Rabiul Awal
Grounding Computer Use Agents on Human Demonstrations
Nov 10, 2025



Abstract:Building reliable computer-use agents requires grounding: accurately connecting natural language instructions to the correct on-screen elements. While large datasets exist for web and mobile interactions, high-quality resources for desktop environments are limited. To address this gap, we introduce GroundCUA, a large-scale desktop grounding dataset built from expert human demonstrations. It covers 87 applications across 12 categories and includes 56K screenshots, with every on-screen element carefully annotated for a total of over 3.56M human-verified annotations. From these demonstrations, we generate diverse instructions that capture a wide range of real-world tasks, providing high-quality data for model training. Using GroundCUA, we develop the GroundNext family of models that map instructions to their target UI elements. At both 3B and 7B scales, GroundNext achieves state-of-the-art results across five benchmarks using supervised fine-tuning, while requiring less than one-tenth the training data of prior work. Reinforcement learning post-training further improves performance, and when evaluated in an agentic setting on the OSWorld benchmark using o3 as planner, GroundNext attains comparable or superior results to models trained with substantially more data,. These results demonstrate the critical role of high-quality, expert-driven datasets in advancing general-purpose computer-use agents.
Rendering-Aware Reinforcement Learning for Vector Graphics Generation
May 27, 2025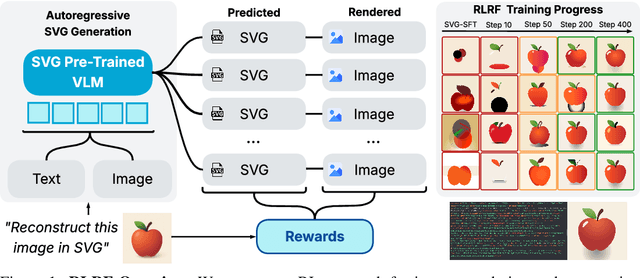
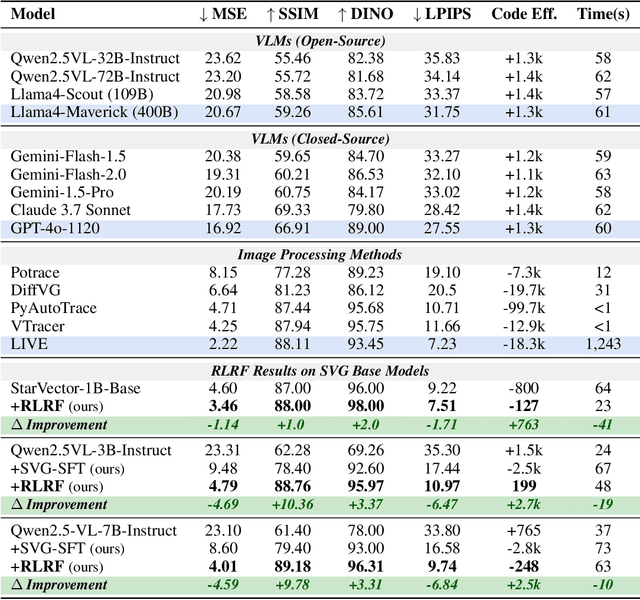
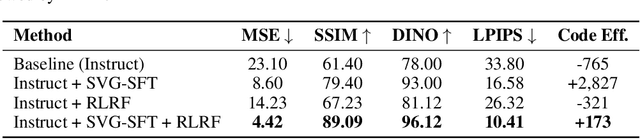
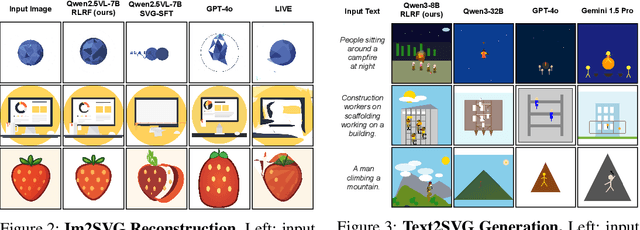
Abstract:Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) offer a powerful format for representing visual designs as interpretable code. Recent advances in vision-language models (VLMs) have enabled high-quality SVG generation by framing the problem as a code generation task and leveraging large-scale pretraining. VLMs are particularly suitable for this task as they capture both global semantics and fine-grained visual patterns, while transferring knowledge across vision, natural language, and code domains. However, existing VLM approaches often struggle to produce faithful and efficient SVGs because they never observe the rendered images during training. Although differentiable rendering for autoregressive SVG code generation remains unavailable, rendered outputs can still be compared to original inputs, enabling evaluative feedback suitable for reinforcement learning (RL). We introduce RLRF(Reinforcement Learning from Rendering Feedback), an RL method that enhances SVG generation in autoregressive VLMs by leveraging feedback from rendered SVG outputs. Given an input image, the model generates SVG roll-outs that are rendered and compared to the original image to compute a reward. This visual fidelity feedback guides the model toward producing more accurate, efficient, and semantically coherent SVGs. RLRF significantly outperforms supervised fine-tuning, addressing common failure modes and enabling precise, high-quality SVG generation with strong structural understanding and generalization.
CTRL-O: Language-Controllable Object-Centric Visual Representation Learning
Mar 27, 2025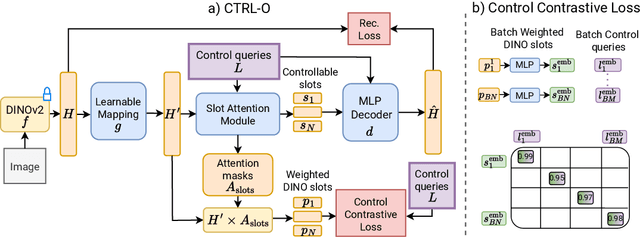
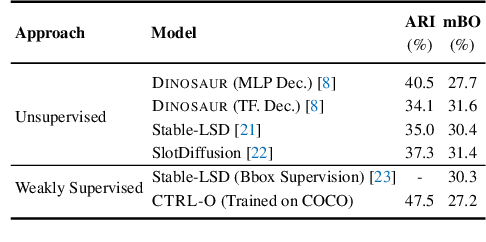
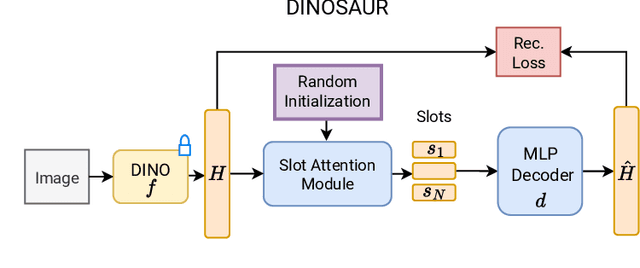
Abstract:Object-centric representation learning aims to decompose visual scenes into fixed-size vectors called "slots" or "object files", where each slot captures a distinct object. Current state-of-the-art object-centric models have shown remarkable success in object discovery in diverse domains, including complex real-world scenes. However, these models suffer from a key limitation: they lack controllability. Specifically, current object-centric models learn representations based on their preconceived understanding of objects, without allowing user input to guide which objects are represented. Introducing controllability into object-centric models could unlock a range of useful capabilities, such as the ability to extract instance-specific representations from a scene. In this work, we propose a novel approach for user-directed control over slot representations by conditioning slots on language descriptions. The proposed ConTRoLlable Object-centric representation learning approach, which we term CTRL-O, achieves targeted object-language binding in complex real-world scenes without requiring mask supervision. Next, we apply these controllable slot representations on two downstream vision language tasks: text-to-image generation and visual question answering. The proposed approach enables instance-specific text-to-image generation and also achieves strong performance on visual question answering.
UI-Vision: A Desktop-centric GUI Benchmark for Visual Perception and Interaction
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:Autonomous agents that navigate Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) to automate tasks like document editing and file management can greatly enhance computer workflows. While existing research focuses on online settings, desktop environments, critical for many professional and everyday tasks, remain underexplored due to data collection challenges and licensing issues. We introduce UI-Vision, the first comprehensive, license-permissive benchmark for offline, fine-grained evaluation of computer use agents in real-world desktop environments. Unlike online benchmarks, UI-Vision provides: (i) dense, high-quality annotations of human demonstrations, including bounding boxes, UI labels, and action trajectories (clicks, drags, and keyboard inputs) across 83 software applications, and (ii) three fine-to-coarse grained tasks-Element Grounding, Layout Grounding, and Action Prediction-with well-defined metrics to rigorously evaluate agents' performance in desktop environments. Our evaluation reveals critical limitations in state-of-the-art models like UI-TARS-72B, including issues with understanding professional software, spatial reasoning, and complex actions like drag-and-drop. These findings highlight the challenges in developing fully autonomous computer use agents. By releasing UI-Vision as open-source, we aim to advance the development of more capable agents for real-world desktop tasks.
BigDocs: An Open and Permissively-Licensed Dataset for Training Multimodal Models on Document and Code Tasks
Dec 05, 2024



Abstract:Multimodal AI has the potential to significantly enhance document-understanding tasks, such as processing receipts, understanding workflows, extracting data from documents, and summarizing reports. Code generation tasks that require long-structured outputs can also be enhanced by multimodality. Despite this, their use in commercial applications is often limited due to limited access to training data and restrictive licensing, which hinders open access. To address these limitations, we introduce BigDocs-7.5M, a high-quality, open-access dataset comprising 7.5 million multimodal documents across 30 tasks. We use an efficient data curation process to ensure our data is high-quality and license-permissive. Our process emphasizes accountability, responsibility, and transparency through filtering rules, traceable metadata, and careful content analysis. Additionally, we introduce BigDocs-Bench, a benchmark suite with 10 novel tasks where we create datasets that reflect real-world use cases involving reasoning over Graphical User Interfaces (GUI) and code generation from images. Our experiments show that training with BigDocs-Bench improves average performance up to 25.8% over closed-source GPT-4o in document reasoning and structured output tasks such as Screenshot2HTML or Image2Latex generation. Finally, human evaluations showed a preference for outputs from models trained on BigDocs over GPT-4o. This suggests that BigDocs can help both academics and the open-source community utilize and improve AI tools to enhance multimodal capabilities and document reasoning. The project is hosted at https://bigdocs.github.io .
Introducing Milabench: Benchmarking Accelerators for AI
Nov 18, 2024



Abstract:AI workloads, particularly those driven by deep learning, are introducing novel usage patterns to high-performance computing (HPC) systems that are not comprehensively captured by standard HPC benchmarks. As one of the largest academic research centers dedicated to deep learning, Mila identified the need to develop a custom benchmarking suite to address the diverse requirements of its community, which consists of over 1,000 researchers. This report introduces Milabench, the resulting benchmarking suite. Its design was informed by an extensive literature review encompassing 867 papers, as well as surveys conducted with Mila researchers. This rigorous process led to the selection of 26 primary benchmarks tailored for procurement evaluations, alongside 16 optional benchmarks for in-depth analysis. We detail the design methodology, the structure of the benchmarking suite, and provide performance evaluations using GPUs from NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel. The Milabench suite is open source and can be accessed at github.com/mila-iqia/milabench.
VisMin: Visual Minimal-Change Understanding
Jul 23, 2024


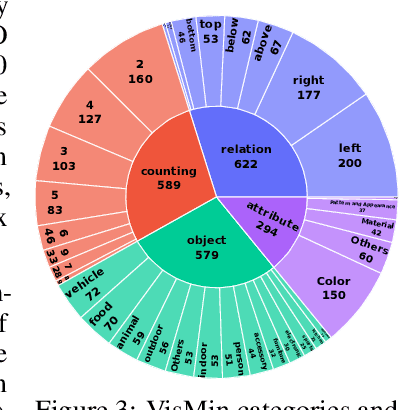
Abstract:Fine-grained understanding of objects, attributes, and relationships between objects is crucial for visual-language models (VLMs). Existing benchmarks primarily focus on evaluating VLMs' capability to distinguish between two very similar \textit{captions} given an image. In this paper, we introduce a new, challenging benchmark termed \textbf{Vis}ual \textbf{Min}imal-Change Understanding (VisMin), which requires models to predict the correct image-caption match given two images and two captions. The image pair and caption pair contain minimal changes, i.e., only one aspect changes at a time from among the following: \textit{object}, \textit{attribute}, \textit{count}, and \textit{spatial relation}. These changes test the models' understanding of objects, attributes (such as color, material, shape), counts, and spatial relationships between objects. We built an automatic framework using large language models and diffusion models, followed by a rigorous 4-step verification process by human annotators. Empirical experiments reveal that current VLMs exhibit notable deficiencies in understanding spatial relationships and counting abilities. We also generate a large-scale training dataset to finetune CLIP and Idefics2, showing significant improvements in fine-grained understanding across benchmarks and in CLIP's general image-text alignment. We release all resources, including the benchmark, training data, and finetuned model checkpoints, at \url{https://vismin.net/}.
Benchmarking Vision Language Models for Cultural Understanding
Jul 15, 2024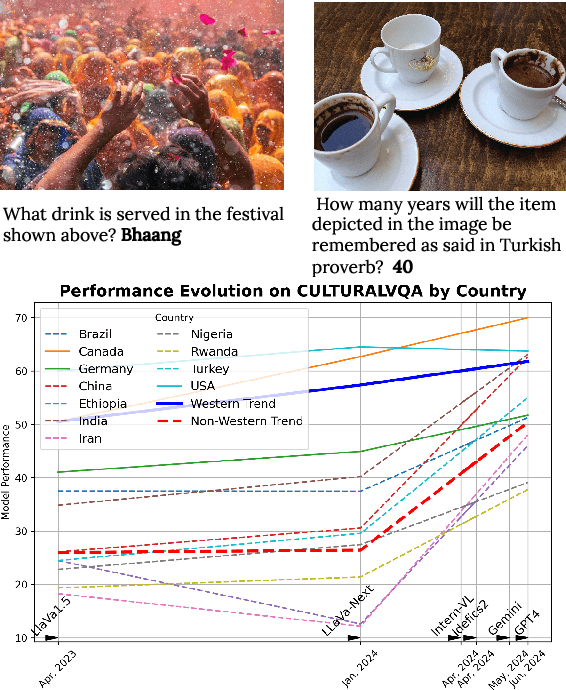
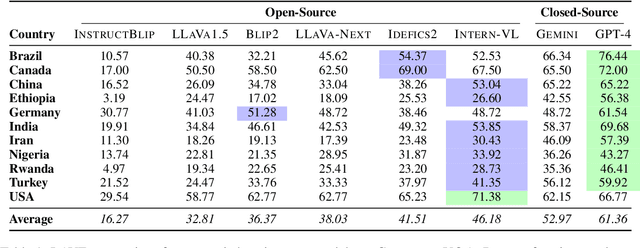

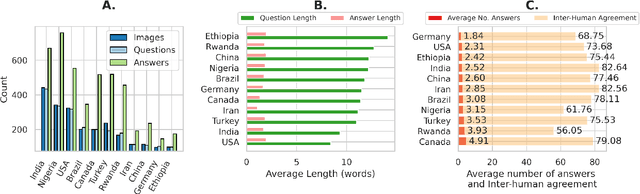
Abstract:Foundation models and vision-language pre-training have notably advanced Vision Language Models (VLMs), enabling multimodal processing of visual and linguistic data. However, their performance has been typically assessed on general scene understanding - recognizing objects, attributes, and actions - rather than cultural comprehension. This study introduces CulturalVQA, a visual question-answering benchmark aimed at assessing VLM's geo-diverse cultural understanding. We curate a collection of 2,378 image-question pairs with 1-5 answers per question representing cultures from 11 countries across 5 continents. The questions probe understanding of various facets of culture such as clothing, food, drinks, rituals, and traditions. Benchmarking VLMs on CulturalVQA, including GPT-4V and Gemini, reveals disparity in their level of cultural understanding across regions, with strong cultural understanding capabilities for North America while significantly lower performance for Africa. We observe disparity in their performance across cultural facets too, with clothing, rituals, and traditions seeing higher performances than food and drink. These disparities help us identify areas where VLMs lack cultural understanding and demonstrate the potential of CulturalVQA as a comprehensive evaluation set for gauging VLM progress in understanding diverse cultures.
Contrasting Intra-Modal and Ranking Cross-Modal Hard Negatives to Enhance Visio-Linguistic Fine-grained Understanding
Jul 02, 2023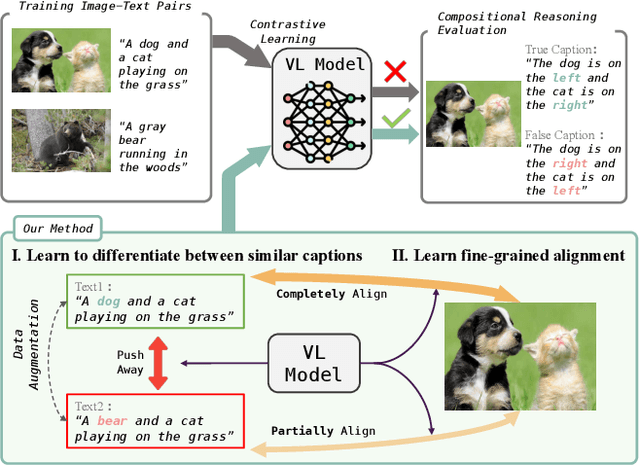
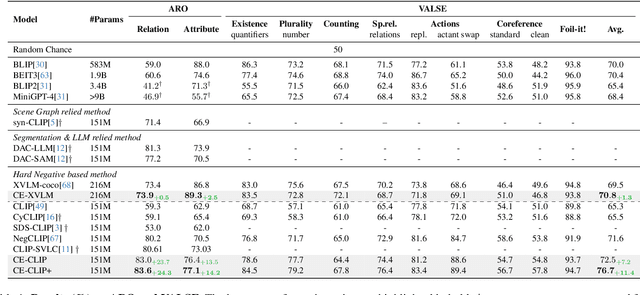
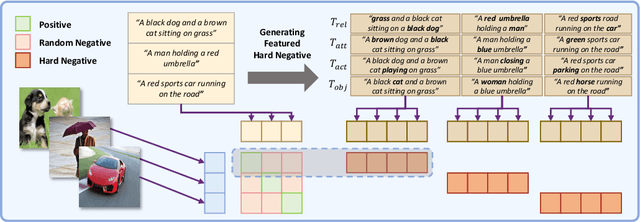
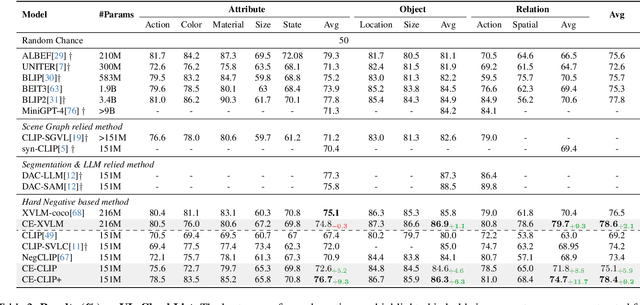
Abstract:Current Vision and Language Models (VLMs) demonstrate strong performance across various vision-language tasks, yet they struggle with fine-grained understanding. This issue stems from weak image-caption alignment in pretraining datasets and a simplified contrastive objective that fails to distinguish nuanced grounding elements such as relations, actions, and attributes. As a result, the models tend to learn bag-of-words representations. To mitigate these challenges, we introduce an intra-modal contrastive loss and a unique cross-modal rank loss with an adaptive threshold that serves as curriculum learning, utilizing our automatically generated hard negatives to augment the model's capacity. Our strategy, which does not necessitate additional annotations or parameters, can be incorporated into any VLM trained with an image-text contrastive loss. Upon application to CLIP, our method leads to significant improvements on four fine-grained benchmarks, and it also enhances the performance of X-VLM, which is the state-of-art moodel on fine-grained reasoning.
Investigating Prompting Techniques for Zero- and Few-Shot Visual Question Answering
Jun 16, 2023



Abstract:Visual question answering (VQA) is a challenging task that requires the ability to comprehend and reason with visual information. While recent vision-language models have made strides, they continue to struggle with zero-shot VQA, particularly in handling complex compositional questions and adapting to new domains i.e. knowledge-based reasoning. This paper explores the use of various prompting strategies, focusing on the BLIP2 model, to enhance zero-shot VQA performance. We conduct a comprehensive investigation across several VQA datasets, examining the effectiveness of different question templates, the role of few-shot exemplars, the impact of chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning, and the benefits of incorporating image captions as additional visual cues. Despite the varied outcomes, our findings demonstrate that carefully designed question templates and the integration of additional visual cues, like image captions, can contribute to improved VQA performance, especially when used in conjunction with few-shot examples. However, we also identify a limitation in the use of chain-of-thought rationalization, which negatively affects VQA accuracy. Our study thus provides critical insights into the potential of prompting for improving zero-shot VQA performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge