Robert Nowak
Semi-Supervised Diversity-Aware Domain Adaptation for 3D Object detection
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:3D object detectors are fundamental components of perception systems in autonomous vehicles. While these detectors achieve remarkable performance on standard autonomous driving benchmarks, they often struggle to generalize across different domains - for instance, a model trained in the U.S. may perform poorly in regions like Asia or Europe. This paper presents a novel lidar domain adaptation method based on neuron activation patterns, demonstrating that state-of-the-art performance can be achieved by annotating only a small, representative, and diverse subset of samples from the target domain if they are correctly selected. The proposed approach requires very small annotation budget and, when combined with post-training techniques inspired by continual learning prevent weight drift from the original model. Empirical evaluation shows that the proposed domain adaptation approach outperforms both linear probing and state-of-the-art domain adaptation techniques.
Semi-Automated Data Annotation in Multisensor Datasets for Autonomous Vehicle Testing
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:This report presents the design and implementation of a semi-automated data annotation pipeline developed within the DARTS project, whose goal is to create a large-scale, multimodal dataset of driving scenarios recorded in Polish conditions. Manual annotation of such heterogeneous data is both costly and time-consuming. To address this challenge, the proposed solution adopts a human-in-the-loop approach that combines artificial intelligence with human expertise to reduce annotation cost and duration. The system automatically generates initial annotations, enables iterative model retraining, and incorporates data anonymization and domain adaptation techniques. At its core, the tool relies on 3D object detection algorithms to produce preliminary annotations. Overall, the developed tools and methodology result in substantial time savings while ensuring consistent, high-quality annotations across different sensor modalities. The solution directly supports the DARTS project by accelerating the preparation of large annotated dataset in the project's standardized format, strengthening the technological base for autonomous vehicle research in Poland.
How and Why LLMs Generalize: A Fine-Grained Analysis of LLM Reasoning from Cognitive Behaviors to Low-Level Patterns
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) display strikingly different generalization behaviors: supervised fine-tuning (SFT) often narrows capability, whereas reinforcement-learning (RL) tuning tends to preserve it. The reasons behind this divergence remain unclear, as prior studies have largely relied on coarse accuracy metrics. We address this gap by introducing a novel benchmark that decomposes reasoning into atomic core skills such as calculation, fact retrieval, simulation, enumeration, and diagnostic, providing a concrete framework for addressing the fundamental question of what constitutes reasoning in LLMs. By isolating and measuring these core skills, the benchmark offers a more granular view of how specific cognitive abilities emerge, transfer, and sometimes collapse during post-training. Combined with analyses of low-level statistical patterns such as distributional divergence and parameter statistics, it enables a fine-grained study of how generalization evolves under SFT and RL across mathematical, scientific reasoning, and non-reasoning tasks. Our meta-probing framework tracks model behavior at different training stages and reveals that RL-tuned models maintain more stable behavioral profiles and resist collapse in reasoning skills, whereas SFT models exhibit sharper drift and overfit to surface patterns. This work provides new insights into the nature of reasoning in LLMs and points toward principles for designing training strategies that foster broad, robust generalization.
BowelRCNN: Region-based Convolutional Neural Network System for Bowel Sound Auscultation
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:Sound events representing intestinal activity detection is a diagnostic tool with potential to identify gastrointestinal conditions. This article introduces BowelRCNN, a novel bowel sound detection system that uses audio recording, spectrogram analysys and region-based convolutional neural network (RCNN) architecture. The system was trained and validated on a real recording dataset gathered from 19 patients, comprising 60 minutes of prepared and annotated audio data. BowelRCNN achieved a classification accuracy of 96% and an F1 score of 71%. This research highlights the feasibility of using CNN architectures for bowel sound auscultation, achieving results comparable to those of recurrent-convolutional methods.
Task Vectors in In-Context Learning: Emergence, Formation, and Benefit
Jan 16, 2025Abstract:In-context learning is a remarkable capability of transformers, referring to their ability to adapt to specific tasks based on a short history or context. Previous research has found that task-specific information is locally encoded within models, though their emergence and functionality remain unclear due to opaque pre-training processes. In this work, we investigate the formation of task vectors in a controlled setting, using models trained from scratch on synthetic datasets. Our findings confirm that task vectors naturally emerge under certain conditions, but the tasks may be relatively weakly and/or non-locally encoded within the model. To promote strong task vectors encoded at a prescribed location within the model, we propose an auxiliary training mechanism based on a task vector prompting loss (TVP-loss). This method eliminates the need to search for task-correlated encodings within the trained model and demonstrably improves robustness and generalization.
Deep Active Learning in the Open World
Nov 10, 2024Abstract:Machine learning models deployed in open-world scenarios often encounter unfamiliar conditions and perform poorly in unanticipated situations. As AI systems advance and find application in safety-critical domains, effectively handling out-of-distribution (OOD) data is crucial to building open-world learning systems. In this work, we introduce ALOE, a novel active learning algorithm for open-world environments designed to enhance model adaptation by incorporating new OOD classes via a two-stage approach. First, diversity sampling selects a representative set of examples, followed by energy-based OOD detection to prioritize likely unknown classes for annotation. This strategy accelerates class discovery and learning, even under constrained annotation budgets. Evaluations on three long-tailed image classification benchmarks demonstrate that ALOE outperforms traditional active learning baselines, effectively expanding known categories while balancing annotation cost. Our findings reveal a crucial tradeoff between enhancing known-class performance and discovering new classes, setting the stage for future advancements in open-world machine learning.
AHA: Human-Assisted Out-of-Distribution Generalization and Detection
Oct 10, 2024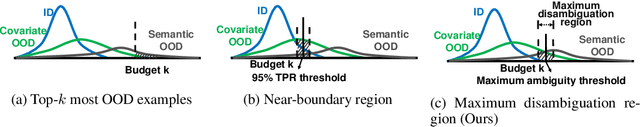
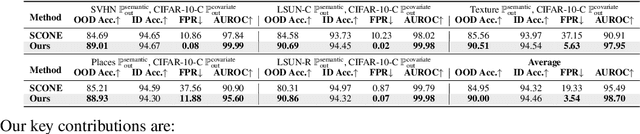
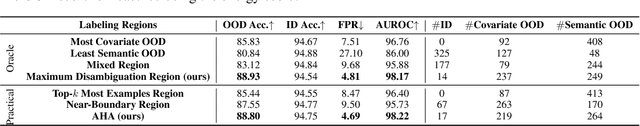
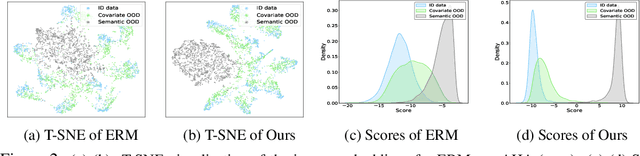
Abstract:Modern machine learning models deployed often encounter distribution shifts in real-world applications, manifesting as covariate or semantic out-of-distribution (OOD) shifts. These shifts give rise to challenges in OOD generalization and OOD detection. This paper introduces a novel, integrated approach AHA (Adaptive Human-Assisted OOD learning) to simultaneously address both OOD generalization and detection through a human-assisted framework by labeling data in the wild. Our approach strategically labels examples within a novel maximum disambiguation region, where the number of semantic and covariate OOD data roughly equalizes. By labeling within this region, we can maximally disambiguate the two types of OOD data, thereby maximizing the utility of the fixed labeling budget. Our algorithm first utilizes a noisy binary search algorithm that identifies the maximal disambiguation region with high probability. The algorithm then continues with annotating inside the identified labeling region, reaping the full benefit of human feedback. Extensive experiments validate the efficacy of our framework. We observed that with only a few hundred human annotations, our method significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods that do not involve human assistance, in both OOD generalization and OOD detection. Code is publicly available at \url{https://github.com/HaoyueBaiZJU/aha}.
SIEVE: General Purpose Data Filtering System Matching GPT-4o Accuracy at 1% the Cost
Oct 03, 2024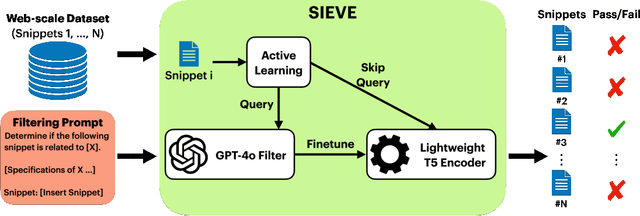
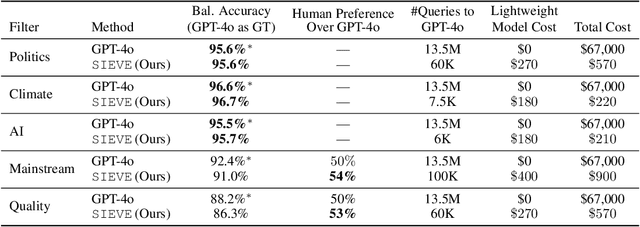
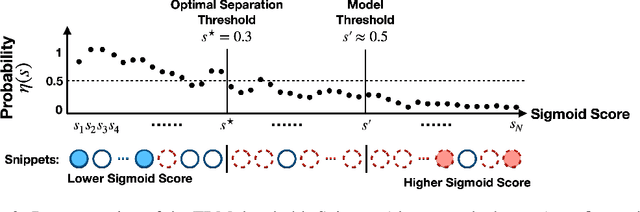
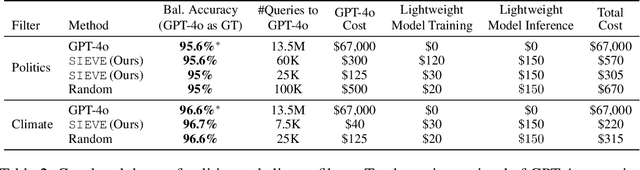
Abstract:Creating specialized large language models requires vast amounts of clean, special purpose data for training and fine-tuning. With only a handful of existing large-scale, domain-specific datasets, creation of new datasets is required in most applications. This requires the development of new application-specific filtering of web-scale data. Filtering with a high-performance, general-purpose LLM such as GPT-4o can be highly effective, but this is extremely expensive at web-scale. This paper proposes SIEVE, a lightweight alternative that matches GPT-4o accuracy at a fraction of the cost. SIEVE can perform up to 500 filtering operations for the cost of one GPT-4o filtering call. The key to SIEVE is a seamless integration of GPT-4o and lightweight T5 models, using active learning to fine-tune T5 in the background with a small number of calls to GPT-4o. Once trained, it performs as well as GPT-4o at a tiny fraction of the cost. We experimentally validate SIEVE on the OpenWebText dataset, using five highly customized filter tasks targeting high quality and domain-specific content. Our results demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of our method in curating large, high-quality datasets for language model training at a substantially lower cost (1%) than existing techniques. To further validate SIEVE, experiments show that SIEVE and GPT-4o achieve similar accuracy, with human evaluators preferring SIEVE's filtering results to those of GPT-4o.
Humor in AI: Massive Scale Crowd-Sourced Preferences and Benchmarks for Cartoon Captioning
Jun 15, 2024

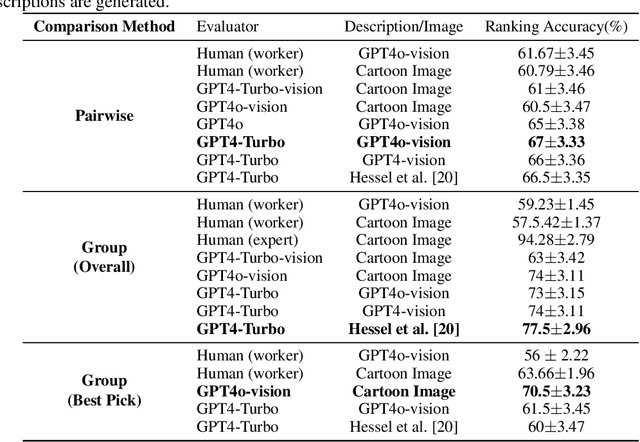
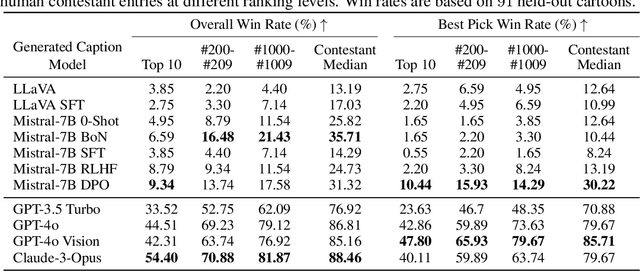
Abstract:We present a novel multimodal preference dataset for creative tasks, consisting of over 250 million human ratings on more than 2.2 million captions, collected through crowdsourcing rating data for The New Yorker's weekly cartoon caption contest over the past eight years. This unique dataset supports the development and evaluation of multimodal large language models and preference-based fine-tuning algorithms for humorous caption generation. We propose novel benchmarks for judging the quality of model-generated captions, utilizing both GPT4 and human judgments to establish ranking-based evaluation strategies. Our experimental results highlight the limitations of current fine-tuning methods, such as RLHF and DPO, when applied to creative tasks. Furthermore, we demonstrate that even state-of-the-art models like GPT4 and Claude currently underperform top human contestants in generating humorous captions. As we conclude this extensive data collection effort, we release the entire preference dataset to the research community, fostering further advancements in AI humor generation and evaluation.
Pretraining Decision Transformers with Reward Prediction for In-Context Multi-task Structured Bandit Learning
Jun 07, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we study multi-task structured bandit problem where the goal is to learn a near-optimal algorithm that minimizes cumulative regret. The tasks share a common structure and the algorithm exploits the shared structure to minimize the cumulative regret for an unseen but related test task. We use a transformer as a decision-making algorithm to learn this shared structure so as to generalize to the test task. The prior work of pretrained decision transformers like DPT requires access to the optimal action during training which may be hard in several scenarios. Diverging from these works, our learning algorithm does not need the knowledge of optimal action per task during training but predicts a reward vector for each of the actions using only the observed offline data from the diverse training tasks. Finally, during inference time, it selects action using the reward predictions employing various exploration strategies in-context for an unseen test task. Our model outperforms other SOTA methods like DPT, and Algorithmic Distillation over a series of experiments on several structured bandit problems (linear, bilinear, latent, non-linear). Interestingly, we show that our algorithm, without the knowledge of the underlying problem structure, can learn a near-optimal policy in-context by leveraging the shared structure across diverse tasks. We further extend the field of pre-trained decision transformers by showing that they can leverage unseen tasks with new actions and still learn the underlying latent structure to derive a near-optimal policy. We validate this over several experiments to show that our proposed solution is very general and has wide applications to potentially emergent online and offline strategies at test time. Finally, we theoretically analyze the performance of our algorithm and obtain generalization bounds in the in-context multi-task learning setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge