Dennis Possart
CyclePose -- Leveraging Cycle-Consistency for Annotation-Free Nuclei Segmentation in Fluorescence Microscopy
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:In recent years, numerous neural network architectures specifically designed for the instance segmentation of nuclei in microscopic images have been released. These models embed nuclei-specific priors to outperform generic architectures like U-Nets; however, they require large annotated datasets, which are often not available. Generative models (GANs, diffusion models) have been used to compensate for this by synthesizing training data. These two-stage approaches are computationally expensive, as first a generative model and then a segmentation model has to be trained. We propose CyclePose, a hybrid framework integrating synthetic data generation and segmentation training. CyclePose builds on a CycleGAN architecture, which allows unpaired translation between microscopy images and segmentation masks. We embed a segmentation model into CycleGAN and leverage a cycle consistency loss for self-supervision. Without annotated data, CyclePose outperforms other weakly or unsupervised methods on two public datasets. Code is available at https://github.com/jonasutz/CyclePose
DiffRenderGAN: Addressing Training Data Scarcity in Deep Segmentation Networks for Quantitative Nanomaterial Analysis through Differentiable Rendering and Generative Modelling
Feb 13, 2025Abstract:Nanomaterials exhibit distinctive properties governed by parameters such as size, shape, and surface characteristics, which critically influence their applications and interactions across technological, biological, and environmental contexts. Accurate quantification and understanding of these materials are essential for advancing research and innovation. In this regard, deep learning segmentation networks have emerged as powerful tools that enable automated insights and replace subjective methods with precise quantitative analysis. However, their efficacy depends on representative annotated datasets, which are challenging to obtain due to the costly imaging of nanoparticles and the labor-intensive nature of manual annotations. To overcome these limitations, we introduce DiffRenderGAN, a novel generative model designed to produce annotated synthetic data. By integrating a differentiable renderer into a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) framework, DiffRenderGAN optimizes textural rendering parameters to generate realistic, annotated nanoparticle images from non-annotated real microscopy images. This approach reduces the need for manual intervention and enhances segmentation performance compared to existing synthetic data methods by generating diverse and realistic data. Tested on multiple ion and electron microscopy cases, including titanium dioxide (TiO$_2$), silicon dioxide (SiO$_2$)), and silver nanowires (AgNW), DiffRenderGAN bridges the gap between synthetic and real data, advancing the quantification and understanding of complex nanomaterial systems.
Differentiable Score-Based Likelihoods: Learning CT Motion Compensation From Clean Images
Apr 23, 2024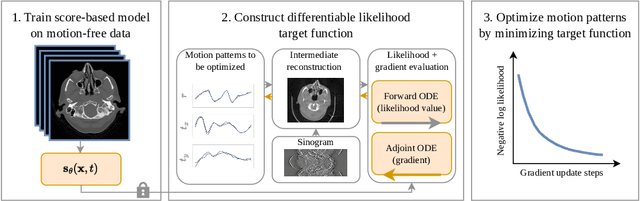
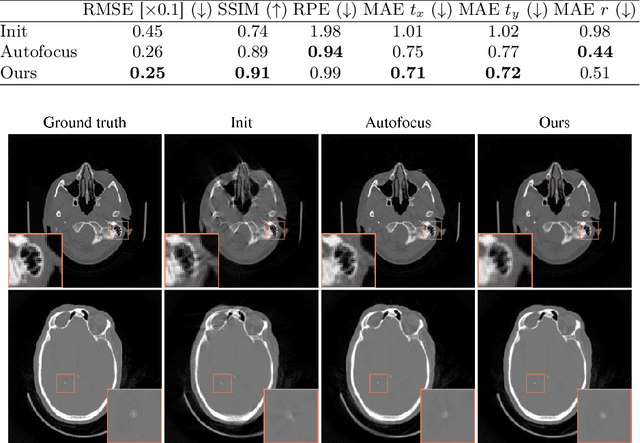
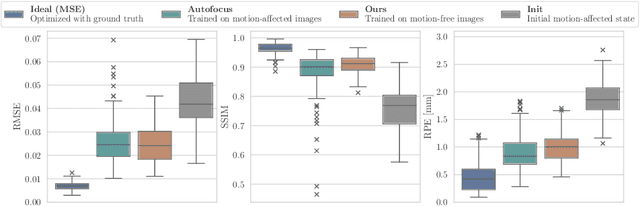
Abstract:Motion artifacts can compromise the diagnostic value of computed tomography (CT) images. Motion correction approaches require a per-scan estimation of patient-specific motion patterns. In this work, we train a score-based model to act as a probability density estimator for clean head CT images. Given the trained model, we quantify the deviation of a given motion-affected CT image from the ideal distribution through likelihood computation. We demonstrate that the likelihood can be utilized as a surrogate metric for motion artifact severity in the CT image facilitating the application of an iterative, gradient-based motion compensation algorithm. By optimizing the underlying motion parameters to maximize likelihood, our method effectively reduces motion artifacts, bringing the image closer to the distribution of motion-free scans. Our approach achieves comparable performance to state-of-the-art methods while eliminating the need for a representative data set of motion-affected samples. This is particularly advantageous in real-world applications, where patient motion patterns may exhibit unforeseen variability, ensuring robustness without implicit assumptions about recoverable motion types.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge