Minjae Kim
Adaptive Information Routing for Multimodal Time Series Forecasting
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Time series forecasting is a critical task for artificial intelligence with numerous real-world applications. Traditional approaches primarily rely on historical time series data to predict the future values. However, in practical scenarios, this is often insufficient for accurate predictions due to the limited information available. To address this challenge, multimodal time series forecasting methods which incorporate additional data modalities, mainly text data, alongside time series data have been explored. In this work, we introduce the Adaptive Information Routing (AIR) framework, a novel approach for multimodal time series forecasting. Unlike existing methods that treat text data on par with time series data as interchangeable auxiliary features for forecasting, AIR leverages text information to dynamically guide the time series model by controlling how and to what extent multivariate time series information should be combined. We also present a text-refinement pipeline that employs a large language model to convert raw text data into a form suitable for multimodal forecasting, and we introduce a benchmark that facilitates multimodal forecasting experiments based on this pipeline. Experiment results with the real world market data such as crude oil price and exchange rates demonstrate that AIR effectively modulates the behavior of the time series model using textual inputs, significantly enhancing forecasting accuracy in various time series forecasting tasks.
Motif-2-12.7B-Reasoning: A Practitioner's Guide to RL Training Recipes
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:We introduce Motif-2-12.7B-Reasoning, a 12.7B parameter language model designed to bridge the gap between open-weight systems and proprietary frontier models in complex reasoning and long-context understanding. Addressing the common challenges of model collapse and training instability in reasoning adaptation, we propose a comprehensive, reproducible training recipe spanning system, data, and algorithmic optimizations. Our approach combines memory-efficient infrastructure for 64K-token contexts using hybrid parallelism and kernel-level optimizations with a two-stage Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) curriculum that mitigates distribution mismatch through verified, aligned synthetic data. Furthermore, we detail a robust Reinforcement Learning Fine-Tuning (RLFT) pipeline that stabilizes training via difficulty-aware data filtering and mixed-policy trajectory reuse. Empirical results demonstrate that Motif-2-12.7B-Reasoning achieves performance comparable to models with significantly larger parameter counts across mathematics, coding, and agentic benchmarks, offering the community a competitive open model and a practical blueprint for scaling reasoning capabilities under realistic compute constraints.
Motif 2 12.7B technical report
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:We introduce Motif-2-12.7B, a new open-weight foundation model that pushes the efficiency frontier of large language models by combining architectural innovation with system-level optimization. Designed for scalable language understanding and robust instruction generalization under constrained compute budgets, Motif-2-12.7B builds upon Motif-2.6B with the integration of Grouped Differential Attention (GDA), which improves representational efficiency by disentangling signal and noise-control attention pathways. The model is pre-trained on 5.5 trillion tokens spanning diverse linguistic, mathematical, scientific, and programming domains using a curriculum-driven data scheduler that gradually changes the data composition ratio. The training system leverages the MuonClip optimizer alongside custom high-performance kernels, including fused PolyNorm activations and the Parallel Muon algorithm, yielding significant throughput and memory efficiency gains in large-scale distributed environments. Post-training employs a three-stage supervised fine-tuning pipeline that successively enhances general instruction adherence, compositional understanding, and linguistic precision. Motif-2-12.7B demonstrates competitive performance across diverse benchmarks, showing that thoughtful architectural scaling and optimized training design can rival the capabilities of much larger models.
THEME : Enhancing Thematic Investing with Semantic Stock Representations and Temporal Dynamics
Aug 23, 2025Abstract:Thematic investing aims to construct portfolios aligned with structural trends, yet selecting relevant stocks remains challenging due to overlapping sector boundaries and evolving market dynamics. To address this challenge, we construct the Thematic Representation Set (TRS), an extended dataset that begins with real-world thematic ETFs and expands upon them by incorporating industry classifications and financial news to overcome their coverage limitations. The final dataset contains both the explicit mapping of themes to their constituent stocks and the rich textual profiles for each. Building on this dataset, we introduce \textsc{THEME}, a hierarchical contrastive learning framework. By representing the textual profiles of themes and stocks as embeddings, \textsc{THEME} first leverages their hierarchical relationship to achieve semantic alignment. Subsequently, it refines these semantic embeddings through a temporal refinement stage that incorporates individual stock returns. The final stock representations are designed for effective retrieval of thematically aligned assets with strong return potential. Empirical results show that \textsc{THEME} outperforms strong baselines across multiple retrieval metrics and significantly improves performance in portfolio construction. By jointly modeling thematic relationships from text and market dynamics from returns, \textsc{THEME} provides a scalable and adaptive solution for navigating complex investment themes.
Fine-Grained Perturbation Guidance via Attention Head Selection
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Recent guidance methods in diffusion models steer reverse sampling by perturbing the model to construct an implicit weak model and guide generation away from it. Among these approaches, attention perturbation has demonstrated strong empirical performance in unconditional scenarios where classifier-free guidance is not applicable. However, existing attention perturbation methods lack principled approaches for determining where perturbations should be applied, particularly in Diffusion Transformer (DiT) architectures where quality-relevant computations are distributed across layers. In this paper, we investigate the granularity of attention perturbations, ranging from the layer level down to individual attention heads, and discover that specific heads govern distinct visual concepts such as structure, style, and texture quality. Building on this insight, we propose "HeadHunter", a systematic framework for iteratively selecting attention heads that align with user-centric objectives, enabling fine-grained control over generation quality and visual attributes. In addition, we introduce SoftPAG, which linearly interpolates each selected head's attention map toward an identity matrix, providing a continuous knob to tune perturbation strength and suppress artifacts. Our approach not only mitigates the oversmoothing issues of existing layer-level perturbation but also enables targeted manipulation of specific visual styles through compositional head selection. We validate our method on modern large-scale DiT-based text-to-image models including Stable Diffusion 3 and FLUX.1, demonstrating superior performance in both general quality enhancement and style-specific guidance. Our work provides the first head-level analysis of attention perturbation in diffusion models, uncovering interpretable specialization within attention layers and enabling practical design of effective perturbation strategies.
Structuring the Unstructured: A Multi-Agent System for Extracting and Querying Financial KPIs and Guidance
May 25, 2025Abstract:Extracting structured and quantitative insights from unstructured financial filings is essential in investment research, yet remains time-consuming and resource-intensive. Conventional approaches in practice rely heavily on labor-intensive manual processes, limiting scalability and delaying the research workflow. In this paper, we propose an efficient and scalable method for accurately extracting quantitative insights from unstructured financial documents, leveraging a multi-agent system composed of large language models. Our proposed multi-agent system consists of two specialized agents: the \emph{Extraction Agent} and the \emph{Text-to-SQL Agent}. The \textit{Extraction Agent} automatically identifies key performance indicators from unstructured financial text, standardizes their formats, and verifies their accuracy. On the other hand, the \textit{Text-to-SQL Agent} generates executable SQL statements from natural language queries, allowing users to access structured data accurately without requiring familiarity with the database schema. Through experiments, we demonstrate that our proposed system effectively transforms unstructured text into structured data accurately and enables precise retrieval of key information. First, we demonstrate that our system achieves approximately 95\% accuracy in transforming financial filings into structured data, matching the performance level typically attained by human annotators. Second, in a human evaluation of the retrieval task -- where natural language queries are used to search information from structured data -- 91\% of the responses were rated as correct by human evaluators. In both evaluations, our system generalizes well across financial document types, consistently delivering reliable performance.
HARDMath2: A Benchmark for Applied Mathematics Built by Students as Part of a Graduate Class
May 17, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have shown remarkable progress in mathematical problem-solving, but evaluation has largely focused on problems that have exact analytical solutions or involve formal proofs, often overlooking approximation-based problems ubiquitous in applied science and engineering. To fill this gap, we build on prior work and present HARDMath2, a dataset of 211 original problems covering the core topics in an introductory graduate applied math class, including boundary-layer analysis, WKB methods, asymptotic solutions of nonlinear partial differential equations, and the asymptotics of oscillatory integrals. This dataset was designed and verified by the students and instructors of a core graduate applied mathematics course at Harvard. We build the dataset through a novel collaborative environment that challenges students to write and refine difficult problems consistent with the class syllabus, peer-validate solutions, test different models, and automatically check LLM-generated solutions against their own answers and numerical ground truths. Evaluation results show that leading frontier models still struggle with many of the problems in the dataset, highlighting a gap in the mathematical reasoning skills of current LLMs. Importantly, students identified strategies to create increasingly difficult problems by interacting with the models and exploiting common failure modes. This back-and-forth with the models not only resulted in a richer and more challenging benchmark but also led to qualitative improvements in the students' understanding of the course material, which is increasingly important as we enter an age where state-of-the-art language models can solve many challenging problems across a wide domain of fields.
A Noise is Worth Diffusion Guidance
Dec 05, 2024
Abstract:Diffusion models excel in generating high-quality images. However, current diffusion models struggle to produce reliable images without guidance methods, such as classifier-free guidance (CFG). Are guidance methods truly necessary? Observing that noise obtained via diffusion inversion can reconstruct high-quality images without guidance, we focus on the initial noise of the denoising pipeline. By mapping Gaussian noise to `guidance-free noise', we uncover that small low-magnitude low-frequency components significantly enhance the denoising process, removing the need for guidance and thus improving both inference throughput and memory. Expanding on this, we propose \ours, a novel method that replaces guidance methods with a single refinement of the initial noise. This refined noise enables high-quality image generation without guidance, within the same diffusion pipeline. Our noise-refining model leverages efficient noise-space learning, achieving rapid convergence and strong performance with just 50K text-image pairs. We validate its effectiveness across diverse metrics and analyze how refined noise can eliminate the need for guidance. See our project page: https://cvlab-kaist.github.io/NoiseRefine/.
HyperCLOVA X Technical Report
Apr 13, 2024Abstract:We introduce HyperCLOVA X, a family of large language models (LLMs) tailored to the Korean language and culture, along with competitive capabilities in English, math, and coding. HyperCLOVA X was trained on a balanced mix of Korean, English, and code data, followed by instruction-tuning with high-quality human-annotated datasets while abiding by strict safety guidelines reflecting our commitment to responsible AI. The model is evaluated across various benchmarks, including comprehensive reasoning, knowledge, commonsense, factuality, coding, math, chatting, instruction-following, and harmlessness, in both Korean and English. HyperCLOVA X exhibits strong reasoning capabilities in Korean backed by a deep understanding of the language and cultural nuances. Further analysis of the inherent bilingual nature and its extension to multilingualism highlights the model's cross-lingual proficiency and strong generalization ability to untargeted languages, including machine translation between several language pairs and cross-lingual inference tasks. We believe that HyperCLOVA X can provide helpful guidance for regions or countries in developing their sovereign LLMs.
Implementation Of MNIST Dataset Learning Using Analog Circuit
Aug 08, 2023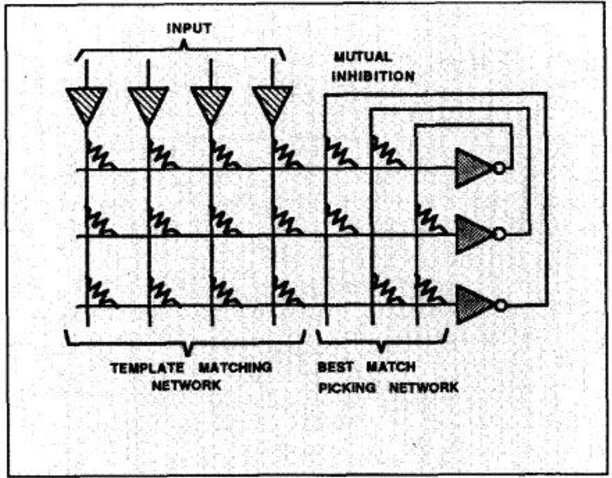

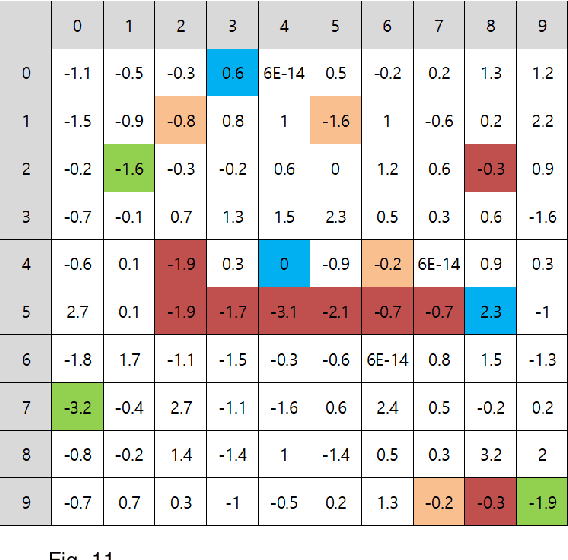
Abstract:There have been many attempts to implement neural networks in the analog circuit. Most of them had a lot of input terms, and most studies implemented neural networks in the analog circuit through a circuit simulation program called Spice to avoid the need to design chips at a high cost and implement circuits directly to input them. In this study, we will implement neural networks using a capacitor and diode and use microcontrollers (Arduino Mega 2560 R3 boards) to drive real-world models and analyze the results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge