Aparna Joshi
ShieldGemma 2: Robust and Tractable Image Content Moderation
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:We introduce ShieldGemma 2, a 4B parameter image content moderation model built on Gemma 3. This model provides robust safety risk predictions across the following key harm categories: Sexually Explicit, Violence \& Gore, and Dangerous Content for synthetic images (e.g. output of any image generation model) and natural images (e.g. any image input to a Vision-Language Model). We evaluated on both internal and external benchmarks to demonstrate state-of-the-art performance compared to LlavaGuard \citep{helff2024llavaguard}, GPT-4o mini \citep{hurst2024gpt}, and the base Gemma 3 model \citep{gemma_2025} based on our policies. Additionally, we present a novel adversarial data generation pipeline which enables a controlled, diverse, and robust image generation. ShieldGemma 2 provides an open image moderation tool to advance multimodal safety and responsible AI development.
Driver Age and Its Effect on Key Driving Metrics: Insights from Dynamic Vehicle Data
Jan 12, 2025Abstract:By 2030, the senior population aged 65 and older is expected to increase by over 50%, significantly raising the number of older drivers on the road. Drivers over 70 face higher crash death rates compared to those in their forties and fifties, underscoring the importance of developing more effective safety interventions for this demographic. Although the impact of aging on driving behavior has been studied, there is limited research on how these behaviors translate into real-world driving scenarios. This study addresses this need by leveraging Naturalistic Driving Data (NDD) to analyze driving performance measures - specifically, speed limit adherence on interstates and deceleration at stop intersections, both of which may be influenced by age-related declines. Using NDD, we developed Cumulative Distribution Functions (CDFs) to establish benchmarks for key driving behaviors among senior and young drivers. Our analysis, which included anomaly detection, benchmark comparisons, and accuracy evaluations, revealed significant differences in driving patterns primarily related to speed limit adherence at 75mph. While our approach shows promising potential for enhancing Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) by providing tailored interventions based on age-specific adherence to speed limit driving patterns, we recognize the need for additional data to refine and validate metrics for other driving behaviors. By establishing precise benchmarks for various driving performance metrics, ADAS can effectively identify anomalies, such as abrupt deceleration, which may indicate impaired driving or other safety concerns. This study lays a strong foundation for future research aimed at improving safety interventions through detailed driving behavior analysis.
Investigating Speed Deviation Patterns During Glucose Episodes: A Quantile Regression Approach
Oct 03, 2023



Abstract:Given the growing prevalence of diabetes, there has been significant interest in determining how diabetes affects instrumental daily functions, like driving. Complication of glucose control in diabetes includes hypoglycemic and hyperglycemic episodes, which may impair cognitive and psychomotor functions needed for safe driving. The goal of this paper was to determine patterns of diabetes speed behavior during acute glucose to drivers with diabetes who were euglycemic or control drivers without diabetes in a naturalistic driving environment. By employing distribution-based analytic methods which capture distribution patterns, our study advances prior literature that has focused on conventional approach of average speed to explore speed deviation patterns.
SEP-28k: A Dataset for Stuttering Event Detection From Podcasts With People Who Stutter
Feb 24, 2021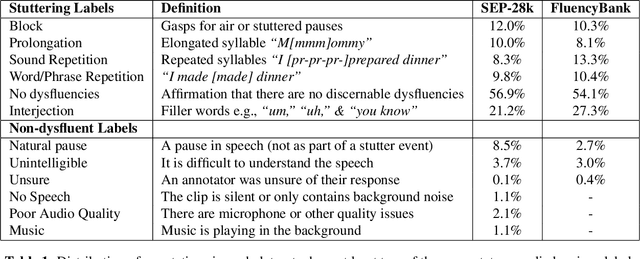
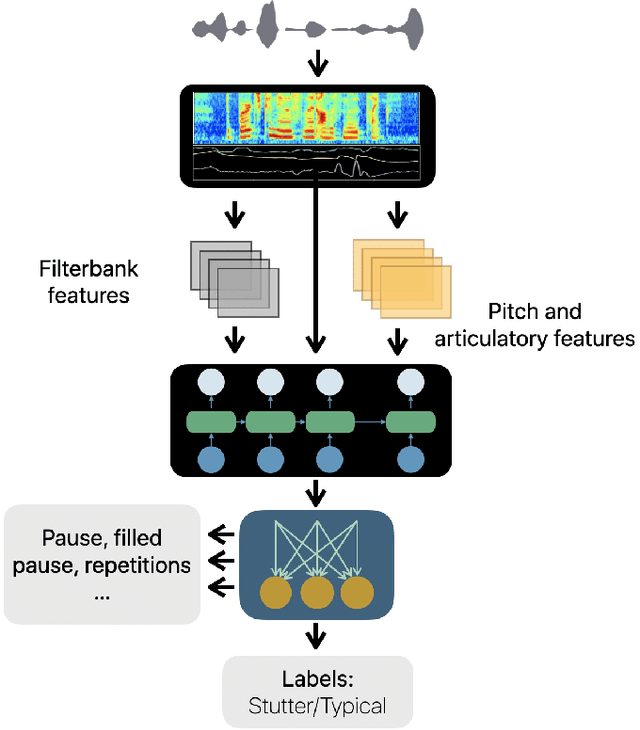
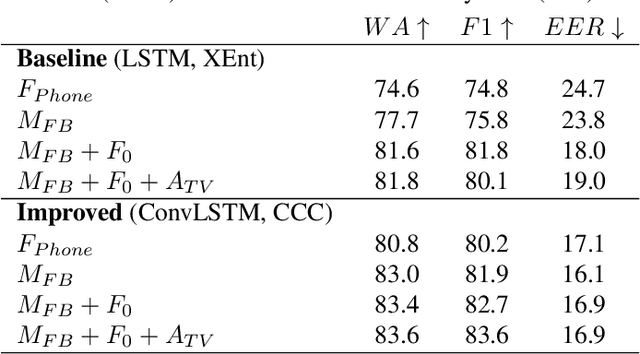
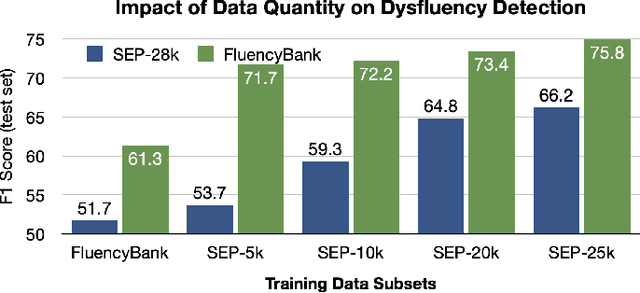
Abstract:The ability to automatically detect stuttering events in speech could help speech pathologists track an individual's fluency over time or help improve speech recognition systems for people with atypical speech patterns. Despite increasing interest in this area, existing public datasets are too small to build generalizable dysfluency detection systems and lack sufficient annotations. In this work, we introduce Stuttering Events in Podcasts (SEP-28k), a dataset containing over 28k clips labeled with five event types including blocks, prolongations, sound repetitions, word repetitions, and interjections. Audio comes from public podcasts largely consisting of people who stutter interviewing other people who stutter. We benchmark a set of acoustic models on SEP-28k and the public FluencyBank dataset and highlight how simply increasing the amount of training data improves relative detection performance by 28\% and 24\% F1 on each. Annotations from over 32k clips across both datasets will be publicly released.
Zeroth Order Non-convex optimization with Dueling-Choice Bandits
Nov 03, 2019


Abstract:We consider a novel setting of zeroth order non-convex optimization, where in addition to querying the function value at a given point, we can also duel two points and get the point with the larger function value. We refer to this setting as optimization with dueling-choice bandits since both direct queries and duels are available for optimization. We give the COMP-GP-UCB algorithm based on GP-UCB (Srinivas et al., 2009), where instead of directly querying the point with the maximum Upper Confidence Bound (UCB), we perform a constrained optimization and use comparisons to filter out suboptimal points. COMP-GP-UCB comes with theoretical guarantee of $O(\frac{\Phi}{\sqrt{T}})$ on simple regret where $T$ is the number of direct queries and $\Phi$ is an improved information gain corresponding to a comparison based constraint set that restricts the search space for the optimum. In contrast, in the direct query only setting, $\Phi$ depends on the entire domain. Finally, we present experimental results to show the efficacy of our algorithm.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge