Siba Smarak Panigrahi
HeurekaBench: A Benchmarking Framework for AI Co-scientist
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:LLM-based reasoning models have enabled the development of agentic systems that act as co-scientists, assisting in multi-step scientific analysis. However, evaluating these systems is challenging, as it requires realistic, end-to-end research scenarios that integrate data analysis, interpretation, and the generation of new insights from the experimental data. To address this limitation, we introduce HeurekaBench, a framework to create benchmarks with exploratory, open-ended research questions for experimental datasets. Each such question is grounded in a scientific study and its corresponding code repository, and is created using a semi-automated pipeline that leverages multiple LLMs to extract insights and generate candidate workflows, which are then verified against reported findings. We instantiate the framework in single-cell biology to obtain sc-HeurekaBench benchmark and use it to compare state-of-the-art single-cell agents. We further showcase the benefits of our benchmark for quantitatively analyzing current design choices in agentic systems. We find that the addition of a critic module can improve ill-formed responses for open-source LLM-based agents by up to 22% and close the gap with their closed-source counterparts. Overall, HeurekaBench sets a path toward rigorous, end-to-end evaluation of scientific agents, grounding benchmark construction in real scientific workflows.
SymmCD: Symmetry-Preserving Crystal Generation with Diffusion Models
Feb 05, 2025Abstract:Generating novel crystalline materials has potential to lead to advancements in fields such as electronics, energy storage, and catalysis. The defining characteristic of crystals is their symmetry, which plays a central role in determining their physical properties. However, existing crystal generation methods either fail to generate materials that display the symmetries of real-world crystals, or simply replicate the symmetry information from examples in a database. To address this limitation, we propose SymmCD, a novel diffusion-based generative model that explicitly incorporates crystallographic symmetry into the generative process. We decompose crystals into two components and learn their joint distribution through diffusion: 1) the asymmetric unit, the smallest subset of the crystal which can generate the whole crystal through symmetry transformations, and; 2) the symmetry transformations needed to be applied to each atom in the asymmetric unit. We also use a novel and interpretable representation for these transformations, enabling generalization across different crystallographic symmetry groups. We showcase the competitive performance of SymmCD on a subset of the Materials Project, obtaining diverse and valid crystals with realistic symmetries and predicted properties.
BigDocs: An Open and Permissively-Licensed Dataset for Training Multimodal Models on Document and Code Tasks
Dec 05, 2024



Abstract:Multimodal AI has the potential to significantly enhance document-understanding tasks, such as processing receipts, understanding workflows, extracting data from documents, and summarizing reports. Code generation tasks that require long-structured outputs can also be enhanced by multimodality. Despite this, their use in commercial applications is often limited due to limited access to training data and restrictive licensing, which hinders open access. To address these limitations, we introduce BigDocs-7.5M, a high-quality, open-access dataset comprising 7.5 million multimodal documents across 30 tasks. We use an efficient data curation process to ensure our data is high-quality and license-permissive. Our process emphasizes accountability, responsibility, and transparency through filtering rules, traceable metadata, and careful content analysis. Additionally, we introduce BigDocs-Bench, a benchmark suite with 10 novel tasks where we create datasets that reflect real-world use cases involving reasoning over Graphical User Interfaces (GUI) and code generation from images. Our experiments show that training with BigDocs-Bench improves average performance up to 25.8% over closed-source GPT-4o in document reasoning and structured output tasks such as Screenshot2HTML or Image2Latex generation. Finally, human evaluations showed a preference for outputs from models trained on BigDocs over GPT-4o. This suggests that BigDocs can help both academics and the open-source community utilize and improve AI tools to enhance multimodal capabilities and document reasoning. The project is hosted at https://bigdocs.github.io .
Improved Canonicalization for Model Agnostic Equivariance
May 23, 2024


Abstract:This work introduces a novel approach to achieving architecture-agnostic equivariance in deep learning, particularly addressing the limitations of traditional equivariant architectures and the inefficiencies of the existing architecture-agnostic methods. Building equivariant models using traditional methods requires designing equivariant versions of existing models and training them from scratch, a process that is both impractical and resource-intensive. Canonicalization has emerged as a promising alternative for inducing equivariance without altering model architecture, but it suffers from the need for highly expressive and expensive equivariant networks to learn canonical orientations accurately. We propose a new method that employs any non-equivariant network for canonicalization. Our method uses contrastive learning to efficiently learn a unique canonical orientation and offers more flexibility for the choice of canonicalization network. We empirically demonstrate that this approach outperforms existing methods in achieving equivariance for large pretrained models and significantly speeds up the canonicalization process, making it up to 2 times faster.
Equivariant Adaptation of Large Pre-Trained Models
Oct 02, 2023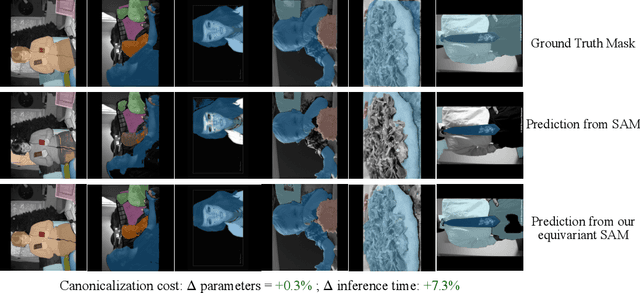



Abstract:Equivariant networks are specifically designed to ensure consistent behavior with respect to a set of input transformations, leading to higher sample efficiency and more accurate and robust predictions. However, redesigning each component of prevalent deep neural network architectures to achieve chosen equivariance is a difficult problem and can result in a computationally expensive network during both training and inference. A recently proposed alternative towards equivariance that removes the architectural constraints is to use a simple canonicalization network that transforms the input to a canonical form before feeding it to an unconstrained prediction network. We show here that this approach can effectively be used to make a large pre-trained network equivariant. However, we observe that the produced canonical orientations can be misaligned with those of the training distribution, hindering performance. Using dataset-dependent priors to inform the canonicalization function, we are able to make large pre-trained models equivariant while maintaining their performance. This significantly improves the robustness of these models to deterministic transformations of the data, such as rotations. We believe this equivariant adaptation of large pre-trained models can help their domain-specific applications with known symmetry priors.
Efficient Dynamics Modeling in Interactive Environments with Koopman Theory
Jul 12, 2023



Abstract:The accurate modeling of dynamics in interactive environments is critical for successful long-range prediction. Such a capability could advance Reinforcement Learning (RL) and Planning algorithms, but achieving it is challenging. Inaccuracies in model estimates can compound, resulting in increased errors over long horizons. We approach this problem from the lens of Koopman theory, where the nonlinear dynamics of the environment can be linearized in a high-dimensional latent space. This allows us to efficiently parallelize the sequential problem of long-range prediction using convolution, while accounting for the agent's action at every time step. Our approach also enables stability analysis and better control over gradients through time. Taken together, these advantages result in significant improvement over the existing approaches, both in the efficiency and the accuracy of modeling dynamics over extended horizons. We also report promising experimental results in dynamics modeling for the scenarios of both model-based planning and model-free RL.
Team Enigma at ArgMining-EMNLP 2021: Leveraging Pre-trained Language Models for Key Point Matching
Oct 24, 2021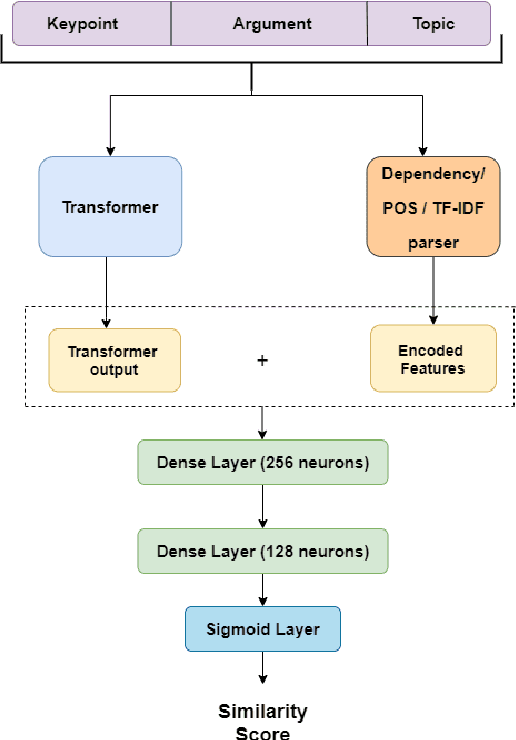
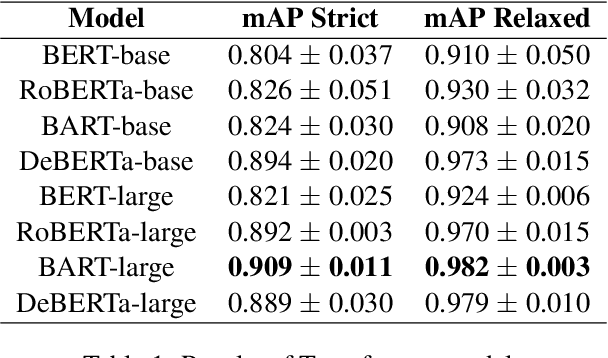
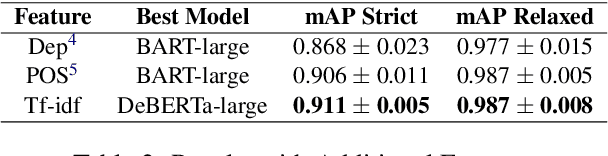
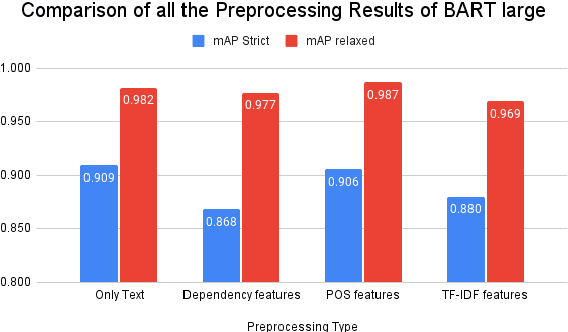
Abstract:We present the system description for our submission towards the Key Point Analysis Shared Task at ArgMining 2021. Track 1 of the shared task requires participants to develop methods to predict the match score between each pair of arguments and keypoints, provided they belong to the same topic under the same stance. We leveraged existing state of the art pre-trained language models along with incorporating additional data and features extracted from the inputs (topics, key points, and arguments) to improve performance. We were able to achieve mAP strict and mAP relaxed score of 0.872 and 0.966 respectively in the evaluation phase, securing 5th place on the leaderboard. In the post evaluation phase, we achieved a mAP strict and mAP relaxed score of 0.921 and 0.982 respectively. All the codes to generate reproducible results on our models are available on Github.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge