Aftab Khan
A Multi-Year Urban Streetlight Imagery Dataset for Visual Monitoring and Spatio-Temporal Drift Detection
Dec 13, 2025



Abstract:We present a large-scale, longitudinal visual dataset of urban streetlights captured by 22 fixed-angle cameras deployed across Bristol, U.K., from 2021 to 2025. The dataset contains over 526,000 images, collected hourly under diverse lighting, weather, and seasonal conditions. Each image is accompanied by rich metadata, including timestamps, GPS coordinates, and device identifiers. This unique real-world dataset enables detailed investigation of visual drift, anomaly detection, and MLOps strategies in smart city deployments. To promtoe seconardary analysis, we additionally provide a self-supervised framework based on convolutional variational autoencoders (CNN-VAEs). Models are trained separately for each camera node and for day/night image sets. We define two per-sample drift metrics: relative centroid drift, capturing latent space deviation from a baseline quarter, and relative reconstruction error, measuring normalized image-domain degradation. This dataset provides a realistic, fine-grained benchmark for evaluating long-term model stability, drift-aware learning, and deployment-ready vision systems. The images and structured metadata are publicly released in JPEG and CSV formats, supporting reproducibility and downstream applications such as streetlight monitoring, weather inference, and urban scene understanding. The dataset can be found at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.17781192 and https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.17859120.
Green MLOps to Green GenOps: An Empirical Study of Energy Consumption in Discriminative and Generative AI Operations
Mar 31, 2025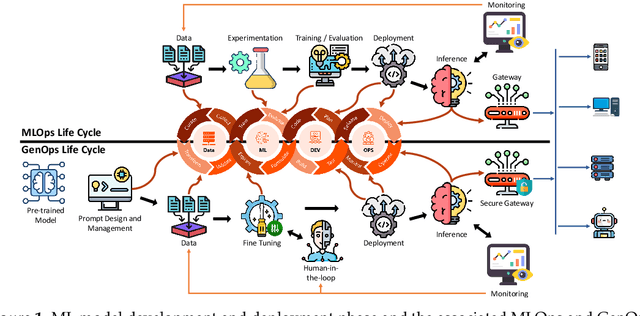
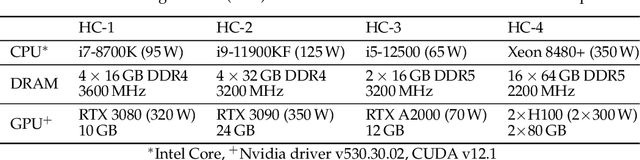

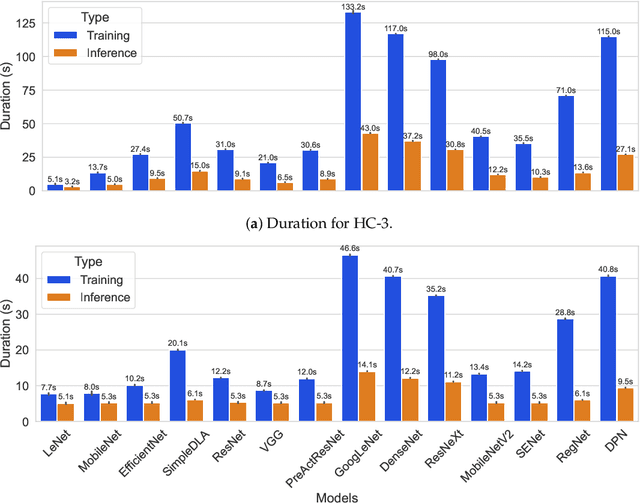
Abstract:This study presents an empirical investigation into the energy consumption of Discriminative and Generative AI models within real-world MLOps pipelines. For Discriminative models, we examine various architectures and hyperparameters during training and inference and identify energy-efficient practices. For Generative AI, Large Language Models (LLMs) are assessed, focusing primarily on energy consumption across different model sizes and varying service requests. Our study employs software-based power measurements, ensuring ease of replication across diverse configurations, models, and datasets. We analyse multiple models and hardware setups to uncover correlations among various metrics, identifying key contributors to energy consumption. The results indicate that for Discriminative models, optimising architectures, hyperparameters, and hardware can significantly reduce energy consumption without sacrificing performance. For LLMs, energy efficiency depends on balancing model size, reasoning complexity, and request-handling capacity, as larger models do not necessarily consume more energy when utilisation remains low. This analysis provides practical guidelines for designing green and sustainable ML operations, emphasising energy consumption and carbon footprint reductions while maintaining performance. This paper can serve as a benchmark for accurately estimating total energy use across different types of AI models.
Gotham Dataset 2025: A Reproducible Large-Scale IoT Network Dataset for Intrusion Detection and Security Research
Feb 05, 2025Abstract:In this paper, a dataset of IoT network traffic is presented. Our dataset was generated by utilising the Gotham testbed, an emulated large-scale Internet of Things (IoT) network designed to provide a realistic and heterogeneous environment for network security research. The testbed includes 78 emulated IoT devices operating on various protocols, including MQTT, CoAP, and RTSP. Network traffic was captured in Packet Capture (PCAP) format using tcpdump, and both benign and malicious traffic were recorded. Malicious traffic was generated through scripted attacks, covering a variety of attack types, such as Denial of Service (DoS), Telnet Brute Force, Network Scanning, CoAP Amplification, and various stages of Command and Control (C&C) communication. The data were subsequently processed in Python for feature extraction using the Tshark tool, and the resulting data was converted to Comma Separated Values (CSV) format and labelled. The data repository includes the raw network traffic in PCAP format and the processed labelled data in CSV format. Our dataset was collected in a distributed manner, where network traffic was captured separately for each IoT device at the interface between the IoT gateway and the device. Our dataset was collected in a distributed manner, where network traffic was separately captured for each IoT device at the interface between the IoT gateway and the device. With its diverse traffic patterns and attack scenarios, this dataset provides a valuable resource for developing Intrusion Detection Systems and security mechanisms tailored to complex, large-scale IoT environments. The dataset is publicly available at Zenodo.
Adapting MLOps for Diverse In-Network Intelligence in 6G Era: Challenges and Solutions
Oct 24, 2024



Abstract:Seamless integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) techniques with wireless systems is a crucial step for 6G AInization. However, such integration faces challenges in terms of model functionality and lifecycle management. ML operations (MLOps) offer a systematic approach to tackle these challenges. Existing approaches toward implementing MLOps in a centralized platform often overlook the challenges posed by diverse learning paradigms and network heterogeneity. This article provides a new approach to MLOps targeting the intricacies of future wireless networks. Considering unique aspects of the future radio access network (RAN), we formulate three operational pipelines, namely reinforcement learning operations (RLOps), federated learning operations (FedOps), and generative AI operations (GenOps). These pipelines form the foundation for seamlessly integrating various learning/inference capabilities into networks. We outline the specific challenges and proposed solutions for each operation, facilitating large-scale deployment of AI-Native 6G networks.
FLAME: Adaptive and Reactive Concept Drift Mitigation for Federated Learning Deployments
Oct 02, 2024Abstract:This paper presents Federated Learning with Adaptive Monitoring and Elimination (FLAME), a novel solution capable of detecting and mitigating concept drift in Federated Learning (FL) Internet of Things (IoT) environments. Concept drift poses significant challenges for FL models deployed in dynamic and real-world settings. FLAME leverages an FL architecture, considers a real-world FL pipeline, and proves capable of maintaining model performance and accuracy while addressing bandwidth and privacy constraints. Introducing various features and extensions on previous works, FLAME offers a robust solution to concept drift, significantly reducing computational load and communication overhead. Compared to well-known lightweight mitigation methods, FLAME demonstrates superior performance in maintaining high F1 scores and reducing resource utilisation in large-scale IoT deployments, making it a promising approach for real-world applications.
FedMap: Iterative Magnitude-Based Pruning for Communication-Efficient Federated Learning
Jun 27, 2024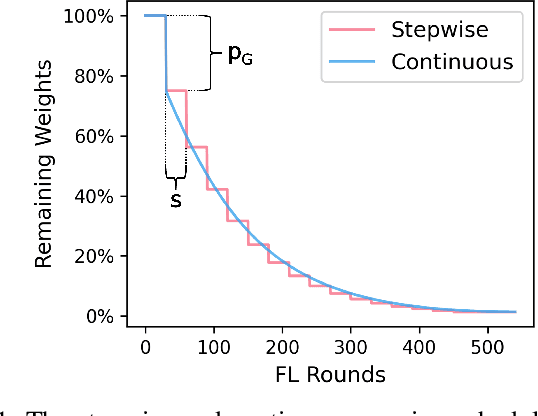
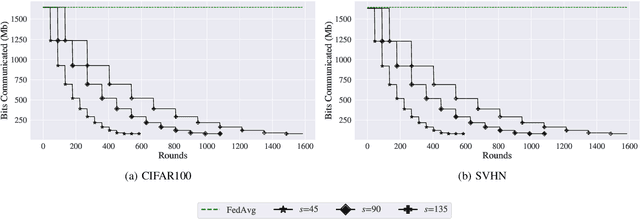
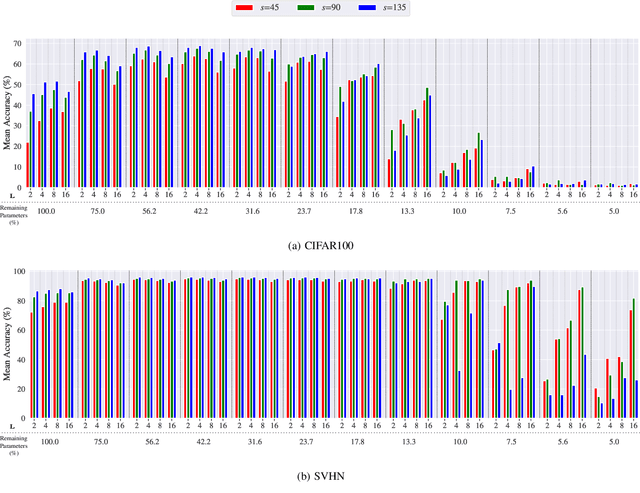
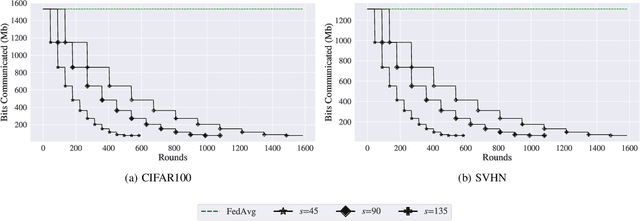
Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) is a distributed machine learning approach that enables training on decentralized data while preserving privacy. However, FL systems often involve resource-constrained client devices with limited computational power, memory, storage, and bandwidth. This paper introduces FedMap, a novel method that aims to enhance the communication efficiency of FL deployments by collaboratively learning an increasingly sparse global model through iterative, unstructured pruning. Importantly, FedMap trains a global model from scratch, unlike other methods reported in the literature, making it ideal for privacy-critical use cases such as in the medical and finance domains, where suitable pre-training data is often limited. FedMap adapts iterative magnitude-based pruning to the FL setting, ensuring all clients prune and refine the same subset of the global model parameters, therefore gradually reducing the global model size and communication overhead. The iterative nature of FedMap, forming subsequent models as subsets of predecessors, avoids parameter reactivation issues seen in prior work, resulting in stable performance. In this paper we provide an extensive evaluation of FedMap across diverse settings, datasets, model architectures, and hyperparameters, assessing performance in both IID and non-IID environments. Comparative analysis against the baseline approach demonstrates FedMap's ability to achieve more stable client model performance. For IID scenarios, FedMap achieves over $90$\% pruning without significant performance degradation. In non-IID settings, it achieves at least $~80$\% pruning while maintaining accuracy. FedMap offers a promising solution to alleviate communication bottlenecks in FL systems while retaining model accuracy.
Computing Within Limits: An Empirical Study of Energy Consumption in ML Training and Inference
Jun 20, 2024
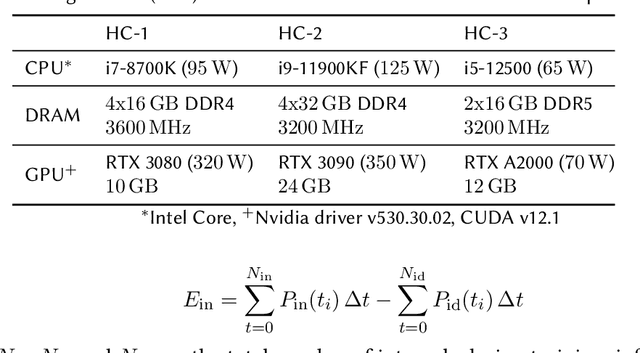
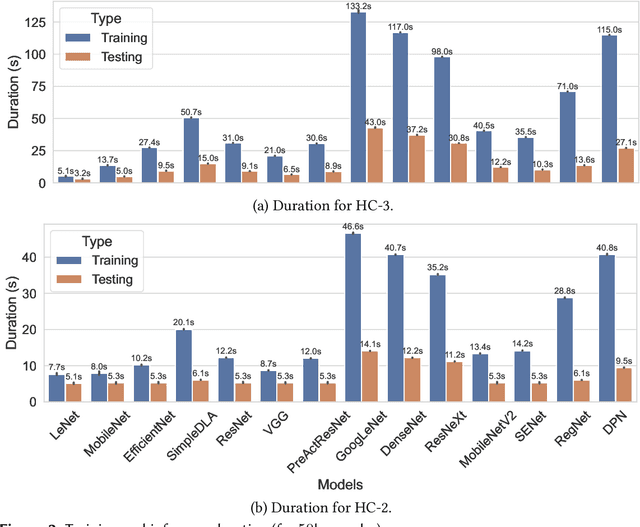
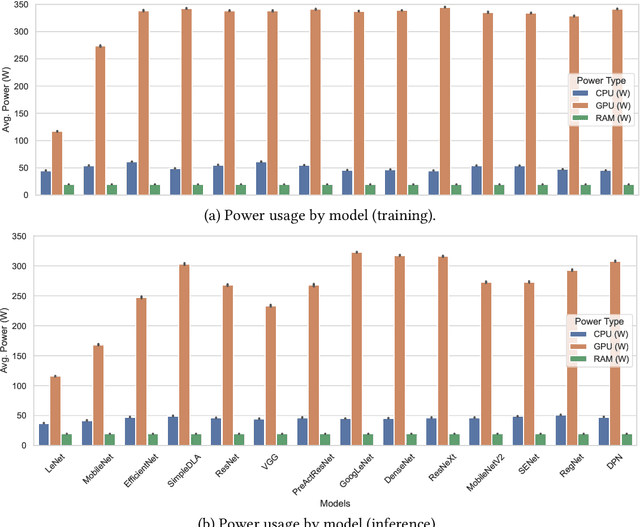
Abstract:Machine learning (ML) has seen tremendous advancements, but its environmental footprint remains a concern. Acknowledging the growing environmental impact of ML this paper investigates Green ML, examining various model architectures and hyperparameters in both training and inference phases to identify energy-efficient practices. Our study leverages software-based power measurements for ease of replication across diverse configurations, models and datasets. In this paper, we examine multiple models and hardware configurations to identify correlations across the various measurements and metrics and key contributors to energy reduction. Our analysis offers practical guidelines for constructing sustainable ML operations, emphasising energy consumption and carbon footprint reductions while maintaining performance. As identified, short-lived profiling can quantify the long-term expected energy consumption. Moreover, model parameters can also be used to accurately estimate the expected total energy without the need for extensive experimentation.
Multi-stage Attack Detection and Prediction Using Graph Neural Networks: An IoT Feasibility Study
Apr 28, 2024Abstract:With the ever-increasing reliance on digital networks for various aspects of modern life, ensuring their security has become a critical challenge. Intrusion Detection Systems play a crucial role in ensuring network security, actively identifying and mitigating malicious behaviours. However, the relentless advancement of cyber-threats has rendered traditional/classical approaches insufficient in addressing the sophistication and complexity of attacks. This paper proposes a novel 3-stage intrusion detection system inspired by a simplified version of the Lockheed Martin cyber kill chain to detect advanced multi-step attacks. The proposed approach consists of three models, each responsible for detecting a group of attacks with common characteristics. The detection outcome of the first two stages is used to conduct a feasibility study on the possibility of predicting attacks in the third stage. Using the ToN IoT dataset, we achieved an average of 94% F1-Score among different stages, outperforming the benchmark approaches based on Random-forest model. Finally, we comment on the feasibility of this approach to be integrated in a real-world system and propose various possible future work.
Mitigating System Bias in Resource Constrained Asynchronous Federated Learning Systems
Feb 01, 2024



Abstract:Federated learning (FL) systems face performance challenges in dealing with heterogeneous devices and non-identically distributed data across clients. We propose a dynamic global model aggregation method within Asynchronous Federated Learning (AFL) deployments to address these issues. Our aggregation method scores and adjusts the weighting of client model updates based on their upload frequency to accommodate differences in device capabilities. Additionally, we also immediately provide an updated global model to clients after they upload their local models to reduce idle time and improve training efficiency. We evaluate our approach within an AFL deployment consisting of 10 simulated clients with heterogeneous compute constraints and non-IID data. The simulation results, using the FashionMNIST dataset, demonstrate over 10% and 19% improvement in global model accuracy compared to state-of-the-art methods PAPAYA and FedAsync, respectively. Our dynamic aggregation method allows reliable global model training despite limiting client resources and statistical data heterogeneity. This improves robustness and scalability for real-world FL deployments.
Past, Present, Future: A Comprehensive Exploration of AI Use Cases in the UMBRELLA IoT Testbed
Feb 01, 2024



Abstract:UMBRELLA is a large-scale, open-access Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem incorporating over 200 multi-sensor multi-wireless nodes, 20 collaborative robots, and edge-intelligence-enabled devices. This paper provides a guide to the implemented and prospective artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities of UMBRELLA in real-world IoT systems. Four existing UMBRELLA applications are presented in detail: 1) An automated streetlight monitoring for detecting issues and triggering maintenance alerts; 2) A Digital twin of building environments providing enhanced air quality sensing with reduced cost; 3) A large-scale Federated Learning framework for reducing communication overhead; and 4) An intrusion detection for containerised applications identifying malicious activities. Additionally, the potential of UMBRELLA is outlined for future smart city and multi-robot crowdsensing applications enhanced by semantic communications and multi-agent planning. Finally, to realise the above use-cases we discuss the need for a tailored MLOps platform to automate UMBRELLA model pipelines and establish trust.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge