Sachin Kajarekar
CALM: Contrastive Aligned Audio-Language Multirate and Multimodal Representations
Feb 08, 2022Abstract:Deriving multimodal representations of audio and lexical inputs is a central problem in Natural Language Understanding (NLU). In this paper, we present Contrastive Aligned Audio-Language Multirate and Multimodal Representations (CALM), an approach for learning multimodal representations using contrastive and multirate information inherent in audio and lexical inputs. The proposed model aligns acoustic and lexical information in the input embedding space of a pretrained language-only contextual embedding model. By aligning audio representations to pretrained language representations and utilizing contrastive information between acoustic inputs, CALM is able to bootstrap audio embedding competitive with existing audio representation models in only a few hours of training time. Operationally, audio spectrograms are processed using linearized patches through a Spectral Transformer (SpecTran) which is trained using a Contrastive Audio-Language Pretraining objective to align audio and language from similar queries. Subsequently, the derived acoustic and lexical tokens representations are input into a multimodal transformer to incorporate utterance level context and derive the proposed CALM representations. We show that these pretrained embeddings can subsequently be used in multimodal supervised tasks and demonstrate the benefits of the proposed pretraining steps in terms of the alignment of the two embedding spaces and the multirate nature of the pretraining. Our system shows 10-25\% improvement over existing emotion recognition systems including state-of-the-art three-modality systems under various evaluation objectives.
Streaming on-device detection of device directed speech from voice and touch-based invocation
Oct 09, 2021
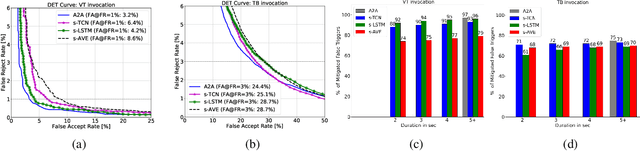
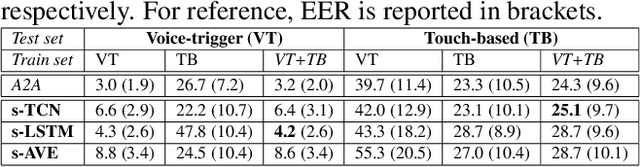
Abstract:When interacting with smart devices such as mobile phones or wearables, the user typically invokes a virtual assistant (VA) by saying a keyword or by pressing a button on the device. However, in many cases, the VA can accidentally be invoked by the keyword-like speech or accidental button press, which may have implications on user experience and privacy. To this end, we propose an acoustic false-trigger-mitigation (FTM) approach for on-device device-directed speech detection that simultaneously handles the voice-trigger and touch-based invocation. To facilitate the model deployment on-device, we introduce a new streaming decision layer, derived using the notion of temporal convolutional networks (TCN) [1], known for their computational efficiency. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first approach that can detect device-directed speech from more than one invocation type in a streaming fashion. We compare this approach with streaming alternatives based on vanilla Average layer, and canonical LSTMs, and show: (i) that all the models show only a small degradation in accuracy compared with the invocation-specific models, and (ii) that the newly introduced streaming TCN consistently performs better or comparable with the alternatives, while mitigating device undirected speech faster in time, and with (relative) reduction in runtime peak-memory over the LSTM-based approach of 33% vs. 7%, when compared to a non-streaming counterpart.
Analysis and Tuning of a Voice Assistant System for Dysfluent Speech
Jun 18, 2021
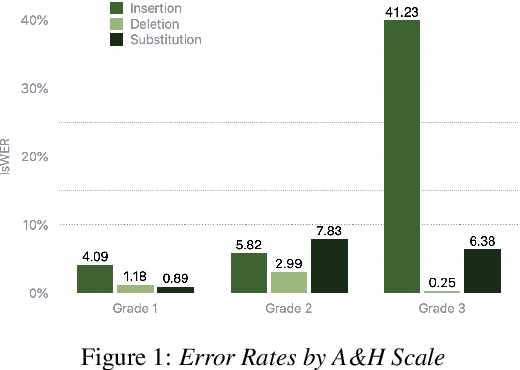
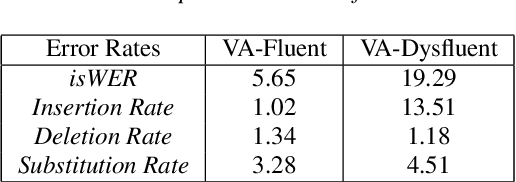
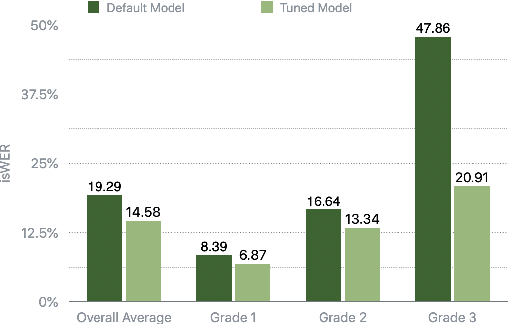
Abstract:Dysfluencies and variations in speech pronunciation can severely degrade speech recognition performance, and for many individuals with moderate-to-severe speech disorders, voice operated systems do not work. Current speech recognition systems are trained primarily with data from fluent speakers and as a consequence do not generalize well to speech with dysfluencies such as sound or word repetitions, sound prolongations, or audible blocks. The focus of this work is on quantitative analysis of a consumer speech recognition system on individuals who stutter and production-oriented approaches for improving performance for common voice assistant tasks (i.e., "what is the weather?"). At baseline, this system introduces a significant number of insertion and substitution errors resulting in intended speech Word Error Rates (isWER) that are 13.64\% worse (absolute) for individuals with fluency disorders. We show that by simply tuning the decoding parameters in an existing hybrid speech recognition system one can improve isWER by 24\% (relative) for individuals with fluency disorders. Tuning these parameters translates to 3.6\% better domain recognition and 1.7\% better intent recognition relative to the default setup for the 18 study participants across all stuttering severities.
SEP-28k: A Dataset for Stuttering Event Detection From Podcasts With People Who Stutter
Feb 24, 2021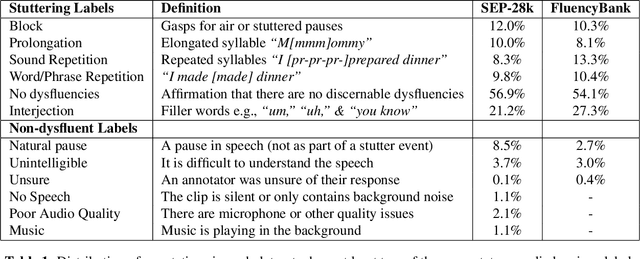
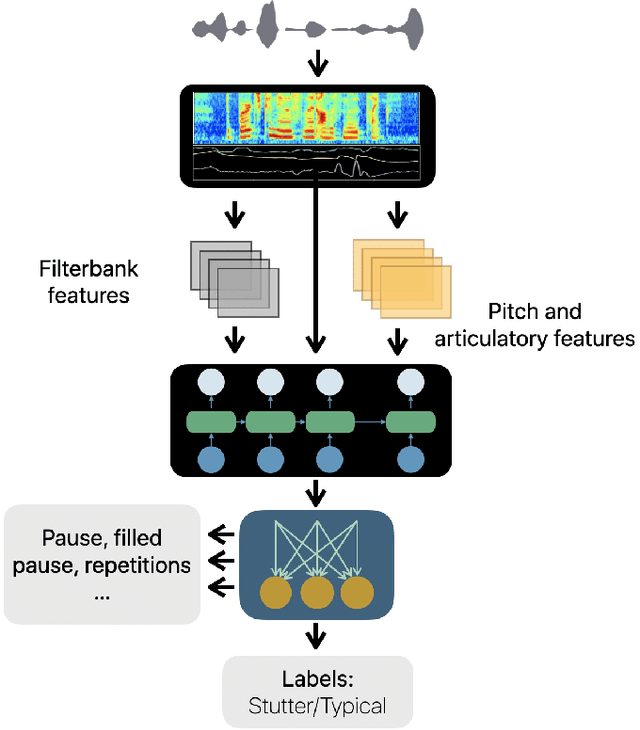
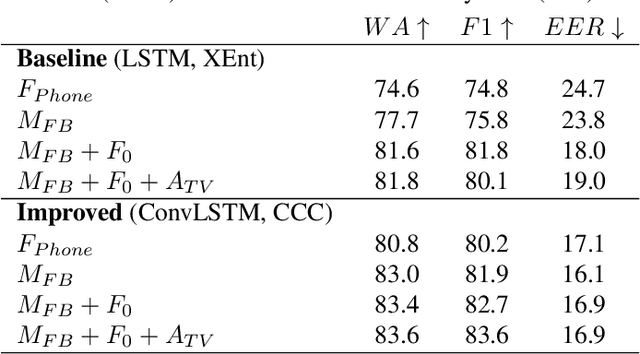
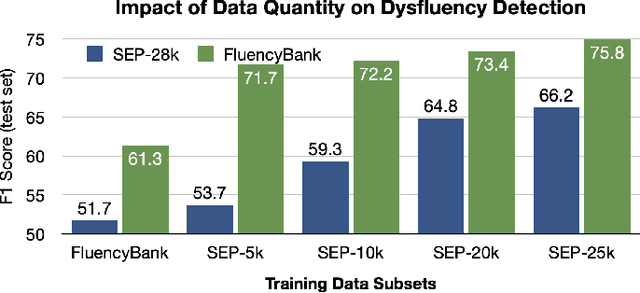
Abstract:The ability to automatically detect stuttering events in speech could help speech pathologists track an individual's fluency over time or help improve speech recognition systems for people with atypical speech patterns. Despite increasing interest in this area, existing public datasets are too small to build generalizable dysfluency detection systems and lack sufficient annotations. In this work, we introduce Stuttering Events in Podcasts (SEP-28k), a dataset containing over 28k clips labeled with five event types including blocks, prolongations, sound repetitions, word repetitions, and interjections. Audio comes from public podcasts largely consisting of people who stutter interviewing other people who stutter. We benchmark a set of acoustic models on SEP-28k and the public FluencyBank dataset and highlight how simply increasing the amount of training data improves relative detection performance by 28\% and 24\% F1 on each. Annotations from over 32k clips across both datasets will be publicly released.
Knowledge Transfer for Efficient On-device False Trigger Mitigation
Oct 20, 2020



Abstract:In this paper, we address the task of determining whether a given utterance is directed towards a voice-enabled smart-assistant device or not. An undirected utterance is termed as a "false trigger" and false trigger mitigation (FTM) is essential for designing a privacy-centric non-intrusive smart assistant. The directedness of an utterance can be identified by running automatic speech recognition (ASR) on it and determining the user intent by analyzing the ASR transcript. But in case of a false trigger, transcribing the audio using ASR itself is strongly undesirable. To alleviate this issue, we propose an LSTM-based FTM architecture which determines the user intent from acoustic features directly without explicitly generating ASR transcripts from the audio. The proposed models are small footprint and can be run on-device with limited computational resources. During training, the model parameters are optimized using a knowledge transfer approach where a more accurate self-attention graph neural network model serves as the teacher. Given the whole audio snippets, our approach mitigates 87% of false triggers at 99% true positive rate (TPR), and in a streaming audio scenario, the system listens to only 1.69s of the false trigger audio before rejecting it while achieving the same TPR.
Audiovisual Speech Synthesis using Tacotron2
Aug 03, 2020



Abstract:Audiovisual speech synthesis is the problem of synthesizing a talking face while maximizing the coherency of the acoustic and visual speech. In this paper, we propose and compare two audiovisual speech synthesis systems for 3D face models. The first system is the AVTacotron2, which is an end-to-end text-to-audiovisual speech synthesizer based on the Tacotron2 architecture. AVTacotron2 converts a sequence of phonemes representing the sentence to synthesize into a sequence of acoustic features and the corresponding controllers of a face model. The output acoustic features are used to condition a WaveRNN to reconstruct the speech waveform, and the output facial controllers are used to generate the corresponding video of the talking face. The second audiovisual speech synthesis system is modular, where acoustic speech is synthesized from text using the traditional Tacotron2. The reconstructed acoustic speech signal is then used to drive the facial controls of the face model using an independently trained audio-to-facial-animation neural network. We further condition both the end-to-end and modular approaches on emotion embeddings that encode the required prosody to generate emotional audiovisual speech. We analyze the performance of the two systems and compare them to the ground truth videos using subjective evaluation tests. The end-to-end and modular systems are able to synthesize close to human-like audiovisual speech with mean opinion scores (MOS) of 4.1 and 3.9, respectively, compared to a MOS of 4.1 for the ground truth generated from professionally recorded videos. While the end-to-end system gives a better overall quality, the modular approach is more flexible and the quality of acoustic speech and visual speech synthesis is almost independent of each other.
Self-supervised Learning of Visual Speech Features with Audiovisual Speech Enhancement
May 06, 2020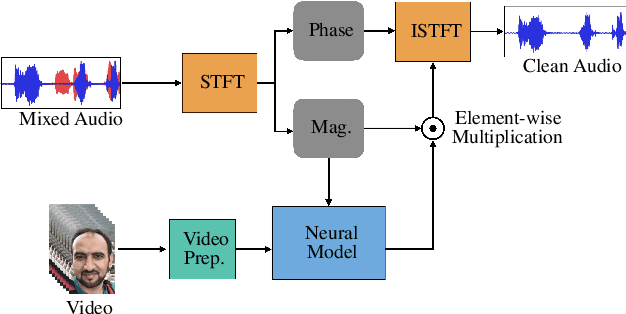
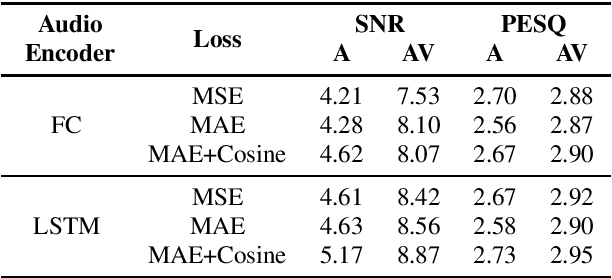
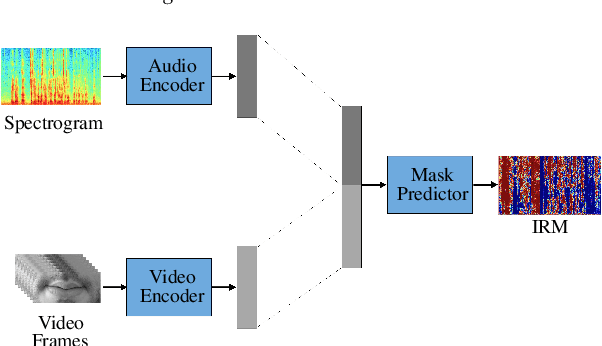
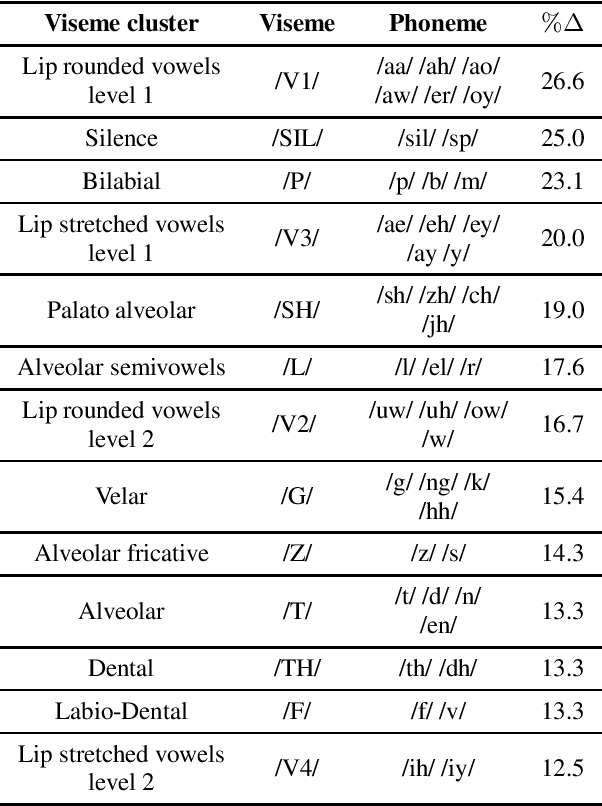
Abstract:We present an introspection of an audiovisual speech enhancement model. In particular, we focus on interpreting how a neural audiovisual speech enhancement model uses visual cues to improve the quality of the target speech signal. We show that visual features provide not only high-level information about speech activity, i.e. speech vs. no speech, but also fine-grained visual information about the place of articulation. An interesting byproduct of this finding is that the learned visual embeddings can be used as features for other visual speech applications. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the learned visual representations for classifying visemes (the visual analogy to phonemes). Our results provide insight into important aspects of audiovisual speech enhancement and demonstrate how such models can be used for self-supervision tasks for visual speech applications.
Detecting Emotion Primitives from Speech and their use in discerning Categorical Emotions
Jan 31, 2020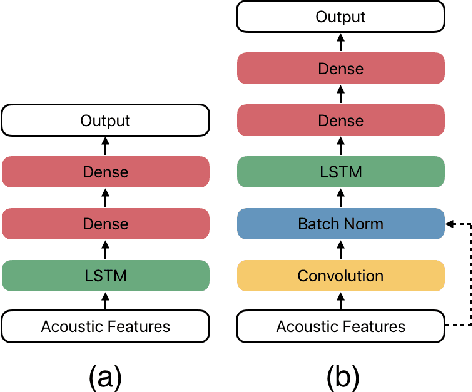
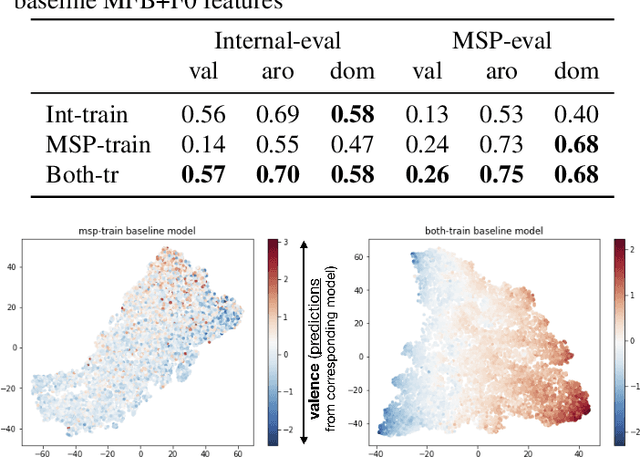
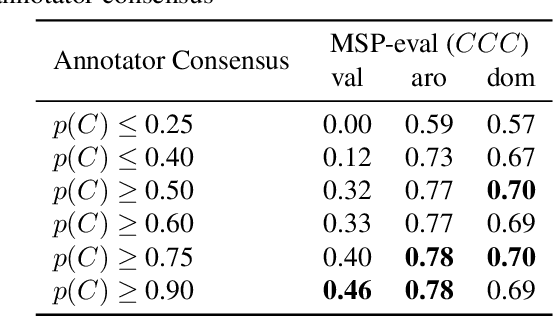
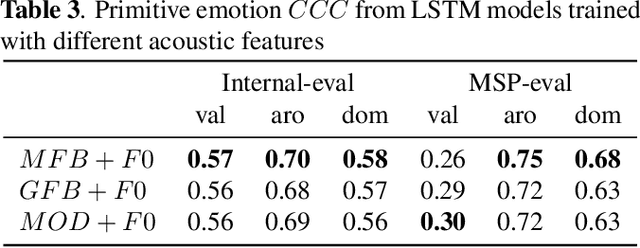
Abstract:Emotion plays an essential role in human-to-human communication, enabling us to convey feelings such as happiness, frustration, and sincerity. While modern speech technologies rely heavily on speech recognition and natural language understanding for speech content understanding, the investigation of vocal expression is increasingly gaining attention. Key considerations for building robust emotion models include characterizing and improving the extent to which a model, given its training data distribution, is able to generalize to unseen data conditions. This work investigated a long-shot-term memory (LSTM) network and a time convolution - LSTM (TC-LSTM) to detect primitive emotion attributes such as valence, arousal, and dominance, from speech. It was observed that training with multiple datasets and using robust features improved the concordance correlation coefficient (CCC) for valence, by 30\% with respect to the baseline system. Additionally, this work investigated how emotion primitives can be used to detect categorical emotions such as happiness, disgust, contempt, anger, and surprise from neutral speech, and results indicated that arousal, followed by dominance was a better detector of such emotions.
Multi-task Learning for Speaker Verification and Voice Trigger Detection
Jan 26, 2020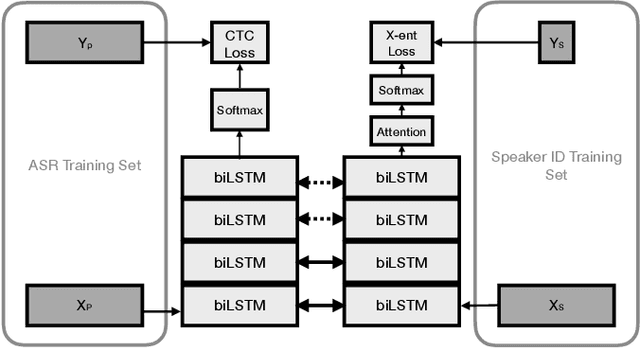
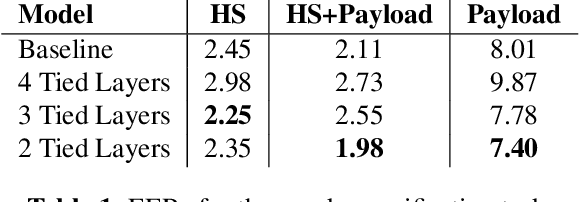
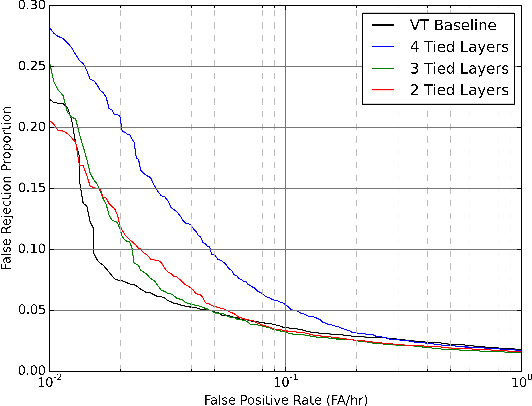
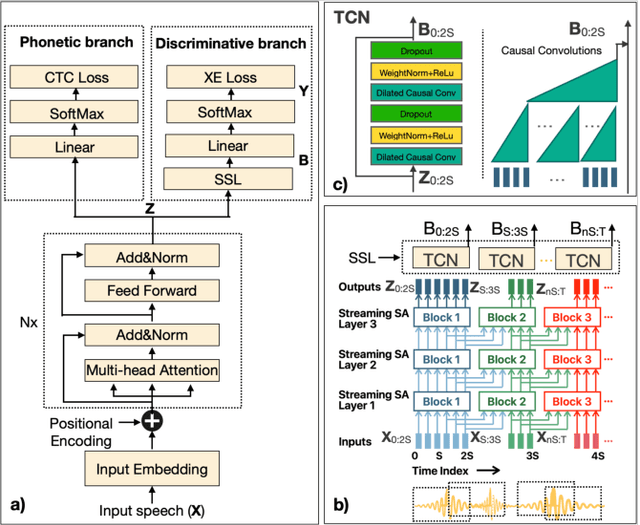
Abstract:Automatic speech transcription and speaker recognition are usually treated as separate tasks even though they are interdependent. In this study, we investigate training a single network to perform both tasks jointly. We train the network in a supervised multi-task learning setup, where the speech transcription branch of the network is trained to minimise a phonetic connectionist temporal classification (CTC) loss while the speaker recognition branch of the network is trained to label the input sequence with the correct label for the speaker. We present a large-scale empirical study where the model is trained using several thousand hours of labelled training data for each task. We evaluate the speech transcription branch of the network on a voice trigger detection task while the speaker recognition branch is evaluated on a speaker verification task. Results demonstrate that the network is able to encode both phonetic \emph{and} speaker information in its learnt representations while yielding accuracies at least as good as the baseline models for each task, with the same number of parameters as the independent models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge