Brian Helba
BCN20000: Dermoscopic Lesions in the Wild
Aug 30, 2019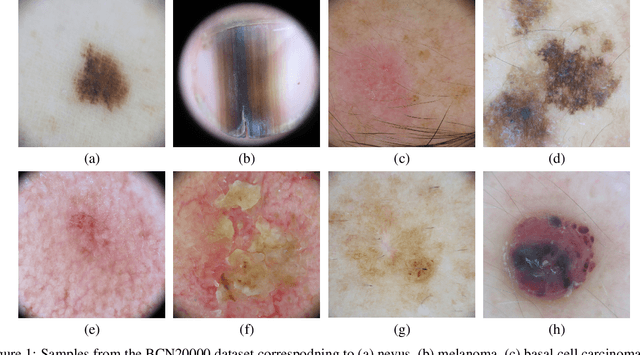
Abstract:This article summarizes the BCN20000 dataset, composed of 19424 dermoscopic images of skin lesions captured from 2010 to 2016 in the facilities of the Hospital Cl\'inic in Barcelona. With this dataset, we aim to study the problem of unconstrained classification of dermoscopic images of skin cancer, including lesions found in hard-to-diagnose locations (nails and mucosa), large lesions which do not fit in the aperture of the dermoscopy device, and hypo-pigmented lesions. The BCN20000 will be provided to the participants of the ISIC Challenge 2019, where they will be asked to train algorithms to classify dermoscopic images of skin cancer automatically.
Skin Lesion Analysis Toward Melanoma Detection 2018: A Challenge Hosted by the International Skin Imaging Collaboration (ISIC)
Mar 29, 2019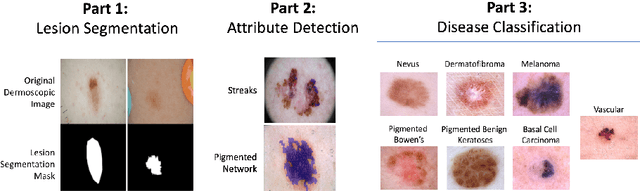
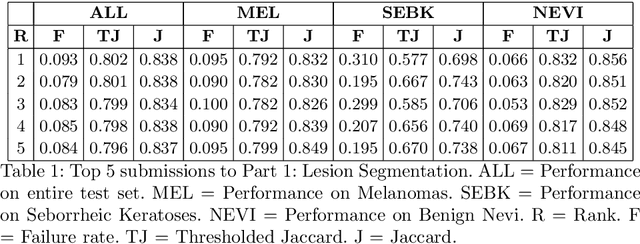
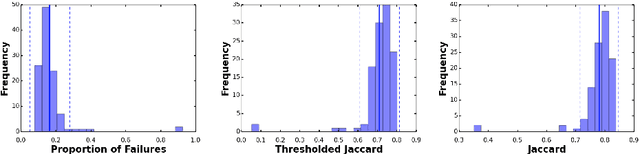
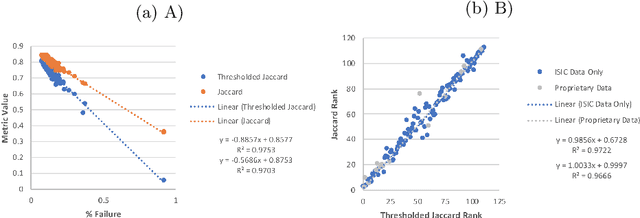
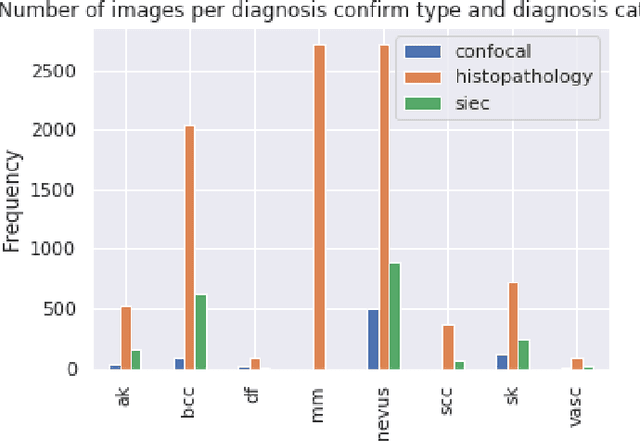
Abstract:This work summarizes the results of the largest skin image analysis challenge in the world, hosted by the International Skin Imaging Collaboration (ISIC), a global partnership that has organized the world's largest public repository of dermoscopic images of skin. The challenge was hosted in 2018 at the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) conference in Granada, Spain. The dataset included over 12,500 images across 3 tasks. 900 users registered for data download, 115 submitted to the lesion segmentation task, 25 submitted to the lesion attribute detection task, and 159 submitted to the disease classification task. Novel evaluation protocols were established, including a new test for segmentation algorithm performance, and a test for algorithm ability to generalize. Results show that top segmentation algorithms still fail on over 10% of images on average, and algorithms with equal performance on test data can have different abilities to generalize. This is an important consideration for agencies regulating the growing set of machine learning tools in the healthcare domain, and sets a new standard for future public challenges in healthcare.
Skin Lesion Analysis Toward Melanoma Detection: A Challenge at the 2017 International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging , Hosted by the International Skin Imaging Collaboration
Jan 08, 2018
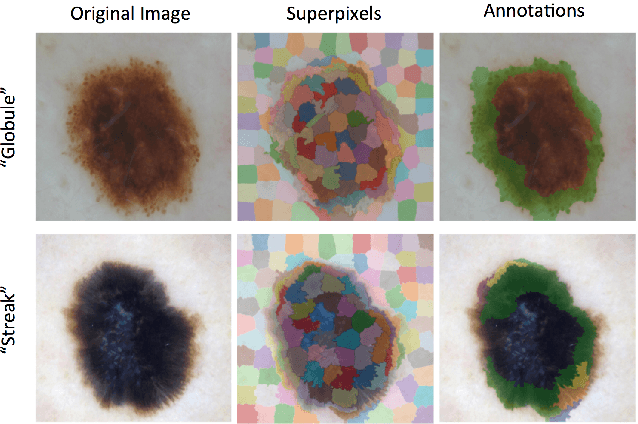
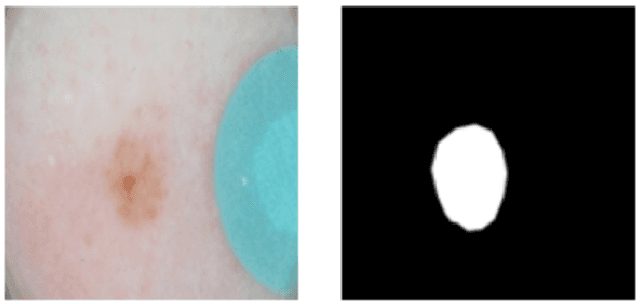

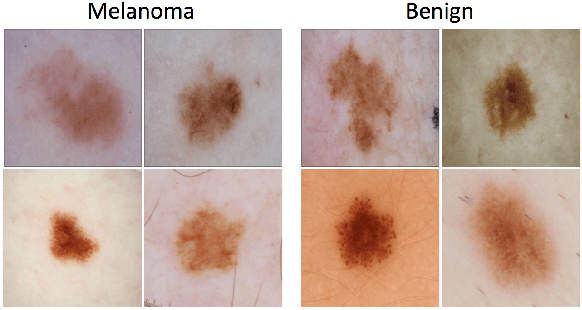
Abstract:This article describes the design, implementation, and results of the latest installment of the dermoscopic image analysis benchmark challenge. The goal is to support research and development of algorithms for automated diagnosis of melanoma, the most lethal skin cancer. The challenge was divided into 3 tasks: lesion segmentation, feature detection, and disease classification. Participation involved 593 registrations, 81 pre-submissions, 46 finalized submissions (including a 4-page manuscript), and approximately 50 attendees, making this the largest standardized and comparative study in this field to date. While the official challenge duration and ranking of participants has concluded, the dataset snapshots remain available for further research and development.
Deep Learning Ensembles for Melanoma Recognition in Dermoscopy Images
Oct 18, 2016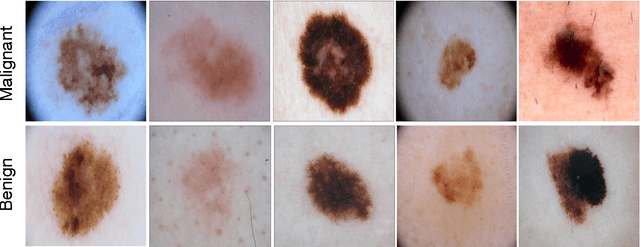

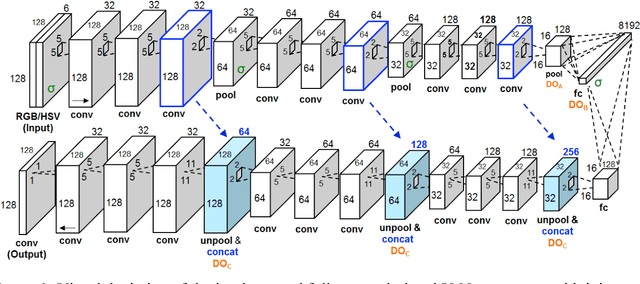
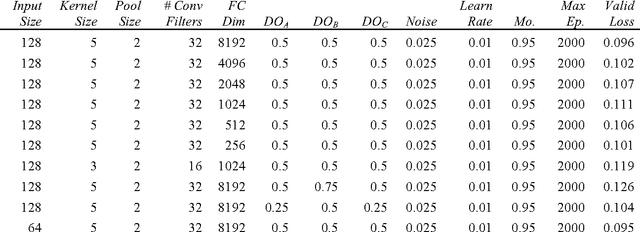
Abstract:Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer. While curable with early detection, only highly trained specialists are capable of accurately recognizing the disease. As expertise is in limited supply, automated systems capable of identifying disease could save lives, reduce unnecessary biopsies, and reduce costs. Toward this goal, we propose a system that combines recent developments in deep learning with established machine learning approaches, creating ensembles of methods that are capable of segmenting skin lesions, as well as analyzing the detected area and surrounding tissue for melanoma detection. The system is evaluated using the largest publicly available benchmark dataset of dermoscopic images, containing 900 training and 379 testing images. New state-of-the-art performance levels are demonstrated, leading to an improvement in the area under receiver operating characteristic curve of 7.5% (0.843 vs. 0.783), in average precision of 4% (0.649 vs. 0.624), and in specificity measured at the clinically relevant 95% sensitivity operating point 2.9 times higher than the previous state-of-the-art (36.8% specificity compared to 12.5%). Compared to the average of 8 expert dermatologists on a subset of 100 test images, the proposed system produces a higher accuracy (76% vs. 70.5%), and specificity (62% vs. 59%) evaluated at an equivalent sensitivity (82%).
* URL for the IBM Journal of Research and Development: http://www.research.ibm.com/journal/
Skin Lesion Analysis toward Melanoma Detection: A Challenge at the International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging 2016, hosted by the International Skin Imaging Collaboration
May 04, 2016



Abstract:In this article, we describe the design and implementation of a publicly accessible dermatology image analysis benchmark challenge. The goal of the challenge is to sup- port research and development of algorithms for automated diagnosis of melanoma, a lethal form of skin cancer, from dermoscopic images. The challenge was divided into sub-challenges for each task involved in image analysis, including lesion segmentation, dermoscopic feature detection within a lesion, and classification of melanoma. Training data included 900 images. A separate test dataset of 379 images was provided to measure resultant performance of systems developed with the training data. Ground truth for both training and test sets was generated by a panel of dermoscopic experts. In total, there were 79 submissions from a group of 38 participants, making this the largest standardized and comparative study for melanoma diagnosis in dermoscopic images to date. While the official challenge duration and ranking of participants has concluded, the datasets remain available for further research and development.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge