Sachin Grover
OpenThoughts: Data Recipes for Reasoning Models
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Reasoning models have made rapid progress on many benchmarks involving math, code, and science. Yet, there are still many open questions about the best training recipes for reasoning since state-of-the-art models often rely on proprietary datasets with little to no public information available. To address this, the goal of the OpenThoughts project is to create open-source datasets for training reasoning models. After initial explorations, our OpenThoughts2-1M dataset led to OpenThinker2-32B, the first model trained on public reasoning data to match DeepSeek-R1-Distill-32B on standard reasoning benchmarks such as AIME and LiveCodeBench. We then improve our dataset further by systematically investigating each step of our data generation pipeline with 1,000+ controlled experiments, which led to OpenThoughts3. Scaling the pipeline to 1.2M examples and using QwQ-32B as teacher yields our OpenThoughts3-7B model, which achieves state-of-the-art results: 53% on AIME 2025, 51% on LiveCodeBench 06/24-01/25, and 54% on GPQA Diamond - improvements of 15.3, 17.2, and 20.5 percentage points compared to the DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B. All of our datasets and models are available on https://openthoughts.ai.
A Domain-Independent Agent Architecture for Adaptive Operation in Evolving Open Worlds
Jun 09, 2023



Abstract:Model-based reasoning agents are ill-equipped to act in novel situations in which their model of the environment no longer sufficiently represents the world. We propose HYDRA - a framework for designing model-based agents operating in mixed discrete-continuous worlds, that can autonomously detect when the environment has evolved from its canonical setup, understand how it has evolved, and adapt the agents' models to perform effectively. HYDRA is based upon PDDL+, a rich modeling language for planning in mixed, discrete-continuous environments. It augments the planning module with visual reasoning, task selection, and action execution modules for closed-loop interaction with complex environments. HYDRA implements a novel meta-reasoning process that enables the agent to monitor its own behavior from a variety of aspects. The process employs a diverse set of computational methods to maintain expectations about the agent's own behavior in an environment. Divergences from those expectations are useful in detecting when the environment has evolved and identifying opportunities to adapt the underlying models. HYDRA builds upon ideas from diagnosis and repair and uses a heuristics-guided search over model changes such that they become competent in novel conditions. The HYDRA framework has been used to implement novelty-aware agents for three diverse domains - CartPole++ (a higher dimension variant of a classic control problem), Science Birds (an IJCAI competition problem), and PogoStick (a specific problem domain in Minecraft). We report empirical observations from these domains to demonstrate the efficacy of various components in the novelty meta-reasoning process.
Heuristic Search For Physics-Based Problems: Angry Birds in PDDL+
Mar 29, 2023



Abstract:This paper studies how a domain-independent planner and combinatorial search can be employed to play Angry Birds, a well established AI challenge problem. To model the game, we use PDDL+, a planning language for mixed discrete/continuous domains that supports durative processes and exogenous events. The paper describes the model and identifies key design decisions that reduce the problem complexity. In addition, we propose several domain-specific enhancements including heuristics and a search technique similar to preferred operators. Together, they alleviate the complexity of combinatorial search. We evaluate our approach by comparing its performance with dedicated domain-specific solvers on a range of Angry Birds levels. The results show that our performance is on par with these domain-specific approaches in most levels, even without using our domain-specific search enhancements.
Characterizing Human Explanation Strategies to Inform the Design of Explainable AI for Building Damage Assessment
Nov 04, 2021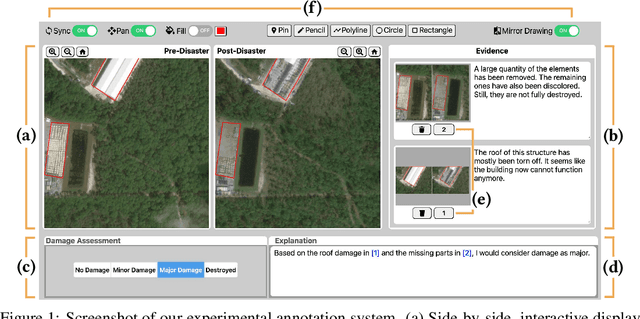
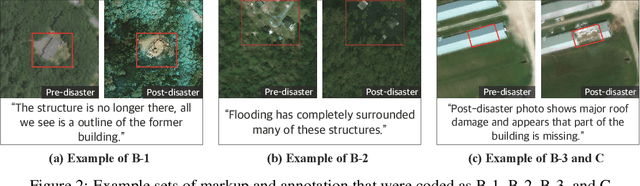
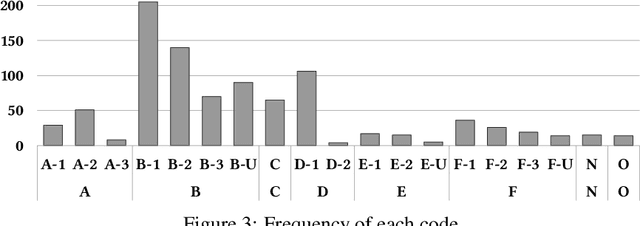
Abstract:Explainable AI (XAI) is a promising means of supporting human-AI collaborations for high-stakes visual detection tasks, such as damage detection tasks from satellite imageries, as fully-automated approaches are unlikely to be perfectly safe and reliable. However, most existing XAI techniques are not informed by the understandings of task-specific needs of humans for explanations. Thus, we took a first step toward understanding what forms of XAI humans require in damage detection tasks. We conducted an online crowdsourced study to understand how people explain their own assessments, when evaluating the severity of building damage based on satellite imagery. Through the study with 60 crowdworkers, we surfaced six major strategies that humans utilize to explain their visual damage assessments. We present implications of our findings for the design of XAI methods for such visual detection contexts, and discuss opportunities for future research.
COVID-19 India Dataset: Parsing Detailed COVID-19 Data in Daily Health Bulletins from States in India
Sep 27, 2021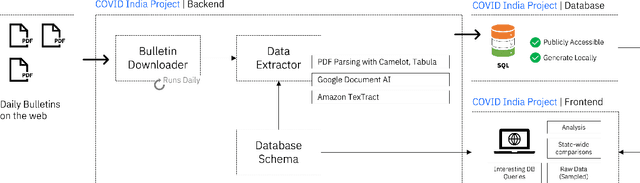
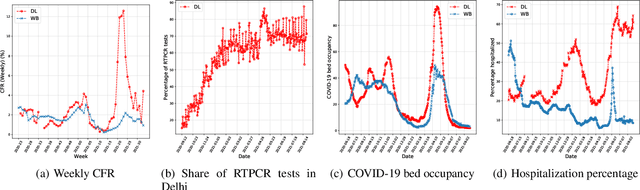
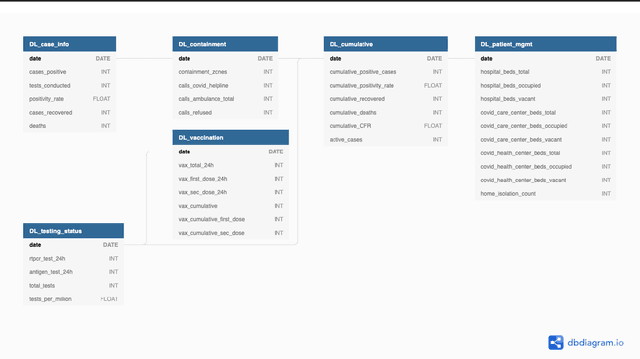
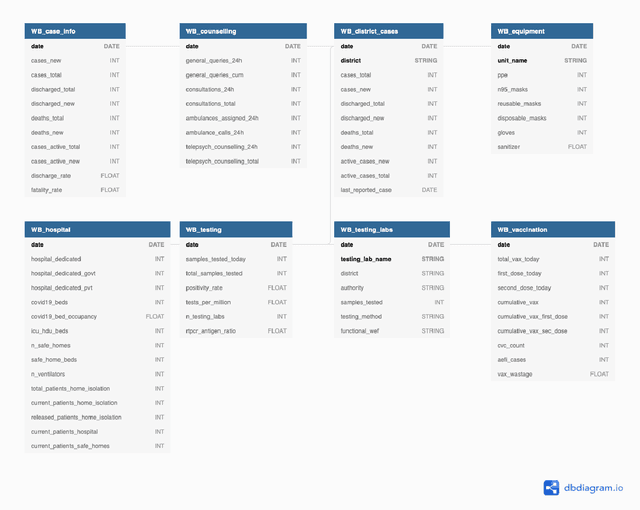
Abstract:While India remains one of the hotspots of the COVID-19 pandemic, data about the pandemic from the country has proved to be largely inaccessible for use at scale. Much of the data exists in an unstructured form on the web, and limited aspects of such data are available through public APIs maintained manually through volunteer efforts. This has proved to be difficult both in terms of ease of access to detailed data as well as with regards to the maintenance of manual data-keeping over time. This paper reports on a recently launched project aimed at automating the extraction of such data from public health bulletins with the help of a combination of classical PDF parsers as well as state-of-the-art ML-based documents extraction APIs. In this paper, we will describe the automated data-extraction technique, the nature of the generated data, and exciting avenues of ongoing work.
Model Elicitation through Direct Questioning
Nov 24, 2020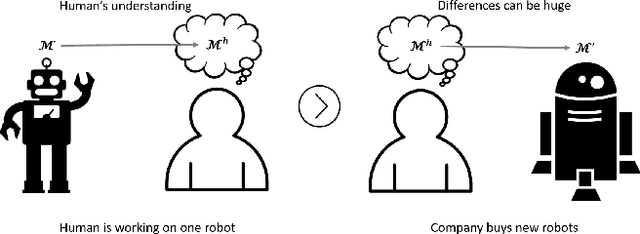
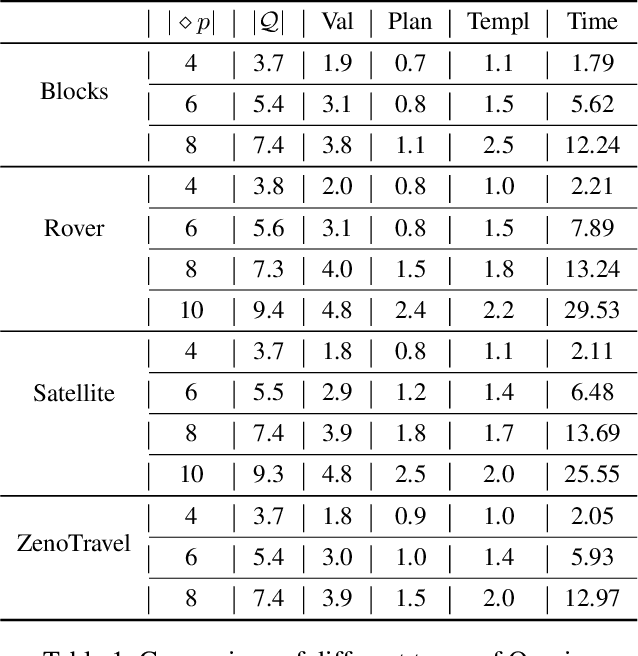
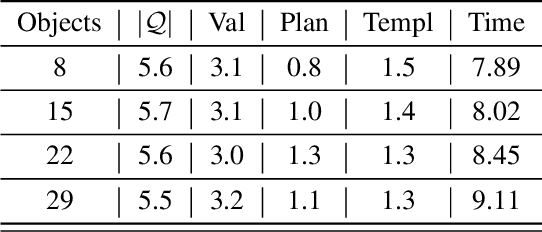
Abstract:The future will be replete with scenarios where humans are robots will be working together in complex environments. Teammates interact, and the robot's interaction has to be about getting useful information about the human's (teammate's) model. There are many challenges before a robot can interact, such as incorporating the structural differences in the human's model, ensuring simpler responses, etc. In this paper, we investigate how a robot can interact to localize the human model from a set of models. We show how to generate questions to refine the robot's understanding of the teammate's model. We evaluate the method in various planning domains. The evaluation shows that these questions can be generated offline, and can help refine the model through simple answers.
Plan Explanations as Model Reconciliation -- An Empirical Study
Feb 03, 2018



Abstract:Recent work in explanation generation for decision making agents has looked at how unexplained behavior of autonomous systems can be understood in terms of differences in the model of the system and the human's understanding of the same, and how the explanation process as a result of this mismatch can be then seen as a process of reconciliation of these models. Existing algorithms in such settings, while having been built on contrastive, selective and social properties of explanations as studied extensively in the psychology literature, have not, to the best of our knowledge, been evaluated in settings with actual humans in the loop. As such, the applicability of such explanations to human-AI and human-robot interactions remains suspect. In this paper, we set out to evaluate these explanation generation algorithms in a series of studies in a mock search and rescue scenario with an internal semi-autonomous robot and an external human commander. We demonstrate to what extent the properties of these algorithms hold as they are evaluated by humans, and how the dynamics of trust between the human and the robot evolve during the process of these interactions.
Texture Synthesis with Recurrent Variational Auto-Encoder
Dec 23, 2017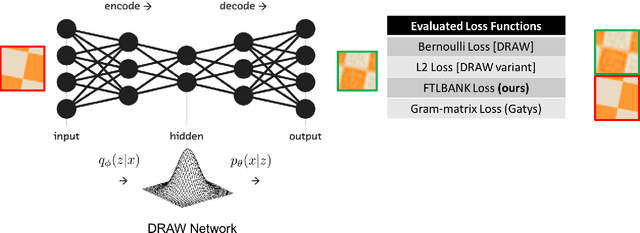
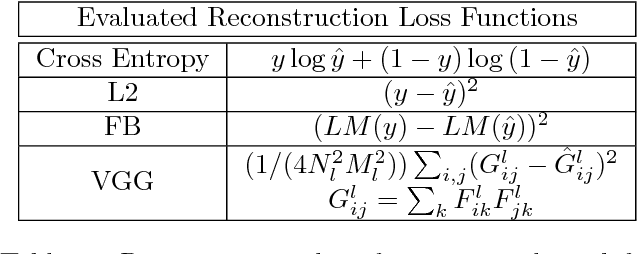
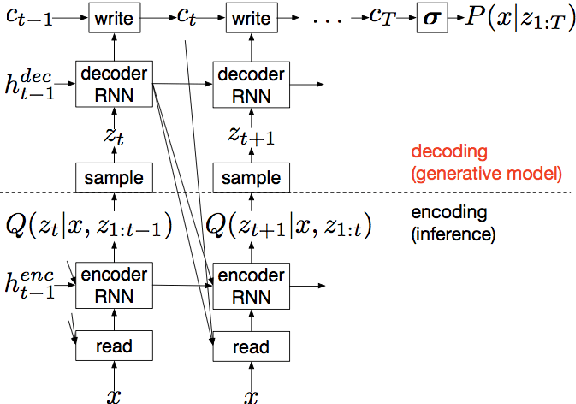

Abstract:We propose a recurrent variational auto-encoder for texture synthesis. A novel loss function, FLTBNK, is used for training the texture synthesizer. It is rotational and partially color invariant loss function. Unlike L2 loss, FLTBNK explicitly models the correlation of color intensity between pixels. Our texture synthesizer generates neighboring tiles to expand a sample texture and is evaluated using various texture patterns from Describable Textures Dataset (DTD). We perform both quantitative and qualitative experiments with various loss functions to evaluate the performance of our proposed loss function (FLTBNK) --- a mini-human subject study is used for the qualitative evaluation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge