Mathis Hoffmann
DiffRenderGAN: Addressing Training Data Scarcity in Deep Segmentation Networks for Quantitative Nanomaterial Analysis through Differentiable Rendering and Generative Modelling
Feb 13, 2025Abstract:Nanomaterials exhibit distinctive properties governed by parameters such as size, shape, and surface characteristics, which critically influence their applications and interactions across technological, biological, and environmental contexts. Accurate quantification and understanding of these materials are essential for advancing research and innovation. In this regard, deep learning segmentation networks have emerged as powerful tools that enable automated insights and replace subjective methods with precise quantitative analysis. However, their efficacy depends on representative annotated datasets, which are challenging to obtain due to the costly imaging of nanoparticles and the labor-intensive nature of manual annotations. To overcome these limitations, we introduce DiffRenderGAN, a novel generative model designed to produce annotated synthetic data. By integrating a differentiable renderer into a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) framework, DiffRenderGAN optimizes textural rendering parameters to generate realistic, annotated nanoparticle images from non-annotated real microscopy images. This approach reduces the need for manual intervention and enhances segmentation performance compared to existing synthetic data methods by generating diverse and realistic data. Tested on multiple ion and electron microscopy cases, including titanium dioxide (TiO$_2$), silicon dioxide (SiO$_2$)), and silver nanowires (AgNW), DiffRenderGAN bridges the gap between synthetic and real data, advancing the quantification and understanding of complex nanomaterial systems.
Anomaly Detection in IR Images of PV Modules using Supervised Contrastive Learning
Dec 06, 2021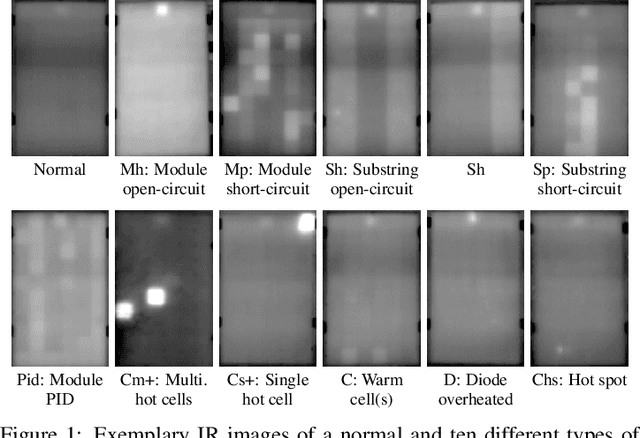
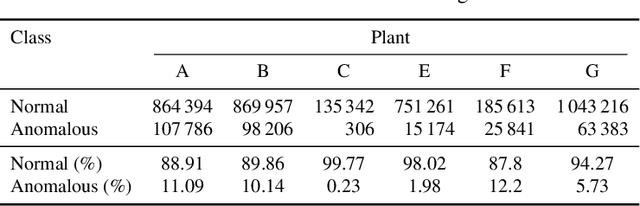

Abstract:Increasing deployment of photovoltaic (PV) plants requires methods for automatic detection of faulty PV modules in modalities, such as infrared (IR) images. Recently, deep learning has become popular for this. However, related works typically sample train and test data from the same distribution ignoring the presence of domain shift between data of different PV plants. Instead, we frame fault detection as more realistic unsupervised domain adaptation problem where we train on labelled data of one source PV plant and make predictions on another target plant. We train a ResNet-34 convolutional neural network with a supervised contrastive loss, on top of which we employ a k-nearest neighbor classifier to detect anomalies. Our method achieves a satisfactory area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) of 73.3 % to 96.6 % on nine combinations of four source and target datasets with 2.92 million IR images of which 8.5 % are anomalous. It even outperforms a binary cross-entropy classifier in some cases. With a fixed decision threshold this results in 79.4 % and 77.1 % correctly classified normal and anomalous images, respectively. Most misclassified anomalies are of low severity, such as hot diodes and small hot spots. Our method is insensitive to hyperparameter settings, converges quickly and reliably detects unknown types of anomalies making it well suited for practice. Possible uses are in automatic PV plant inspection systems or to streamline manual labelling of IR datasets by filtering out normal images. Furthermore, our work serves the community with a more realistic view on PV module fault detection using unsupervised domain adaptation to develop more performant methods with favorable generalization capabilities.
Module-Power Prediction from PL Measurements using Deep Learning
Aug 31, 2021
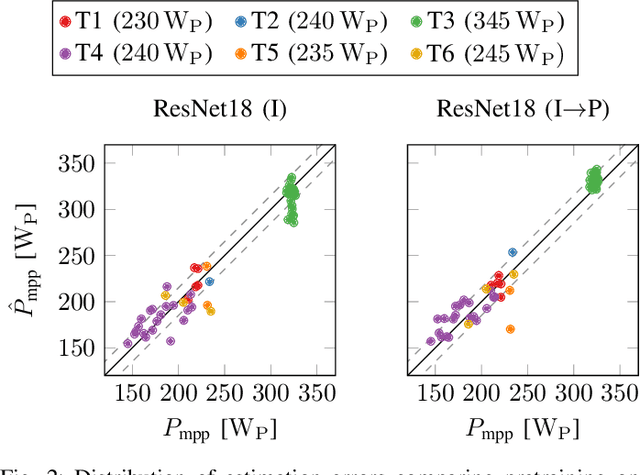
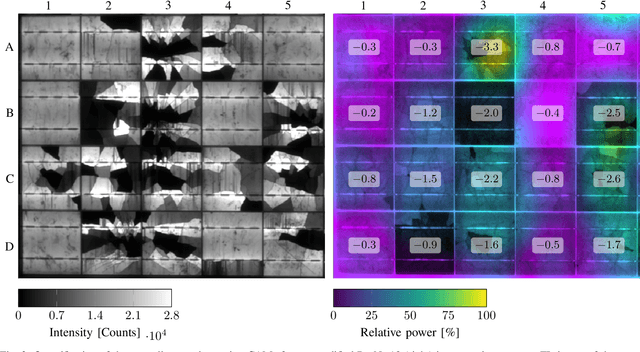
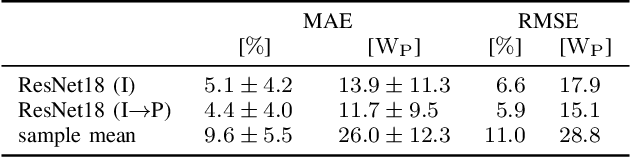
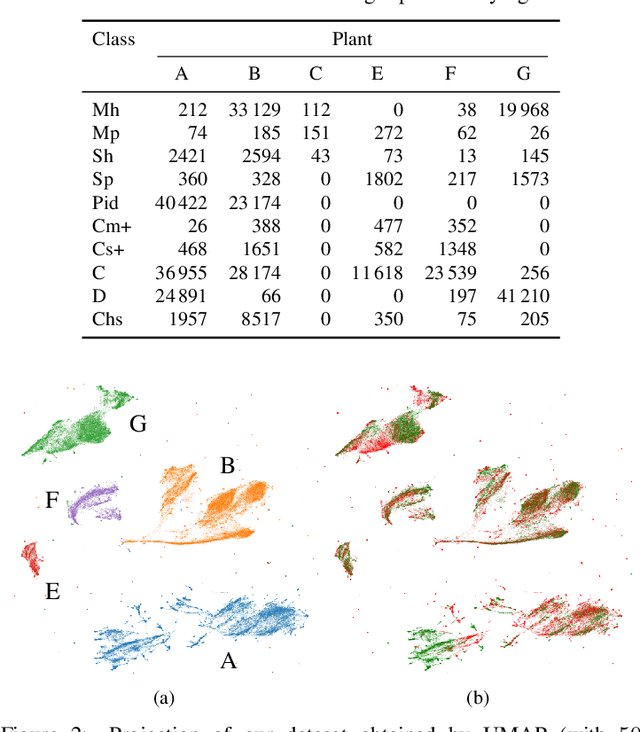
Abstract:The individual causes for power loss of photovoltaic modules are investigated for quite some time. Recently, it has been shown that the power loss of a module is, for example, related to the fraction of inactive areas. While these areas can be easily identified from electroluminescense (EL) images, this is much harder for photoluminescence (PL) images. With this work, we close the gap between power regression from EL and PL images. We apply a deep convolutional neural network to predict the module power from PL images with a mean absolute error (MAE) of 4.4% or 11.7WP. Furthermore, we depict that regression maps computed from the embeddings of the trained network can be used to compute the localized power loss. Finally, we show that these regression maps can be used to identify inactive regions in PL images as well.
Joint Super-Resolution and Rectification for Solar Cell Inspection
Nov 10, 2020



Abstract:Visual inspection of solar modules is an important monitoring facility in photovoltaic power plants. Since a single measurement of fast CMOS sensors is limited in spatial resolution and often not sufficient to reliably detect small defects, we apply multi-frame super-resolution (MFSR) to a sequence of low resolution measurements. In addition, the rectification and removal of lens distortion simplifies subsequent analysis. Therefore, we propose to fuse this pre-processing with standard MFSR algorithms. This is advantageous, because we omit a separate processing step, the motion estimation becomes more stable and the spacing of high-resolution (HR) pixels on the rectified module image becomes uniform w.r.t. the module plane, regardless of perspective distortion. We present a comprehensive user study showing that MFSR is beneficial for defect recognition by human experts and that the proposed method performs better than the state of the art. Furthermore, we apply automated crack segmentation and show that the proposed method performs 3x better than bicubic upsampling and 2x better than the state of the art for automated inspection.
Deep Learning-based Pipeline for Module Power Prediction from EL Measurements
Sep 30, 2020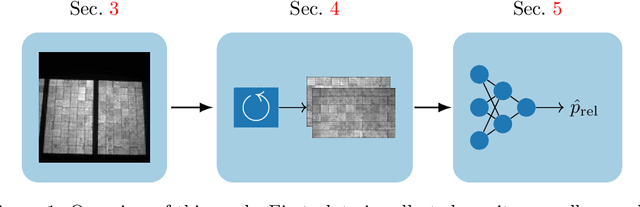

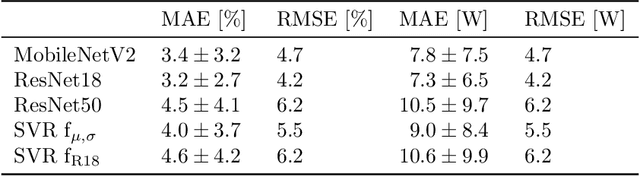
Abstract:Automated inspection plays an important role in monitoring large-scale photovoltaic power plants. Commonly, electroluminescense measurements are used to identify various types of defects on solar modules but have not been used to determine the power of a module. However, knowledge of the power at maximum power point is important as well, since drops in the power of a single module can affect the performance of an entire string. By now, this is commonly determined by measurements that require to discontact or even dismount the module, rendering a regular inspection of individual modules infeasible. In this work, we bridge the gap between electroluminescense measurements and the power determination of a module. We compile a large dataset of 719 electroluminescense measurementsof modules at various stages of degradation, especially cell cracks and fractures, and the corresponding power at maximum power point. Here,we focus on inactive regions and cracks as the predominant type of defect. We set up a baseline regression model to predict the power from electroluminescense measurements with a mean absolute error of 9.0+/-3.7W (4.0+/-8.4%). Then, we show that deep-learning can be used to train a model that performs significantly better (7.3+/-2.7W or 3.2+/-6.5%). With this work, we aim to open a new research topic. Therefore, we publicly release the dataset, the code and trained models to empower other researchers to compare against our results. Finally, we present a thorough evaluation of certain boundary conditions like the dataset size and an automated preprocessing pipeline for on-site measurements showing multiple modules at once.
Weakly Supervised Segmentation of Cracks on Solar Cells using Normalized Lp Norm
Jan 30, 2020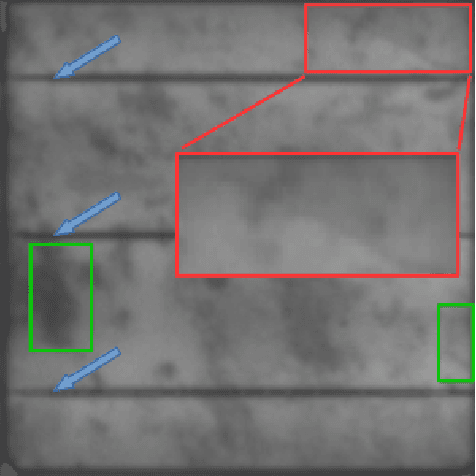
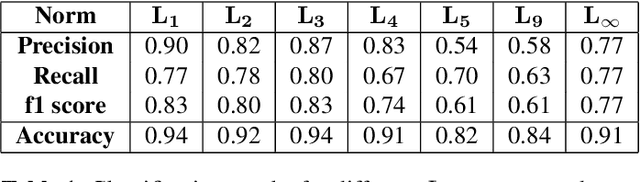
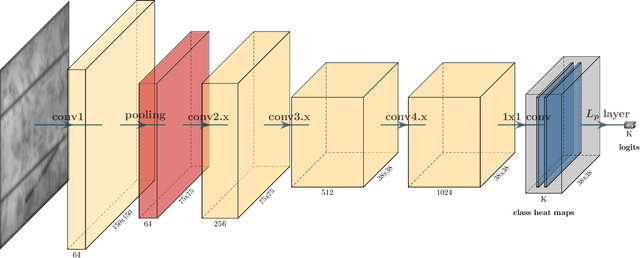
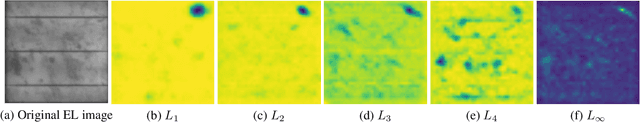
Abstract:Photovoltaic is one of the most important renewable energy sources for dealing with world-wide steadily increasing energy consumption. This raises the demand for fast and scalable automatic quality management during production and operation. However, the detection and segmentation of cracks on electroluminescence (EL) images of mono- or polycrystalline solar modules is a challenging task. In this work, we propose a weakly supervised learning strategy that only uses image-level annotations to obtain a method that is capable of segmenting cracks on EL images of solar cells. We use a modified ResNet-50 to derive a segmentation from network activation maps. We use defect classification as a surrogate task to train the network. To this end, we apply normalized Lp normalization to aggregate the activation maps into single scores for classification. In addition, we provide a study how different parameterizations of the normalized Lp layer affect the segmentation performance. This approach shows promising results for the given task. However, we think that the method has the potential to solve other weakly supervised segmentation problems as well.
Fast and robust detection of solar modules in electroluminescence images
Jul 19, 2019



Abstract:Fast, non-destructive and on-site quality control tools, mainly high sensitive imaging techniques, are important to assess the reliability of photovoltaic plants. To minimize the risk of further damages and electrical yield losses, electroluminescence (EL) imaging is used to detect local defects in an early stage, which might cause future electric losses. For an automated defect recognition on EL measurements, a robust detection and rectification of modules, as well as an optional segmentation into cells is required. This paper introduces a method to detect solar modules and crossing points between solar cells in EL images. We only require 1-D image statistics for the detection, resulting in an approach that is computationally efficient. In addition, the method is able to detect the modules under perspective distortion and in scenarios, where multiple modules are visible in the image. We compare our method to the state of the art and show that it is superior in presence of perspective distortion while the performance on images, where the module is roughly coplanar to the detector, is similar to the reference method. Finally, we show that we greatly improve in terms of computational time in comparison to the reference method.
Learning with Known Operators reduces Maximum Training Error Bounds
Jul 03, 2019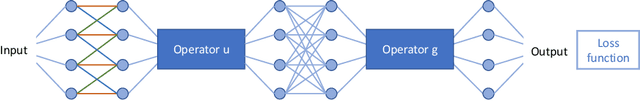
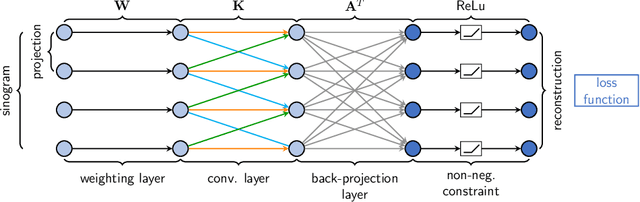
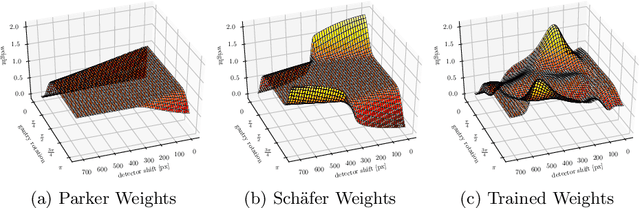
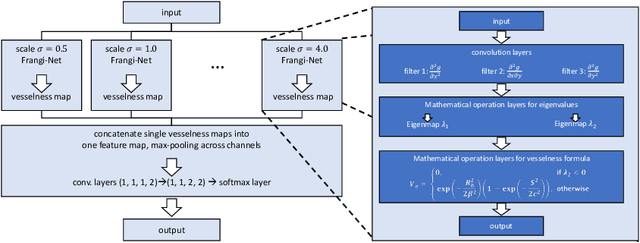
Abstract:We describe an approach for incorporating prior knowledge into machine learning algorithms. We aim at applications in physics and signal processing in which we know that certain operations must be embedded into the algorithm. Any operation that allows computation of a gradient or sub-gradient towards its inputs is suited for our framework. We derive a maximal error bound for deep nets that demonstrates that inclusion of prior knowledge results in its reduction. Furthermore, we also show experimentally that known operators reduce the number of free parameters. We apply this approach to various tasks ranging from CT image reconstruction over vessel segmentation to the derivation of previously unknown imaging algorithms. As such the concept is widely applicable for many researchers in physics, imaging, and signal processing. We assume that our analysis will support further investigation of known operators in other fields of physics, imaging, and signal processing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge