KimiaNet using three public datasets, namely TCGA, endometrial cancer images, and colorectal cancer images by evaluating the performance of search and classification when corresponding features of different networks are used for image representation. As well, we designed and trained multiple convolutional batch-normalized ReLU (CBR) networks. The results show that KimiaNet provides superior results compared to the original DenseNet and smaller CBR networks when used as feature extractor to represent histopathology images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge