Nathaniel Hudson
Topology-Aware Knowledge Propagation in Decentralized Learning
May 16, 2025Abstract:Decentralized learning enables collaborative training of models across naturally distributed data without centralized coordination or maintenance of a global model. Instead, devices are organized in arbitrary communication topologies, in which they can only communicate with neighboring devices. Each device maintains its own local model by training on its local data and integrating new knowledge via model aggregation with neighbors. Therefore, knowledge is propagated across the topology via successive aggregation rounds. We study, in particular, the propagation of out-of-distribution (OOD) knowledge. We find that popular decentralized learning algorithms struggle to propagate OOD knowledge effectively to all devices. Further, we find that both the location of OOD data within a topology, and the topology itself, significantly impact OOD knowledge propagation. We then propose topology-aware aggregation strategies to accelerate (OOD) knowledge propagation across devices. These strategies improve OOD data accuracy, compared to topology-unaware baselines, by 123% on average across models in a topology.
MOFA: Discovering Materials for Carbon Capture with a GenAI- and Simulation-Based Workflow
Jan 18, 2025Abstract:We present MOFA, an open-source generative AI (GenAI) plus simulation workflow for high-throughput generation of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) on large-scale high-performance computing (HPC) systems. MOFA addresses key challenges in integrating GPU-accelerated computing for GPU-intensive GenAI tasks, including distributed training and inference, alongside CPU- and GPU-optimized tasks for screening and filtering AI-generated MOFs using molecular dynamics, density functional theory, and Monte Carlo simulations. These heterogeneous tasks are unified within an online learning framework that optimizes the utilization of available CPU and GPU resources across HPC systems. Performance metrics from a 450-node (14,400 AMD Zen 3 CPUs + 1800 NVIDIA A100 GPUs) supercomputer run demonstrate that MOFA achieves high-throughput generation of novel MOF structures, with CO$_2$ adsorption capacities ranking among the top 10 in the hypothetical MOF (hMOF) dataset. Furthermore, the production of high-quality MOFs exhibits a linear relationship with the number of nodes utilized. The modular architecture of MOFA will facilitate its integration into other scientific applications that dynamically combine GenAI with large-scale simulations.
SoK: On Finding Common Ground in Loss Landscapes Using Deep Model Merging Techniques
Oct 16, 2024



Abstract:Understanding neural networks is crucial to creating reliable and trustworthy deep learning models. Most contemporary research in interpretability analyzes just one model at a time via causal intervention or activation analysis. Yet despite successes, these methods leave significant gaps in our understanding of the training behaviors of neural networks, how their inner representations emerge, and how we can predictably associate model components with task-specific behaviors. Seeking new insights from work in related fields, here we survey literature in the field of model merging, a field that aims to combine the abilities of various neural networks by merging their parameters and identifying task-specific model components in the process. We analyze the model merging literature through the lens of loss landscape geometry, an approach that enables us to connect observations from empirical studies on interpretability, security, model merging, and loss landscape analysis to phenomena that govern neural network training and the emergence of their inner representations. To systematize knowledge in this area, we present a novel taxonomy of model merging techniques organized by their core algorithmic principles. Additionally, we distill repeated empirical observations from the literature in these fields into characterizations of four major aspects of loss landscape geometry: mode convexity, determinism, directedness, and connectivity. We argue that by improving our understanding of the principles underlying model merging and loss landscape geometry, this work contributes to the goal of ensuring secure and trustworthy machine learning in practice.
Mitigating Memorization In Language Models
Oct 03, 2024



Abstract:Language models (LMs) can "memorize" information, i.e., encode training data in their weights in such a way that inference-time queries can lead to verbatim regurgitation of that data. This ability to extract training data can be problematic, for example, when data are private or sensitive. In this work, we investigate methods to mitigate memorization: three regularizer-based, three finetuning-based, and eleven machine unlearning-based methods, with five of the latter being new methods that we introduce. We also introduce TinyMem, a suite of small, computationally-efficient LMs for the rapid development and evaluation of memorization-mitigation methods. We demonstrate that the mitigation methods that we develop using TinyMem can successfully be applied to production-grade LMs, and we determine via experiment that: regularizer-based mitigation methods are slow and ineffective at curbing memorization; fine-tuning-based methods are effective at curbing memorization, but overly expensive, especially for retaining higher accuracies; and unlearning-based methods are faster and more effective, allowing for the precise localization and removal of memorized information from LM weights prior to inference. We show, in particular, that our proposed unlearning method BalancedSubnet outperforms other mitigation methods at removing memorized information while preserving performance on target tasks.
Flight: A FaaS-Based Framework for Complex and Hierarchical Federated Learning
Sep 24, 2024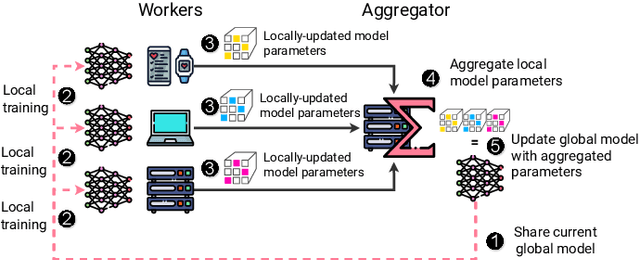
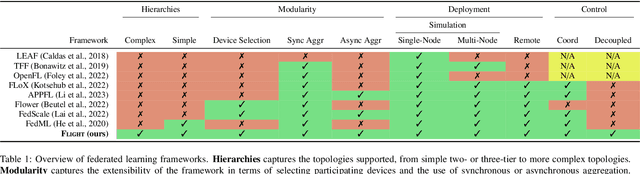
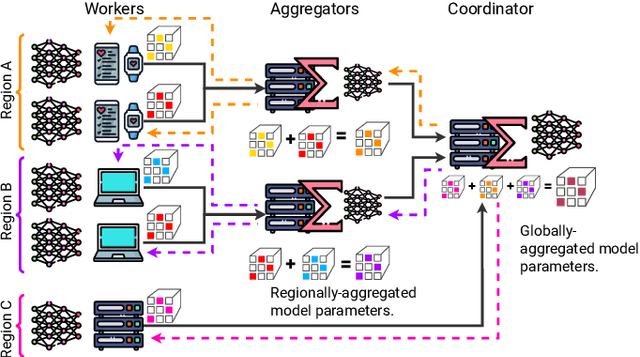
Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) is a decentralized machine learning paradigm where models are trained on distributed devices and are aggregated at a central server. Existing FL frameworks assume simple two-tier network topologies where end devices are directly connected to the aggregation server. While this is a practical mental model, it does not exploit the inherent topology of real-world distributed systems like the Internet-of-Things. We present Flight, a novel FL framework that supports complex hierarchical multi-tier topologies, asynchronous aggregation, and decouples the control plane from the data plane. We compare the performance of Flight against Flower, a state-of-the-art FL framework. Our results show that Flight scales beyond Flower, supporting up to 2048 simultaneous devices, and reduces FL makespan across several models. Finally, we show that Flight's hierarchical FL model can reduce communication overheads by more than 60%.
Causal Discovery over High-Dimensional Structured Hypothesis Spaces with Causal Graph Partitioning
Jun 10, 2024Abstract:The aim in many sciences is to understand the mechanisms that underlie the observed distribution of variables, starting from a set of initial hypotheses. Causal discovery allows us to infer mechanisms as sets of cause and effect relationships in a generalized way -- without necessarily tailoring to a specific domain. Causal discovery algorithms search over a structured hypothesis space, defined by the set of directed acyclic graphs, to find the graph that best explains the data. For high-dimensional problems, however, this search becomes intractable and scalable algorithms for causal discovery are needed to bridge the gap. In this paper, we define a novel causal graph partition that allows for divide-and-conquer causal discovery with theoretical guarantees. We leverage the idea of a superstructure -- a set of learned or existing candidate hypotheses -- to partition the search space. We prove under certain assumptions that learning with a causal graph partition always yields the Markov Equivalence Class of the true causal graph. We show our algorithm achieves comparable accuracy and a faster time to solution for biologically-tuned synthetic networks and networks up to ${10^4}$ variables. This makes our method applicable to gene regulatory network inference and other domains with high-dimensional structured hypothesis spaces.
Trillion Parameter AI Serving Infrastructure for Scientific Discovery: A Survey and Vision
Feb 05, 2024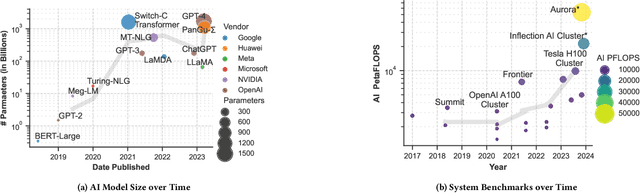
Abstract:Deep learning methods are transforming research, enabling new techniques, and ultimately leading to new discoveries. As the demand for more capable AI models continues to grow, we are now entering an era of Trillion Parameter Models (TPM), or models with more than a trillion parameters -- such as Huawei's PanGu-$\Sigma$. We describe a vision for the ecosystem of TPM users and providers that caters to the specific needs of the scientific community. We then outline the significant technical challenges and open problems in system design for serving TPMs to enable scientific research and discovery. Specifically, we describe the requirements of a comprehensive software stack and interfaces to support the diverse and flexible requirements of researchers.
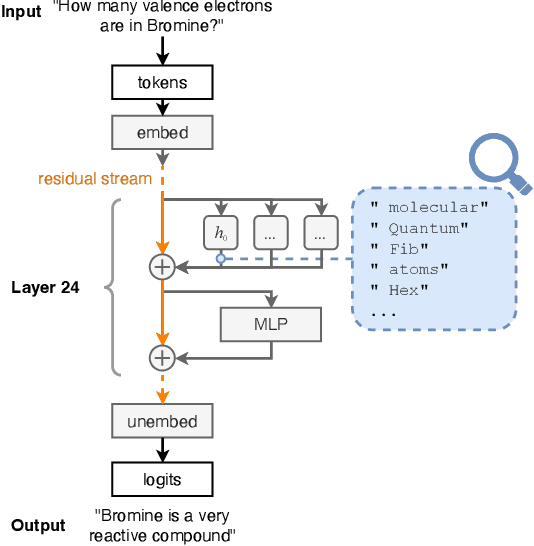
Attention Lens: A Tool for Mechanistically Interpreting the Attention Head Information Retrieval Mechanism
Oct 25, 2023

Abstract:Transformer-based Large Language Models (LLMs) are the state-of-the-art for natural language tasks. Recent work has attempted to decode, by reverse engineering the role of linear layers, the internal mechanisms by which LLMs arrive at their final predictions for text completion tasks. Yet little is known about the specific role of attention heads in producing the final token prediction. We propose Attention Lens, a tool that enables researchers to translate the outputs of attention heads into vocabulary tokens via learned attention-head-specific transformations called lenses. Preliminary findings from our trained lenses indicate that attention heads play highly specialized roles in language models. The code for Attention Lens is available at github.com/msakarvadia/AttentionLens.
Memory Injections: Correcting Multi-Hop Reasoning Failures during Inference in Transformer-Based Language Models
Sep 12, 2023Abstract:Answering multi-hop reasoning questions requires retrieving and synthesizing information from diverse sources. Large Language Models (LLMs) struggle to perform such reasoning consistently. Here we propose an approach to pinpoint and rectify multi-hop reasoning failures through targeted memory injections on LLM attention heads. First, we analyze the per-layer activations of GPT-2 models in response to single and multi-hop prompts. We then propose a mechanism that allows users to inject pertinent prompt-specific information, which we refer to as "memories," at critical LLM locations during inference. By thus enabling the LLM to incorporate additional relevant information during inference, we enhance the quality of multi-hop prompt completions. We show empirically that a simple, efficient, and targeted memory injection into a key attention layer can often increase the probability of the desired next token in multi-hop tasks, by up to 424%.
Adversarial Predictions of Data Distributions Across Federated Internet-of-Things Devices
Aug 28, 2023Abstract:Federated learning (FL) is increasingly becoming the default approach for training machine learning models across decentralized Internet-of-Things (IoT) devices. A key advantage of FL is that no raw data are communicated across the network, providing an immediate layer of privacy. Despite this, recent works have demonstrated that data reconstruction can be done with the locally trained model updates which are communicated across the network. However, many of these works have limitations with regard to how the gradients are computed in backpropagation. In this work, we demonstrate that the model weights shared in FL can expose revealing information about the local data distributions of IoT devices. This leakage could expose sensitive information to malicious actors in a distributed system. We further discuss results which show that injecting noise into model weights is ineffective at preventing data leakage without seriously harming the global model accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge