M. Emre Celebi
A Survey on Deep Learning for Skin Lesion Segmentation
Jun 01, 2022



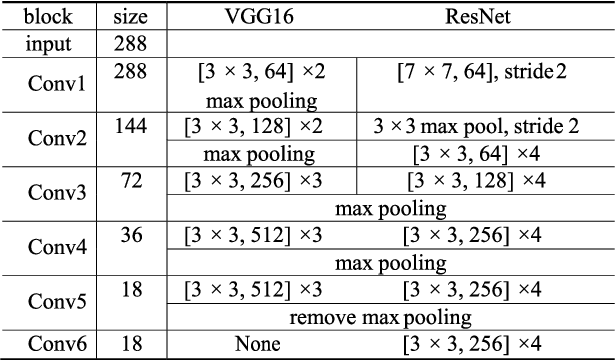
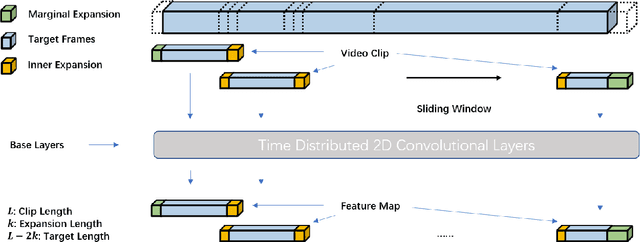
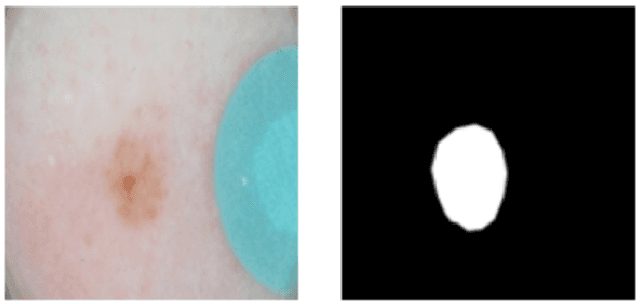
Abstract:Skin cancer is a major public health problem that could benefit from computer-aided diagnosis to reduce the burden of this common disease. Skin lesion segmentation from images is an important step toward achieving this goal. However, the presence of natural and artificial artifacts (e.g., hair and air bubbles), intrinsic factors (e.g., lesion shape and contrast), and variations in image acquisition conditions make skin lesion segmentation a challenging task. Recently, various researchers have explored the applicability of deep learning models to skin lesion segmentation. In this survey, we cross-examine 134 research papers that deal with deep learning based segmentation of skin lesions. We analyze these works along several dimensions, including input data (datasets, preprocessing, and synthetic data generation), model design (architecture, modules, and losses), and evaluation aspects (data annotation requirements and segmentation performance). We discuss these dimensions both from the viewpoint of select seminal works, and from a systematic viewpoint, examining how those choices have influenced current trends, and how their limitations should be addressed. We summarize all examined works in a comprehensive table to facilitate comparisons.
Image Synthesis with Adversarial Networks: a Comprehensive Survey and Case Studies
Dec 26, 2020



Abstract:Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have been extremely successful in various application domains such as computer vision, medicine, and natural language processing. Moreover, transforming an object or person to a desired shape become a well-studied research in the GANs. GANs are powerful models for learning complex distributions to synthesize semantically meaningful samples. However, there is a lack of comprehensive review in this field, especially lack of a collection of GANs loss-variant, evaluation metrics, remedies for diverse image generation, and stable training. Given the current fast GANs development, in this survey, we provide a comprehensive review of adversarial models for image synthesis. We summarize the synthetic image generation methods, and discuss the categories including image-to-image translation, fusion image generation, label-to-image mapping, and text-to-image translation. We organize the literature based on their base models, developed ideas related to architectures, constraints, loss functions, evaluation metrics, and training datasets. We present milestones of adversarial models, review an extensive selection of previous works in various categories, and present insights on the development route from the model-based to data-driven methods. Further, we highlight a range of potential future research directions. One of the unique features of this review is that all software implementations of these GAN methods and datasets have been collected and made available in one place at https://github.com/pshams55/GAN-Case-Study.
Skin Lesion Analysis Toward Melanoma Detection 2018: A Challenge Hosted by the International Skin Imaging Collaboration (ISIC)
Mar 29, 2019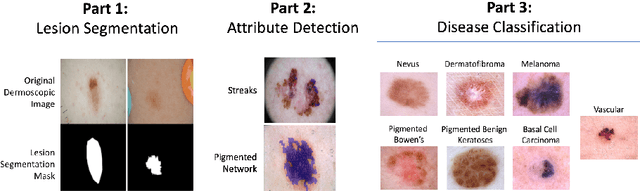
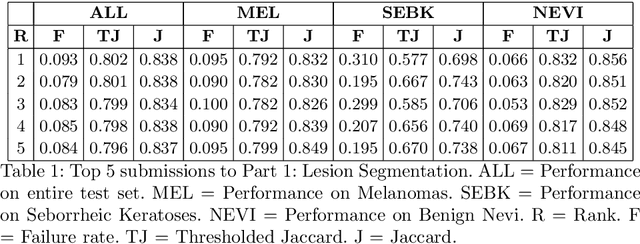
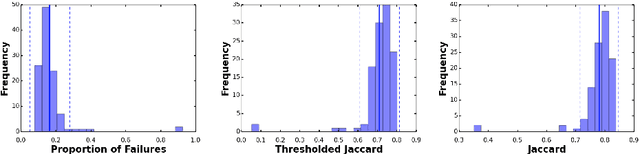
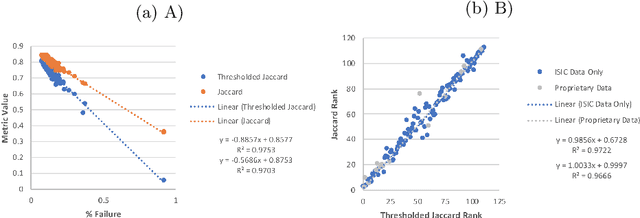
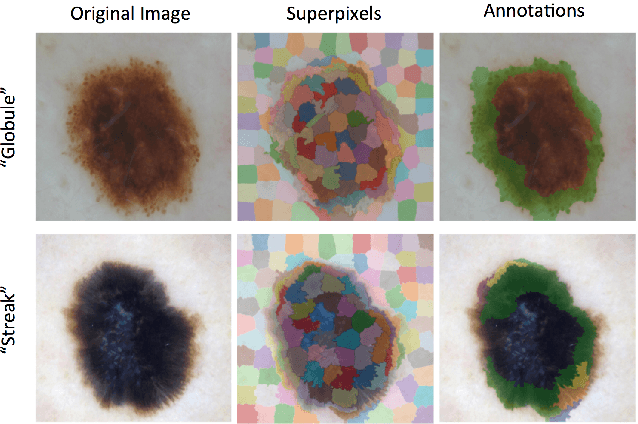
Abstract:This work summarizes the results of the largest skin image analysis challenge in the world, hosted by the International Skin Imaging Collaboration (ISIC), a global partnership that has organized the world's largest public repository of dermoscopic images of skin. The challenge was hosted in 2018 at the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) conference in Granada, Spain. The dataset included over 12,500 images across 3 tasks. 900 users registered for data download, 115 submitted to the lesion segmentation task, 25 submitted to the lesion attribute detection task, and 159 submitted to the disease classification task. Novel evaluation protocols were established, including a new test for segmentation algorithm performance, and a test for algorithm ability to generalize. Results show that top segmentation algorithms still fail on over 10% of images on average, and algorithms with equal performance on test data can have different abilities to generalize. This is an important consideration for agencies regulating the growing set of machine learning tools in the healthcare domain, and sets a new standard for future public challenges in healthcare.
Social Behavioral Phenotyping of Drosophila with a2D-3D Hybrid CNN Framework
Mar 27, 2019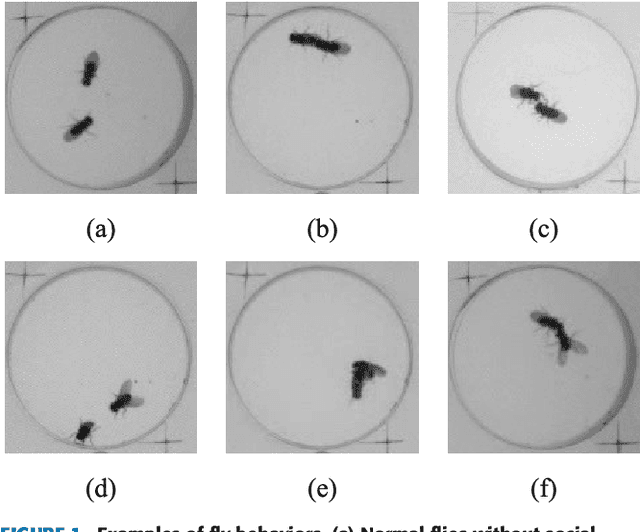

Abstract:Behavioural phenotyping of Drosophila is an important means in biological and medical research to identify genetic, pathologic or psychologic impact on animal behaviour.
Skin Lesion Analysis Toward Melanoma Detection: A Challenge at the 2017 International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging , Hosted by the International Skin Imaging Collaboration
Jan 08, 2018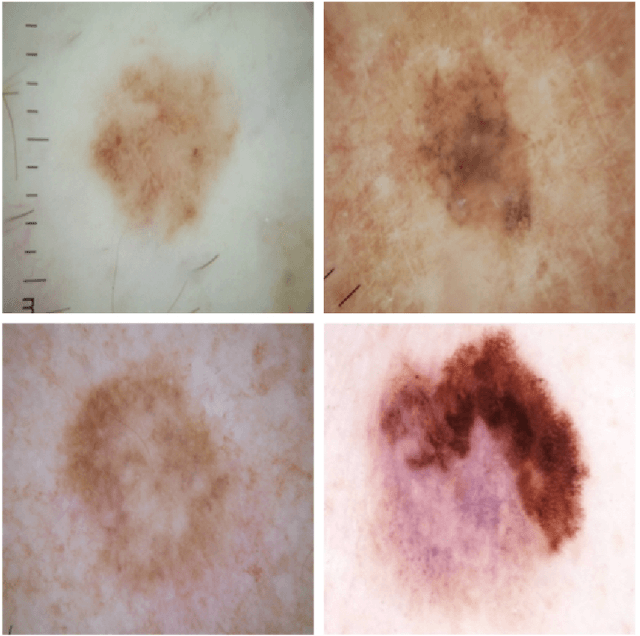

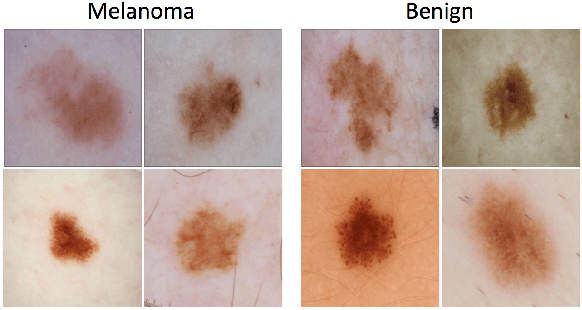
Abstract:This article describes the design, implementation, and results of the latest installment of the dermoscopic image analysis benchmark challenge. The goal is to support research and development of algorithms for automated diagnosis of melanoma, the most lethal skin cancer. The challenge was divided into 3 tasks: lesion segmentation, feature detection, and disease classification. Participation involved 593 registrations, 81 pre-submissions, 46 finalized submissions (including a 4-page manuscript), and approximately 50 attendees, making this the largest standardized and comparative study in this field to date. While the official challenge duration and ranking of participants has concluded, the dataset snapshots remain available for further research and development.
An Overview of Melanoma Detection in Dermoscopy Images Using Image Processing and Machine Learning
Jan 28, 2016


Abstract:The incidence of malignant melanoma continues to increase worldwide. This cancer can strike at any age; it is one of the leading causes of loss of life in young persons. Since this cancer is visible on the skin, it is potentially detectable at a very early stage when it is curable. New developments have converged to make fully automatic early melanoma detection a real possibility. First, the advent of dermoscopy has enabled a dramatic boost in clinical diagnostic ability to the point that melanoma can be detected in the clinic at the very earliest stages. The global adoption of this technology has allowed accumulation of large collections of dermoscopy images of melanomas and benign lesions validated by histopathology. The development of advanced technologies in the areas of image processing and machine learning have given us the ability to allow distinction of malignant melanoma from the many benign mimics that require no biopsy. These new technologies should allow not only earlier detection of melanoma, but also reduction of the large number of needless and costly biopsy procedures. Although some of the new systems reported for these technologies have shown promise in preliminary trials, widespread implementation must await further technical progress in accuracy and reproducibility. In this paper, we provide an overview of computerized detection of melanoma in dermoscopy images. First, we discuss the various aspects of lesion segmentation. Then, we provide a brief overview of clinical feature segmentation. Finally, we discuss the classification stage where machine learning algorithms are applied to the attributes generated from the segmented features to predict the existence of melanoma.
Linear, Deterministic, and Order-Invariant Initialization Methods for the K-Means Clustering Algorithm
Sep 12, 2014



Abstract:Over the past five decades, k-means has become the clustering algorithm of choice in many application domains primarily due to its simplicity, time/space efficiency, and invariance to the ordering of the data points. Unfortunately, the algorithm's sensitivity to the initial selection of the cluster centers remains to be its most serious drawback. Numerous initialization methods have been proposed to address this drawback. Many of these methods, however, have time complexity superlinear in the number of data points, which makes them impractical for large data sets. On the other hand, linear methods are often random and/or sensitive to the ordering of the data points. These methods are generally unreliable in that the quality of their results is unpredictable. Therefore, it is common practice to perform multiple runs of such methods and take the output of the run that produces the best results. Such a practice, however, greatly increases the computational requirements of the otherwise highly efficient k-means algorithm. In this chapter, we investigate the empirical performance of six linear, deterministic (non-random), and order-invariant k-means initialization methods on a large and diverse collection of data sets from the UCI Machine Learning Repository. The results demonstrate that two relatively unknown hierarchical initialization methods due to Su and Dy outperform the remaining four methods with respect to two objective effectiveness criteria. In addition, a recent method due to Erisoglu et al. performs surprisingly poorly.
Lesion Border Detection in Dermoscopy Images Using Ensembles of Thresholding Methods
Dec 26, 2013



Abstract:Dermoscopy is one of the major imaging modalities used in the diagnosis of melanoma and other pigmented skin lesions. Due to the difficulty and subjectivity of human interpretation, automated analysis of dermoscopy images has become an important research area. Border detection is often the first step in this analysis. In many cases, the lesion can be roughly separated from the background skin using a thresholding method applied to the blue channel. However, no single thresholding method appears to be robust enough to successfully handle the wide variety of dermoscopy images encountered in clinical practice. In this paper, we present an automated method for detecting lesion borders in dermoscopy images using ensembles of thresholding methods. Experiments on a difficult set of 90 images demonstrate that the proposed method is robust, fast, and accurate when compared to nine state-of-the-art methods.
* 8 pages, 3 figures, 2 tables. arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:1009.1362
Deterministic Initialization of the K-Means Algorithm Using Hierarchical Clustering
Apr 28, 2013



Abstract:K-means is undoubtedly the most widely used partitional clustering algorithm. Unfortunately, due to its gradient descent nature, this algorithm is highly sensitive to the initial placement of the cluster centers. Numerous initialization methods have been proposed to address this problem. Many of these methods, however, have superlinear complexity in the number of data points, making them impractical for large data sets. On the other hand, linear methods are often random and/or order-sensitive, which renders their results unrepeatable. Recently, Su and Dy proposed two highly successful hierarchical initialization methods named Var-Part and PCA-Part that are not only linear, but also deterministic (non-random) and order-invariant. In this paper, we propose a discriminant analysis based approach that addresses a common deficiency of these two methods. Experiments on a large and diverse collection of data sets from the UCI Machine Learning Repository demonstrate that Var-Part and PCA-Part are highly competitive with one of the best random initialization methods to date, i.e., k-means++, and that the proposed approach significantly improves the performance of both hierarchical methods.
* 23 pages, 3 figures, 10 tables. arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:1209.1960
A Comparative Study of Efficient Initialization Methods for the K-Means Clustering Algorithm
Sep 10, 2012



Abstract:K-means is undoubtedly the most widely used partitional clustering algorithm. Unfortunately, due to its gradient descent nature, this algorithm is highly sensitive to the initial placement of the cluster centers. Numerous initialization methods have been proposed to address this problem. In this paper, we first present an overview of these methods with an emphasis on their computational efficiency. We then compare eight commonly used linear time complexity initialization methods on a large and diverse collection of data sets using various performance criteria. Finally, we analyze the experimental results using non-parametric statistical tests and provide recommendations for practitioners. We demonstrate that popular initialization methods often perform poorly and that there are in fact strong alternatives to these methods.
* 17 pages, 1 figure, 7 tables
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge