Arnab Mondal
Rendering-Aware Reinforcement Learning for Vector Graphics Generation
May 27, 2025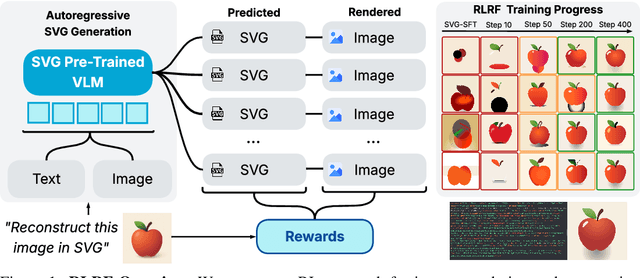
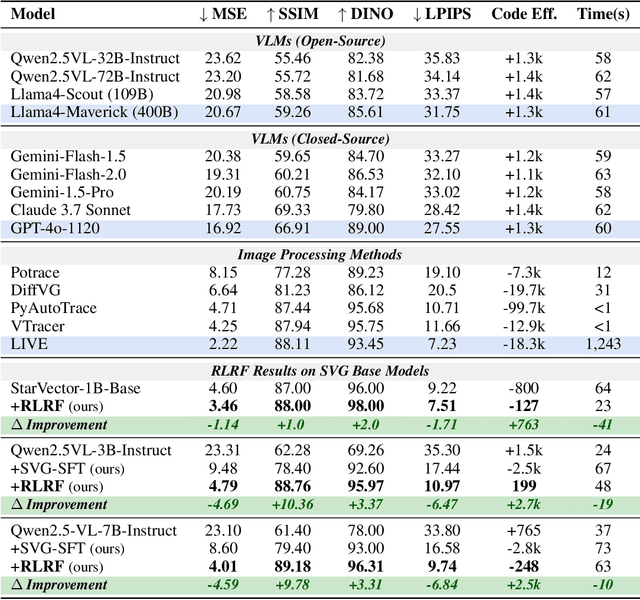
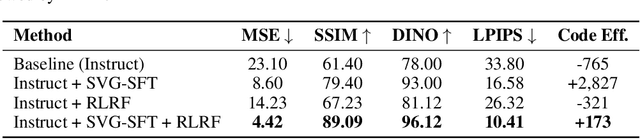
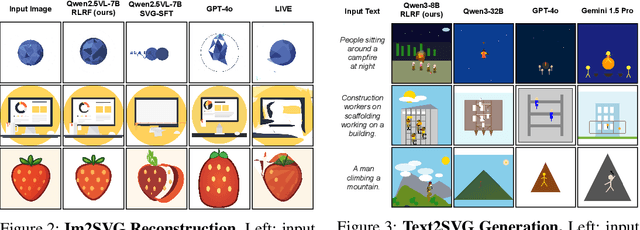
Abstract:Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) offer a powerful format for representing visual designs as interpretable code. Recent advances in vision-language models (VLMs) have enabled high-quality SVG generation by framing the problem as a code generation task and leveraging large-scale pretraining. VLMs are particularly suitable for this task as they capture both global semantics and fine-grained visual patterns, while transferring knowledge across vision, natural language, and code domains. However, existing VLM approaches often struggle to produce faithful and efficient SVGs because they never observe the rendered images during training. Although differentiable rendering for autoregressive SVG code generation remains unavailable, rendered outputs can still be compared to original inputs, enabling evaluative feedback suitable for reinforcement learning (RL). We introduce RLRF(Reinforcement Learning from Rendering Feedback), an RL method that enhances SVG generation in autoregressive VLMs by leveraging feedback from rendered SVG outputs. Given an input image, the model generates SVG roll-outs that are rendered and compared to the original image to compute a reward. This visual fidelity feedback guides the model toward producing more accurate, efficient, and semantically coherent SVGs. RLRF significantly outperforms supervised fine-tuning, addressing common failure modes and enabling precise, high-quality SVG generation with strong structural understanding and generalization.
Retinal Vessel Segmentation under Extreme Low Annotation: A Generative Adversarial Network Approach
Sep 05, 2018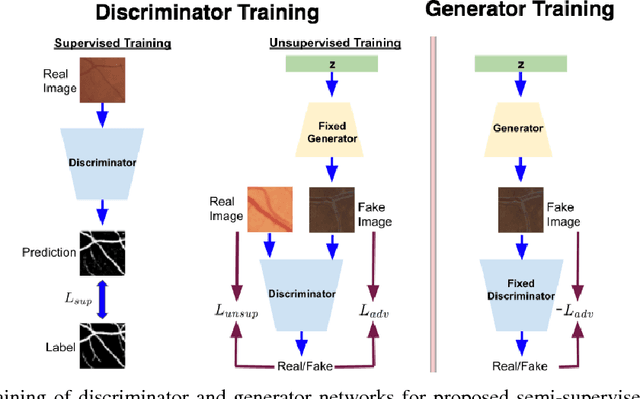
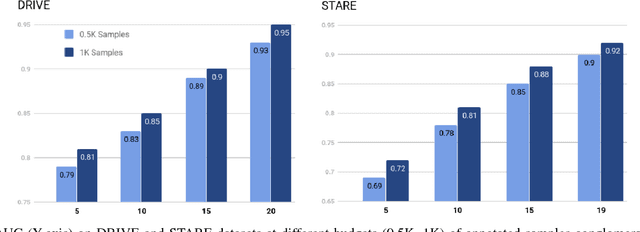
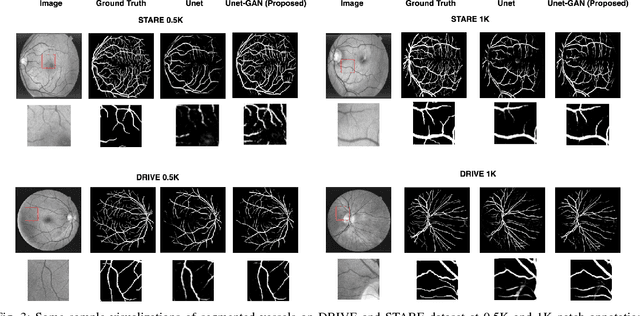
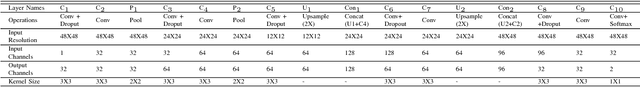
Abstract:Contemporary deep learning based medical image segmentation algorithms require hours of annotation labor by domain experts. These data hungry deep models perform sub-optimally in the presence of limited amount of labeled data. In this paper, we present a data efficient learning framework using the recent concept of Generative Adversarial Networks; this allows a deep neural network to perform significantly better than its fully supervised counterpart in low annotation regime. The proposed method is an extension of our previous work with the addition of a new unsupervised adversarial loss and a structured prediction based architecture. To the best of our knowledge, this work is the first demonstration of an adversarial framework based structured prediction model for medical image segmentation. Though generic, we apply our method for segmentation of blood vessels in retinal fundus images. We experiment with extreme low annotation budget (0.8 - 1.6% of contemporary annotation size). On DRIVE and STARE datasets, the proposed method outperforms our previous method and other fully supervised benchmark models by significant margins especially with very low number of annotated examples. In addition, our systematic ablation studies suggest some key recipes for successfully training GAN based semi-supervised algorithms with an encoder-decoder style network architecture.
Low Cost Autonomous Navigation and Control of a Mechanically Balanced Bicycle with Dual Locomotion Mode
Nov 01, 2016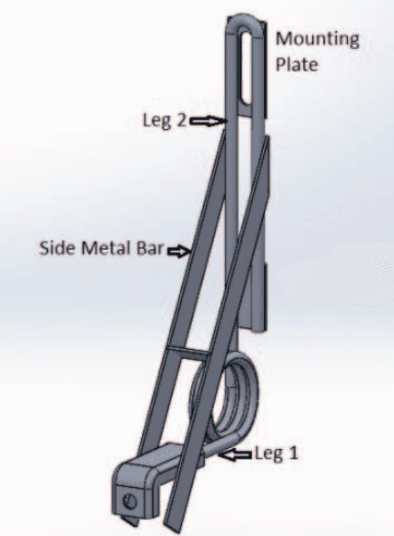
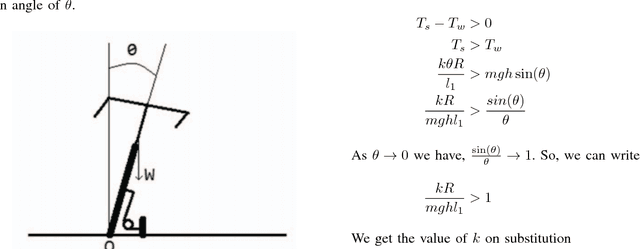
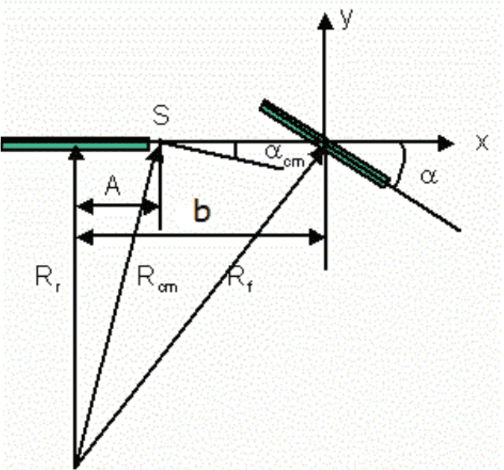
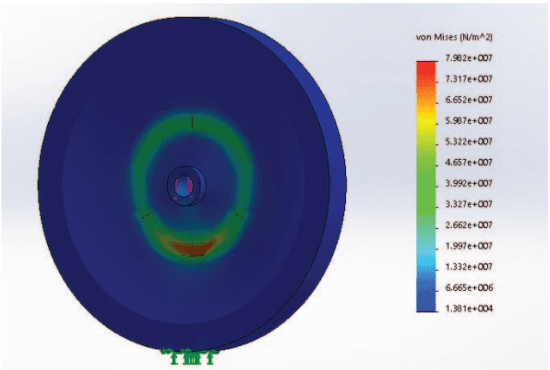
Abstract:On the lines of the huge and varied efforts in the field of automation with respect to technology development and innovation of vehicles to make them run autonomously, this paper presents an innovation to a bicycle. A normal daily use bicycle was modified at low cost such that it runs autonomously, while maintaining its original form i.e. the manual drive. Hence, a bicycle which could be normally driven by any human and with a press of switch could run autonomously according to the needs of the user has been developed.
* Published in the International Transportation Electrification Conference (ITEC) in 2015 organized by IEEE Industrial Application Society (IAS) and SAE India in Chennai, India
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge