Mareike Thies
Pattern Recognition Lab, FAU Erlangen-Nürnberg, Germany
CyclePose -- Leveraging Cycle-Consistency for Annotation-Free Nuclei Segmentation in Fluorescence Microscopy
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:In recent years, numerous neural network architectures specifically designed for the instance segmentation of nuclei in microscopic images have been released. These models embed nuclei-specific priors to outperform generic architectures like U-Nets; however, they require large annotated datasets, which are often not available. Generative models (GANs, diffusion models) have been used to compensate for this by synthesizing training data. These two-stage approaches are computationally expensive, as first a generative model and then a segmentation model has to be trained. We propose CyclePose, a hybrid framework integrating synthetic data generation and segmentation training. CyclePose builds on a CycleGAN architecture, which allows unpaired translation between microscopy images and segmentation masks. We embed a segmentation model into CycleGAN and leverage a cycle consistency loss for self-supervision. Without annotated data, CyclePose outperforms other weakly or unsupervised methods on two public datasets. Code is available at https://github.com/jonasutz/CyclePose
DiffRenderGAN: Addressing Training Data Scarcity in Deep Segmentation Networks for Quantitative Nanomaterial Analysis through Differentiable Rendering and Generative Modelling
Feb 13, 2025Abstract:Nanomaterials exhibit distinctive properties governed by parameters such as size, shape, and surface characteristics, which critically influence their applications and interactions across technological, biological, and environmental contexts. Accurate quantification and understanding of these materials are essential for advancing research and innovation. In this regard, deep learning segmentation networks have emerged as powerful tools that enable automated insights and replace subjective methods with precise quantitative analysis. However, their efficacy depends on representative annotated datasets, which are challenging to obtain due to the costly imaging of nanoparticles and the labor-intensive nature of manual annotations. To overcome these limitations, we introduce DiffRenderGAN, a novel generative model designed to produce annotated synthetic data. By integrating a differentiable renderer into a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) framework, DiffRenderGAN optimizes textural rendering parameters to generate realistic, annotated nanoparticle images from non-annotated real microscopy images. This approach reduces the need for manual intervention and enhances segmentation performance compared to existing synthetic data methods by generating diverse and realistic data. Tested on multiple ion and electron microscopy cases, including titanium dioxide (TiO$_2$), silicon dioxide (SiO$_2$)), and silver nanowires (AgNW), DiffRenderGAN bridges the gap between synthetic and real data, advancing the quantification and understanding of complex nanomaterial systems.
Compressibility Analysis for the differentiable shift-variant Filtered Backprojection Model
Jan 20, 2025



Abstract:The differentiable shift-variant filtered backprojection (FBP) model enables the reconstruction of cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) data for any non-circular trajectories. This method employs deep learning technique to estimate the redundancy weights required for reconstruction, given knowledge of the specific trajectory at optimization time. However, computing the redundancy weight for each projection remains computationally intensive. This paper presents a novel approach to compress and optimize the differentiable shift-variant FBP model based on Principal Component Analysis (PCA). We apply PCA to the redundancy weights learned from sinusoidal trajectory projection data, revealing significant parameter redundancy in the original model. By integrating PCA directly into the differentiable shift-variant FBP reconstruction pipeline, we develop a method that decomposes the redundancy weight layer parameters into a trainable eigenvector matrix, compressed weights, and a mean vector. This innovative technique achieves a remarkable 97.25% reduction in trainable parameters without compromising reconstruction accuracy. As a result, our algorithm significantly decreases the complexity of the differentiable shift-variant FBP model and greatly improves training speed. These improvements make the model substantially more practical for real-world applications.
DRACO: Differentiable Reconstruction for Arbitrary CBCT Orbits
Oct 18, 2024
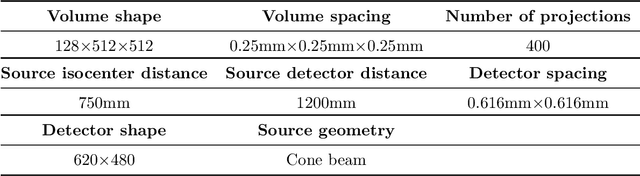
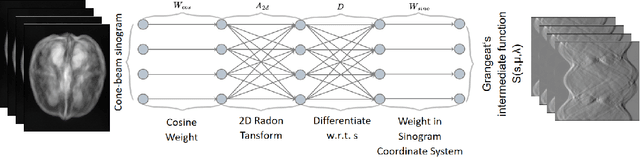
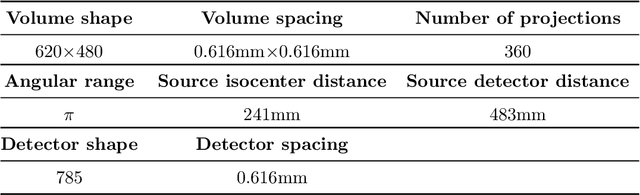
Abstract:This paper introduces a novel method for reconstructing cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) images for arbitrary orbits using a differentiable shift-variant filtered backprojection (FBP) neural network. Traditional CBCT reconstruction methods for arbitrary orbits, like iterative reconstruction algorithms, are computationally expensive and memory-intensive. The proposed method addresses these challenges by employing a shift-variant FBP algorithm optimized for arbitrary trajectories through a deep learning approach that adapts to a specific orbit geometry. This approach overcomes the limitations of existing techniques by integrating known operators into the learning model, minimizing the number of parameters, and improving the interpretability of the model. The proposed method is a significant advancement in interventional medical imaging, particularly for robotic C-arm CT systems, enabling faster and more accurate CBCT reconstructions with customized orbits. Especially this method can also be used for the analytical reconstruction of non-continuous orbits like circular plus arc. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method significantly accelerates the reconstruction process compared to conventional iterative algorithms. It achieves comparable or superior image quality, as evidenced by metrics such as the mean squared error (MSE), the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR), and the structural similarity index measure (SSIM). The validation experiments show that the method can handle data from different trajectories, demonstrating its flexibility and robustness across different scan geometries. Our method demonstrates a significant improvement, particularly for the sinusoidal trajectory, achieving a 38.6% reduction in MSE, a 7.7% increase in PSNR, and a 5.0% improvement in SSIM. Furthermore, the computation time for reconstruction was reduced by more than 97%.
On the Influence of Smoothness Constraints in Computed Tomography Motion Compensation
May 29, 2024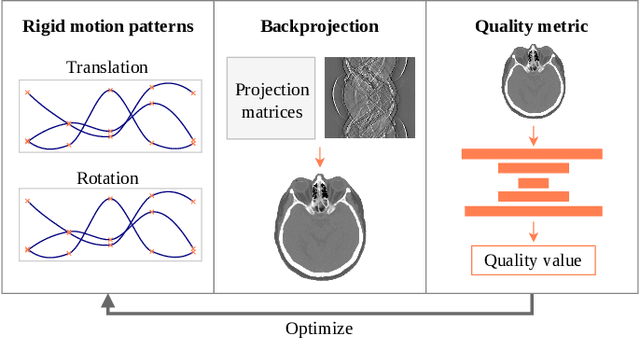
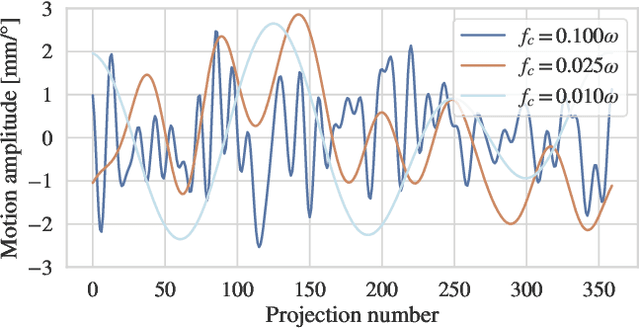
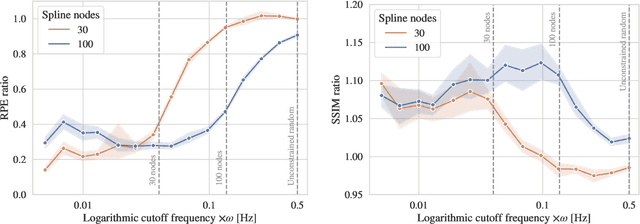
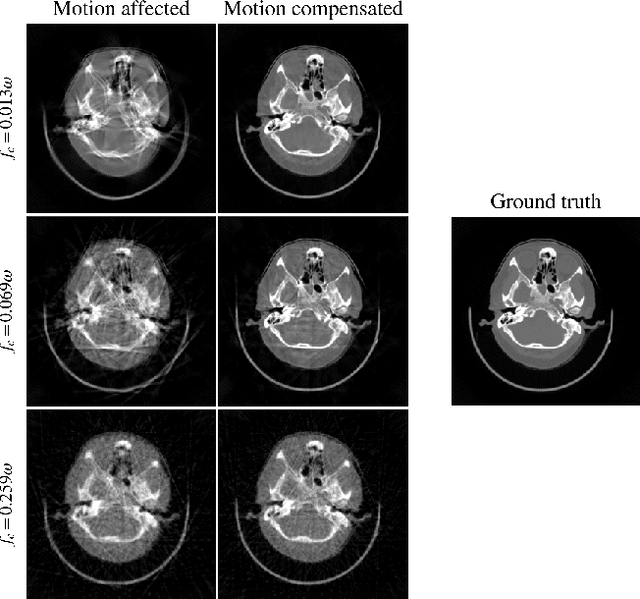
Abstract:Computed tomography (CT) relies on precise patient immobilization during image acquisition. Nevertheless, motion artifacts in the reconstructed images can persist. Motion compensation methods aim to correct such artifacts post-acquisition, often incorporating temporal smoothness constraints on the estimated motion patterns. This study analyzes the influence of a spline-based motion model within an existing rigid motion compensation algorithm for cone-beam CT on the recoverable motion frequencies. Results demonstrate that the choice of motion model crucially influences recoverable frequencies. The optimization-based motion compensation algorithm is able to accurately fit the spline nodes for frequencies almost up to the node-dependent theoretical limit according to the Nyquist-Shannon theorem. Notably, a higher node count does not compromise reconstruction performance for slow motion patterns, but can extend the range of recoverable high frequencies for the investigated algorithm. Eventually, the optimal motion model is dependent on the imaged anatomy, clinical use case, and scanning protocol and should be tailored carefully to the expected motion frequency spectrum to ensure accurate motion compensation.
Reference-Free Multi-Modality Volume Registration of X-Ray Microscopy and Light-Sheet Fluorescence Microscopy
Apr 23, 2024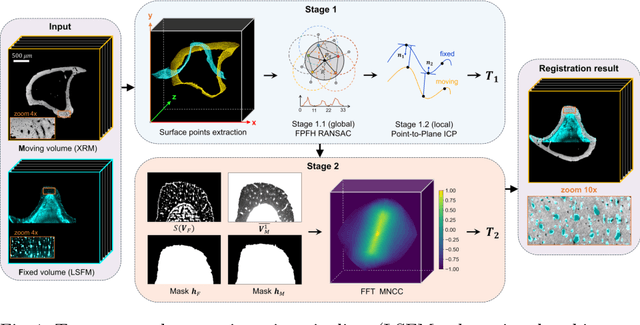
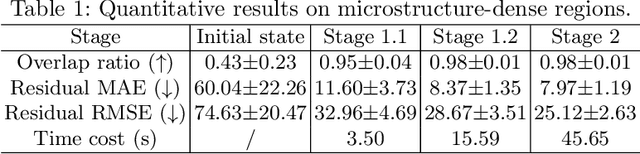
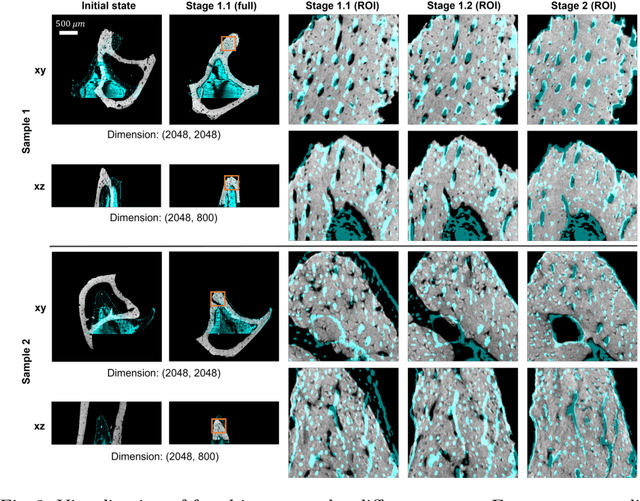
Abstract:Recently, X-ray microscopy (XRM) and light-sheet fluorescence microscopy (LSFM) have emerged as two pivotal imaging tools in preclinical research on bone remodeling diseases, offering micrometer-level resolution. Integrating these complementary modalities provides a holistic view of bone microstructures, facilitating function-oriented volume analysis across different disease cycles. However, registering such independently acquired large-scale volumes is extremely challenging under real and reference-free scenarios. This paper presents a fast two-stage pipeline for volume registration of XRM and LSFM. The first stage extracts the surface features and employs two successive point cloud-based methods for coarse alignment. The second stage fine-tunes the initial alignment using a modified cross-correlation method, ensuring precise volumetric registration. Moreover, we propose residual similarity as a novel metric to assess the alignment of two complementary modalities. The results imply robust gradual improvement across the stages. In the end, all correlating microstructures, particularly lacunae in XRM and bone cells in LSFM, are precisely matched, enabling new insights into bone diseases like osteoporosis which are a substantial burden in aging societies.
Differentiable Score-Based Likelihoods: Learning CT Motion Compensation From Clean Images
Apr 23, 2024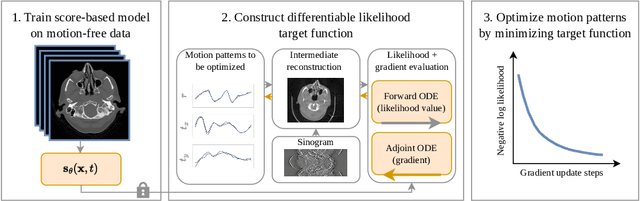
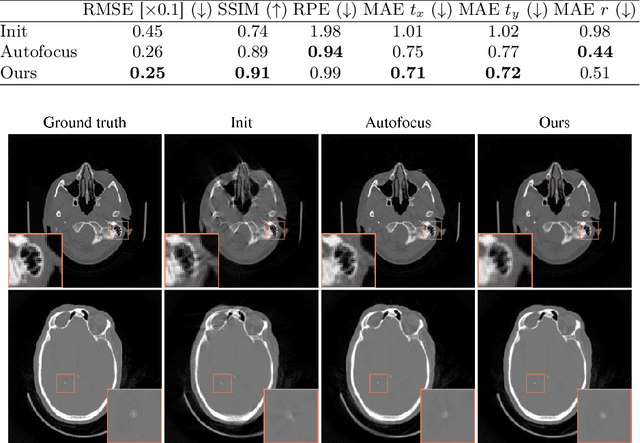
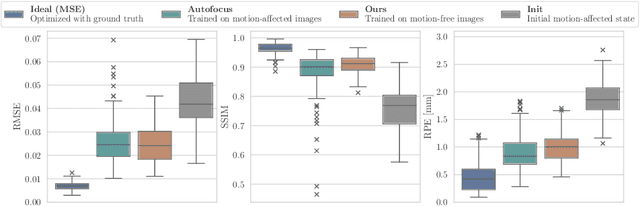
Abstract:Motion artifacts can compromise the diagnostic value of computed tomography (CT) images. Motion correction approaches require a per-scan estimation of patient-specific motion patterns. In this work, we train a score-based model to act as a probability density estimator for clean head CT images. Given the trained model, we quantify the deviation of a given motion-affected CT image from the ideal distribution through likelihood computation. We demonstrate that the likelihood can be utilized as a surrogate metric for motion artifact severity in the CT image facilitating the application of an iterative, gradient-based motion compensation algorithm. By optimizing the underlying motion parameters to maximize likelihood, our method effectively reduces motion artifacts, bringing the image closer to the distribution of motion-free scans. Our approach achieves comparable performance to state-of-the-art methods while eliminating the need for a representative data set of motion-affected samples. This is particularly advantageous in real-world applications, where patient motion patterns may exhibit unforeseen variability, ensuring robustness without implicit assumptions about recoverable motion types.
Segmentation-Guided Knee Radiograph Generation using Conditional Diffusion Models
Apr 04, 2024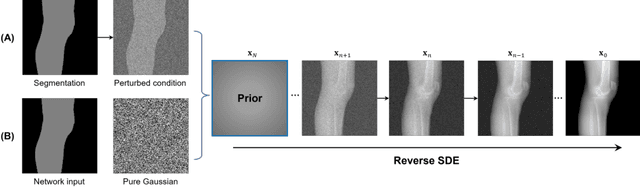
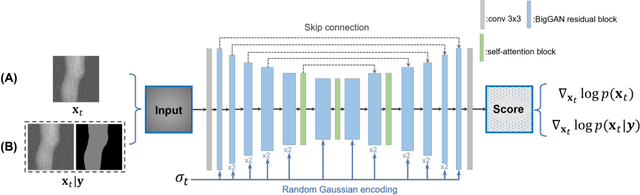
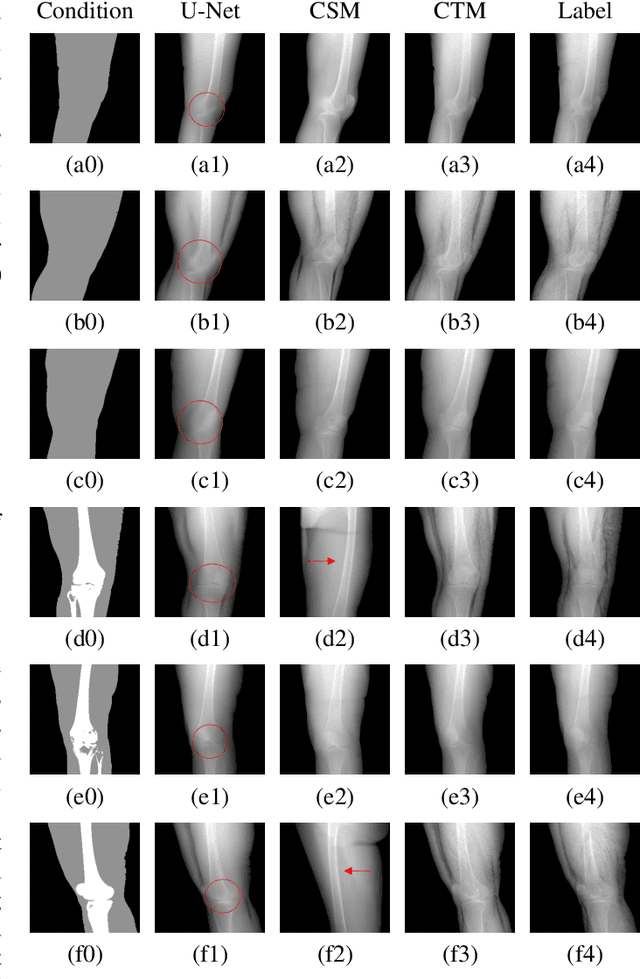
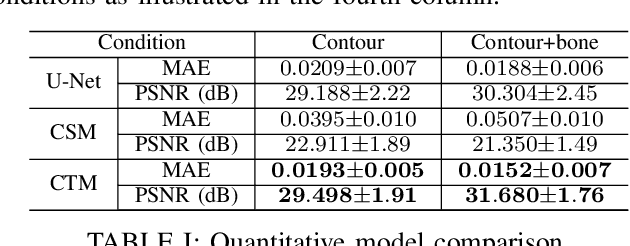
Abstract:Deep learning-based medical image processing algorithms require representative data during development. In particular, surgical data might be difficult to obtain, and high-quality public datasets are limited. To overcome this limitation and augment datasets, a widely adopted solution is the generation of synthetic images. In this work, we employ conditional diffusion models to generate knee radiographs from contour and bone segmentations. Remarkably, two distinct strategies are presented by incorporating the segmentation as a condition into the sampling and training process, namely, conditional sampling and conditional training. The results demonstrate that both methods can generate realistic images while adhering to the conditioning segmentation. The conditional training method outperforms the conditional sampling method and the conventional U-Net.
EAGLE: An Edge-Aware Gradient Localization Enhanced Loss for CT Image Reconstruction
Mar 15, 2024Abstract:Computed Tomography (CT) image reconstruction is crucial for accurate diagnosis and deep learning approaches have demonstrated significant potential in improving reconstruction quality. However, the choice of loss function profoundly affects the reconstructed images. Traditional mean squared error loss often produces blurry images lacking fine details, while alternatives designed to improve may introduce structural artifacts or other undesirable effects. To address these limitations, we propose Eagle-Loss, a novel loss function designed to enhance the visual quality of CT image reconstructions. Eagle-Loss applies spectral analysis of localized features within gradient changes to enhance sharpness and well-defined edges. We evaluated Eagle-Loss on two public datasets across low-dose CT reconstruction and CT field-of-view extension tasks. Our results show that Eagle-Loss consistently improves the visual quality of reconstructed images, surpassing state-of-the-art methods across various network architectures. Code and data are available at \url{https://github.com/sypsyp97/Eagle_Loss}.
Physics-Informed Learning for Time-Resolved Angiographic Contrast Agent Concentration Reconstruction
Mar 04, 2024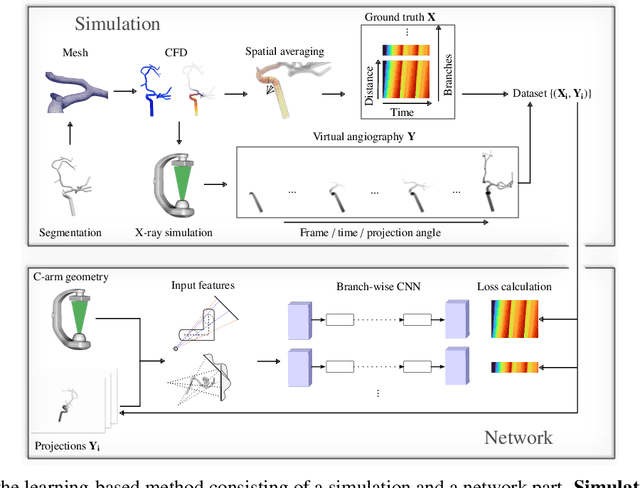
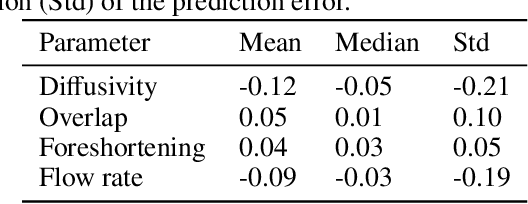
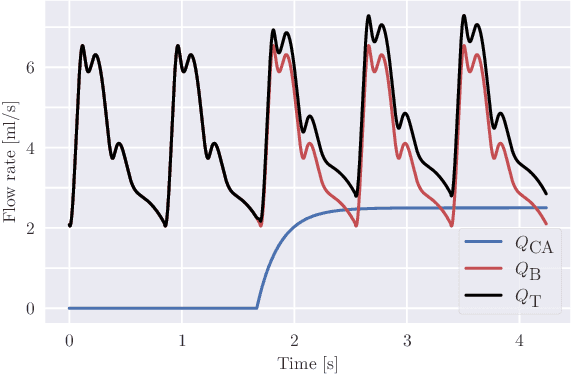
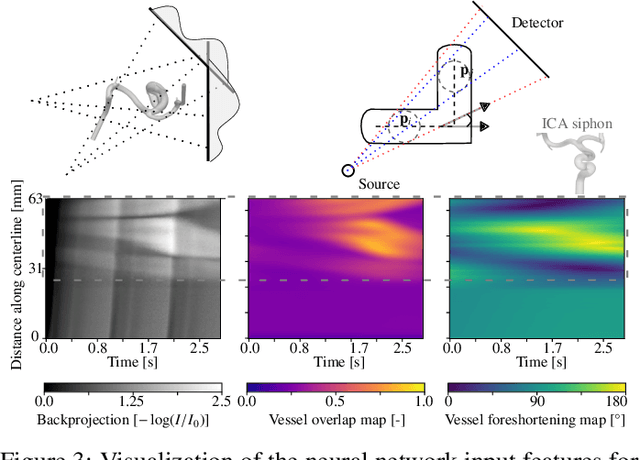
Abstract:Three-dimensional Digital Subtraction Angiography (3D-DSA) is a well-established X-ray-based technique for visualizing vascular anatomy. Recently, four-dimensional DSA (4D-DSA) reconstruction algorithms have been developed to enable the visualization of volumetric contrast flow dynamics through time-series of volumes. . This reconstruction problem is ill-posed mainly due to vessel overlap in the projection direction and geometric vessel foreshortening, which leads to information loss in the recorded projection images. However, knowledge about the underlying fluid dynamics can be leveraged to constrain the solution space. In our work, we implicitly include this information in a neural network-based model that is trained on a dataset of image-based blood flow simulations. The model predicts the spatially averaged contrast agent concentration for each centerline point of the vasculature over time, lowering the overall computational demand. The trained network enables the reconstruction of relative contrast agent concentrations with a mean absolute error of 0.02 $\pm$ 0.02 and a mean absolute percentage error of 5.31 % $\pm$ 9.25 %. Moreover, the network is robust to varying degrees of vessel overlap and vessel foreshortening. Our approach demonstrates the potential of the integration of machine learning and blood flow simulations in time-resolved angiographic flow reconstruction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge