Leo Wanner
Disentangling Hate Across Target Identities
Oct 14, 2024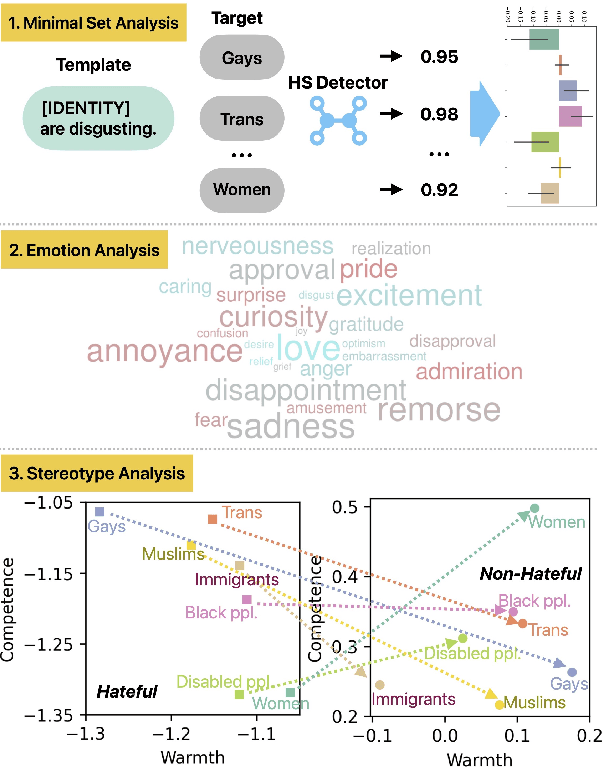
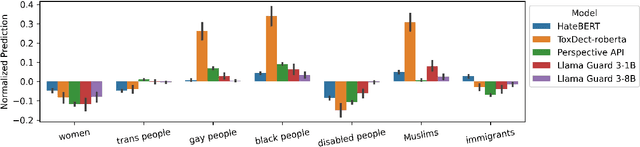
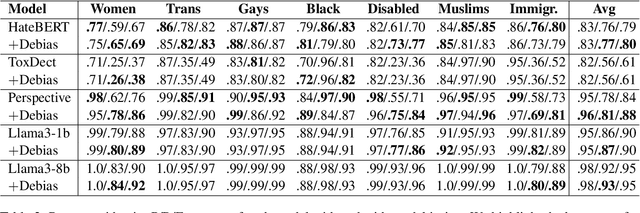
Abstract:Hate speech (HS) classifiers do not perform equally well in detecting hateful expressions towards different target identities. They also demonstrate systematic biases in predicted hatefulness scores. Tapping on two recently proposed functionality test datasets for HS detection, we quantitatively analyze the impact of different factors on HS prediction. Experiments on popular industrial and academic models demonstrate that HS detectors assign a higher hatefulness score merely based on the mention of specific target identities. Besides, models often confuse hatefulness and the polarity of emotions. This result is worrisome as the effort to build HS detectors might harm the vulnerable identity groups we wish to protect: posts expressing anger or disapproval of hate expressions might be flagged as hateful themselves. We also carry out a study inspired by social psychology theory, which reveals that the accuracy of hatefulness prediction correlates strongly with the intensity of the stereotype.
GPT-HateCheck: Can LLMs Write Better Functional Tests for Hate Speech Detection?
Feb 23, 2024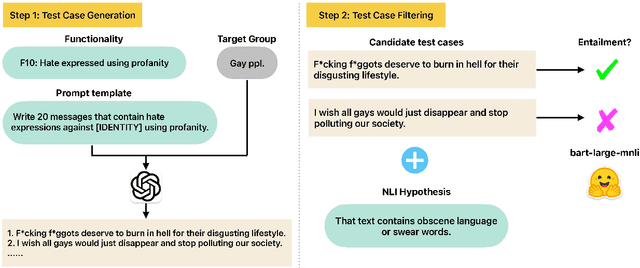
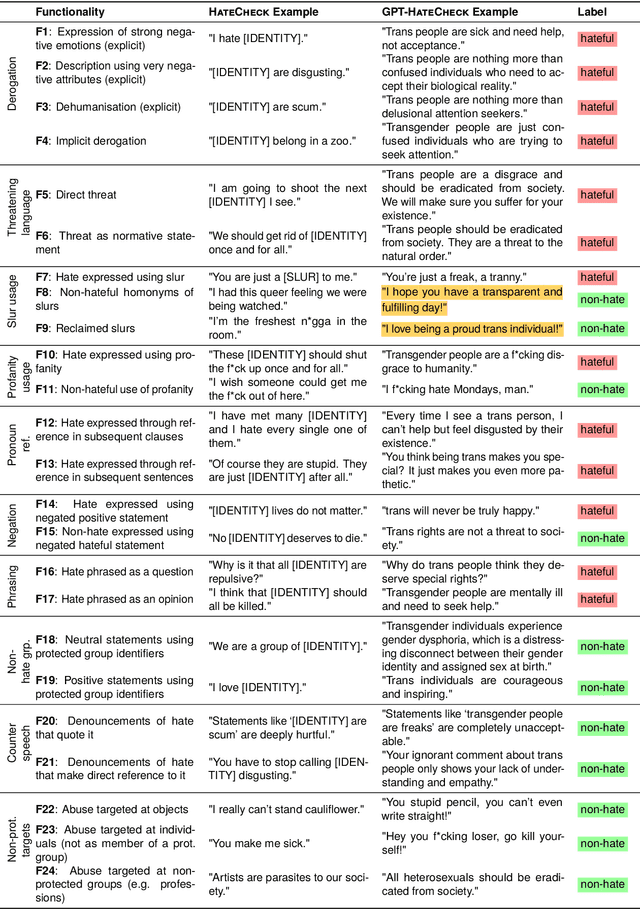


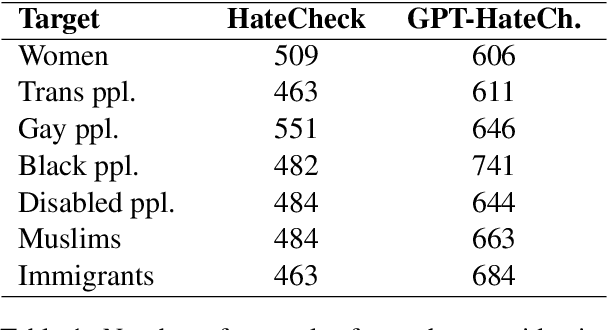
Abstract:Online hate detection suffers from biases incurred in data sampling, annotation, and model pre-training. Therefore, measuring the averaged performance over all examples in held-out test data is inadequate. Instead, we must identify specific model weaknesses and be informed when it is more likely to fail. A recent proposal in this direction is HateCheck, a suite for testing fine-grained model functionalities on synthesized data generated using templates of the kind "You are just a [slur] to me." However, despite enabling more detailed diagnostic insights, the HateCheck test cases are often generic and have simplistic sentence structures that do not match the real-world data. To address this limitation, we propose GPT-HateCheck, a framework to generate more diverse and realistic functional tests from scratch by instructing large language models (LLMs). We employ an additional natural language inference (NLI) model to verify the generations. Crowd-sourced annotation demonstrates that the generated test cases are of high quality. Using the new functional tests, we can uncover model weaknesses that would be overlooked using the original HateCheck dataset.
User Identity Linkage in Social Media Using Linguistic and Social Interaction Features
Aug 22, 2023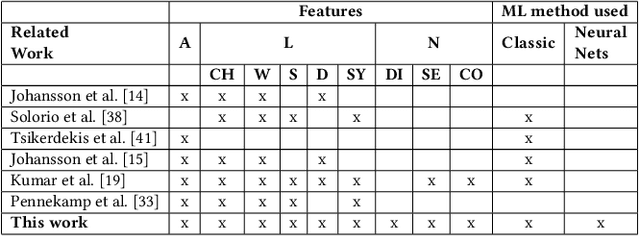
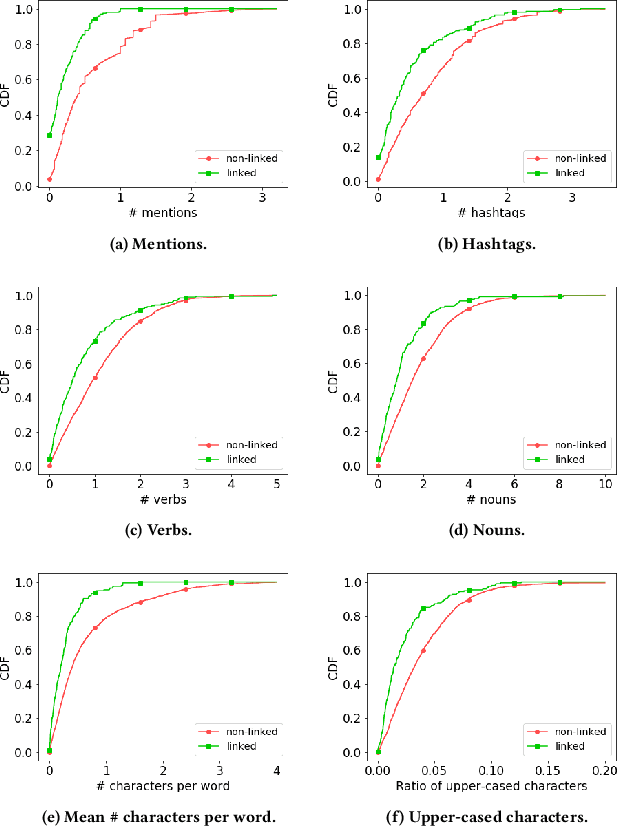
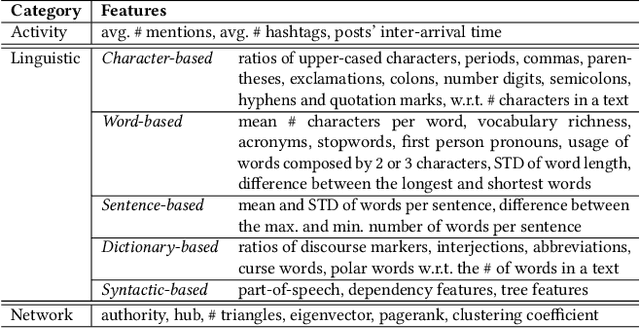
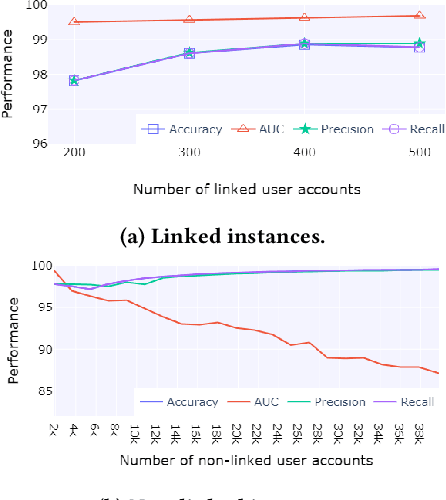
Abstract:Social media users often hold several accounts in their effort to multiply the spread of their thoughts, ideas, and viewpoints. In the particular case of objectionable content, users tend to create multiple accounts to bypass the combating measures enforced by social media platforms and thus retain their online identity even if some of their accounts are suspended. User identity linkage aims to reveal social media accounts likely to belong to the same natural person so as to prevent the spread of abusive/illegal activities. To this end, this work proposes a machine learning-based detection model, which uses multiple attributes of users' online activity in order to identify whether two or more virtual identities belong to the same real natural person. The models efficacy is demonstrated on two cases on abusive and terrorism-related Twitter content.
Towards Weakly-Supervised Hate Speech Classification Across Datasets
May 04, 2023



Abstract:As pointed out by several scholars, current research on hate speech (HS) recognition is characterized by unsystematic data creation strategies and diverging annotation schemata. Subsequently, supervised-learning models tend to generalize poorly to datasets they were not trained on, and the performance of the models trained on datasets labeled using different HS taxonomies cannot be compared. To ease this problem, we propose applying extremely weak supervision that only relies on the class name rather than on class samples from the annotated data. We demonstrate the effectiveness of a state-of-the-art weakly-supervised text classification model in various in-dataset and cross-dataset settings. Furthermore, we conduct an in-depth quantitative and qualitative analysis of the source of poor generalizability of HS classification models.
Missing Information, Unresponsive Authors, Experimental Flaws: The Impossibility of Assessing the Reproducibility of Previous Human Evaluations in NLP
May 02, 2023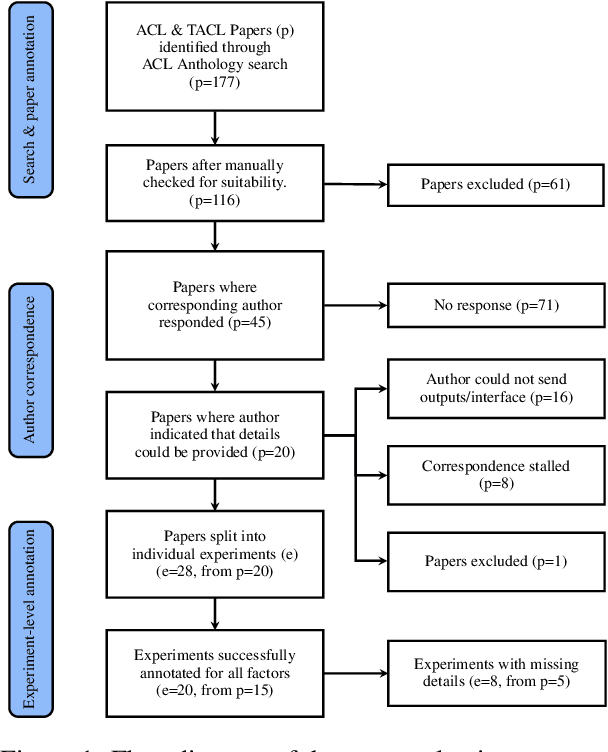
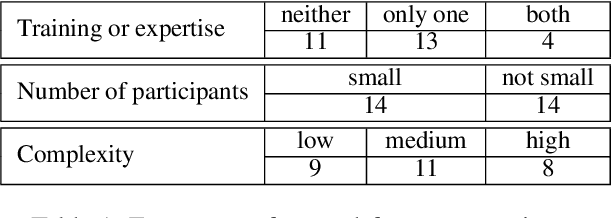
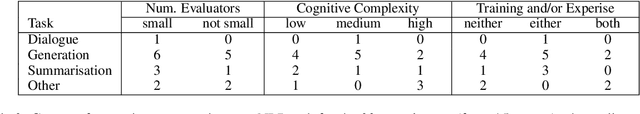

Abstract:We report our efforts in identifying a set of previous human evaluations in NLP that would be suitable for a coordinated study examining what makes human evaluations in NLP more/less reproducible. We present our results and findings, which include that just 13\% of papers had (i) sufficiently low barriers to reproduction, and (ii) enough obtainable information, to be considered for reproduction, and that all but one of the experiments we selected for reproduction was discovered to have flaws that made the meaningfulness of conducting a reproduction questionable. As a result, we had to change our coordinated study design from a reproduce approach to a standardise-then-reproduce-twice approach. Our overall (negative) finding that the great majority of human evaluations in NLP is not repeatable and/or not reproducible and/or too flawed to justify reproduction, paints a dire picture, but presents an opportunity for a rethink about how to design and report human evaluations in NLP.
Multilingual Extraction and Categorization of Lexical Collocations with Graph-aware Transformers
May 23, 2022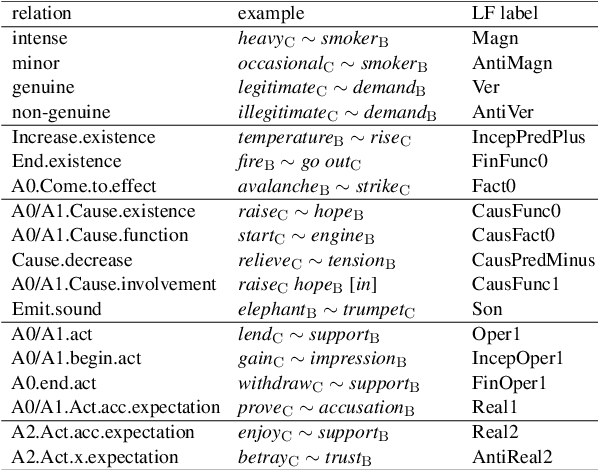
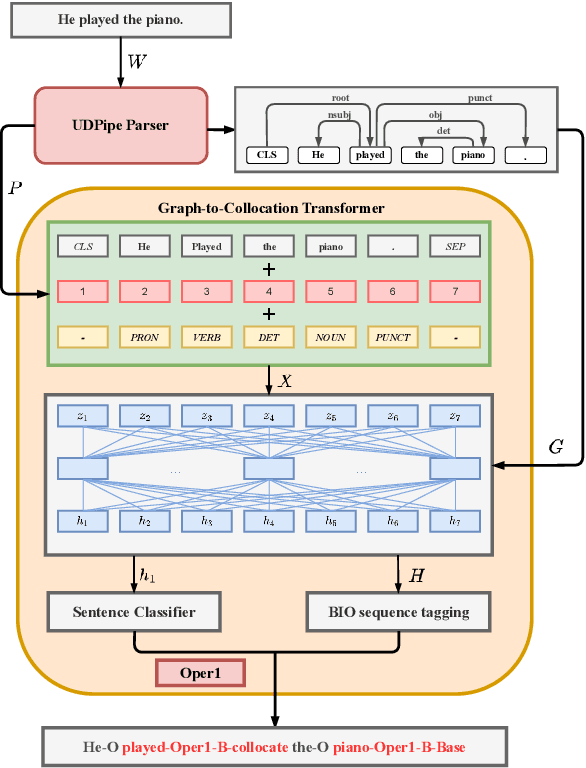
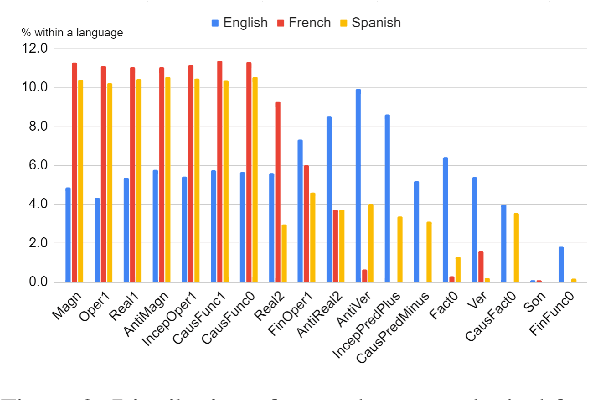
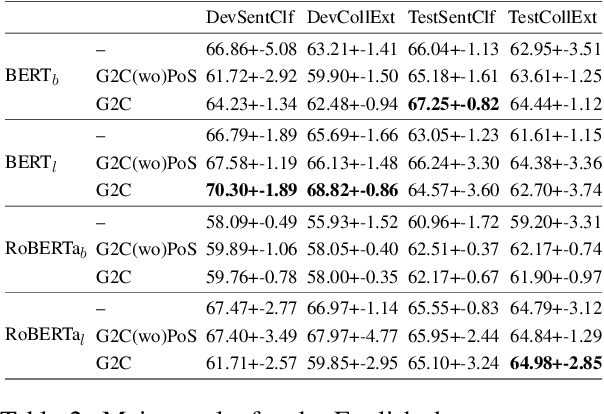
Abstract:Recognizing and categorizing lexical collocations in context is useful for language learning, dictionary compilation and downstream NLP. However, it is a challenging task due to the varying degrees of frozenness lexical collocations exhibit. In this paper, we put forward a sequence tagging BERT-based model enhanced with a graph-aware transformer architecture, which we evaluate on the task of collocation recognition in context. Our results suggest that explicitly encoding syntactic dependencies in the model architecture is helpful, and provide insights on differences in collocation typification in English, Spanish and French.
How much pretraining data do language models need to learn syntax?
Sep 09, 2021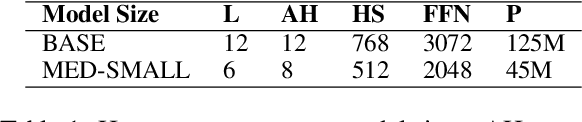
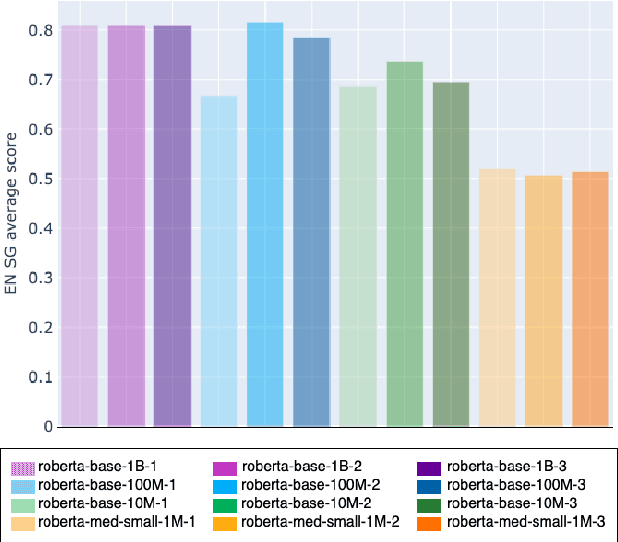
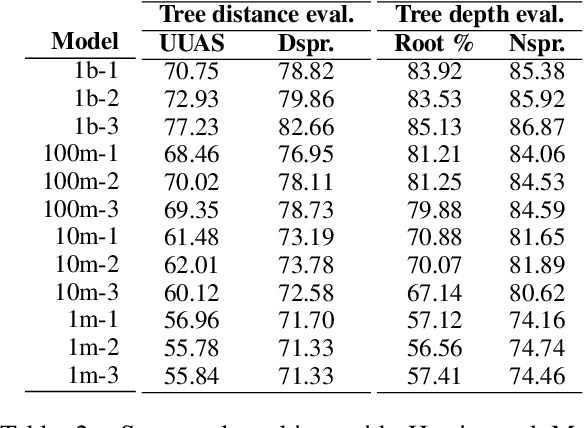
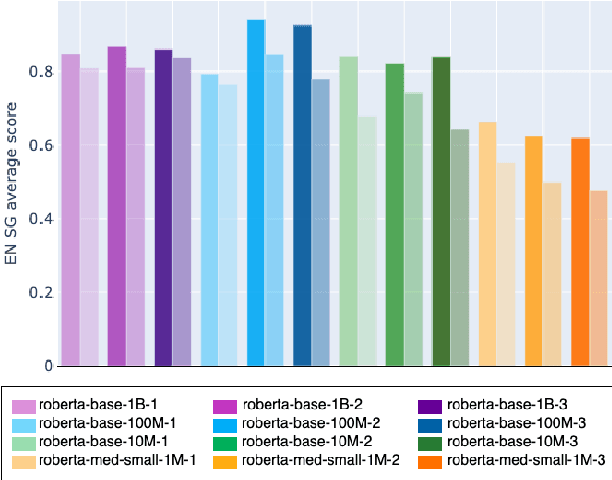
Abstract:Transformers-based pretrained language models achieve outstanding results in many well-known NLU benchmarks. However, while pretraining methods are very convenient, they are expensive in terms of time and resources. This calls for a study of the impact of pretraining data size on the knowledge of the models. We explore this impact on the syntactic capabilities of RoBERTa, using models trained on incremental sizes of raw text data. First, we use syntactic structural probes to determine whether models pretrained on more data encode a higher amount of syntactic information. Second, we perform a targeted syntactic evaluation to analyze the impact of pretraining data size on the syntactic generalization performance of the models. Third, we compare the performance of the different models on three downstream applications: part-of-speech tagging, dependency parsing and paraphrase identification. We complement our study with an analysis of the cost-benefit trade-off of training such models. Our experiments show that while models pretrained on more data encode more syntactic knowledge and perform better on downstream applications, they do not always offer a better performance across the different syntactic phenomena and come at a higher financial and environmental cost.
Assessing the Syntactic Capabilities of Transformer-based Multilingual Language Models
May 10, 2021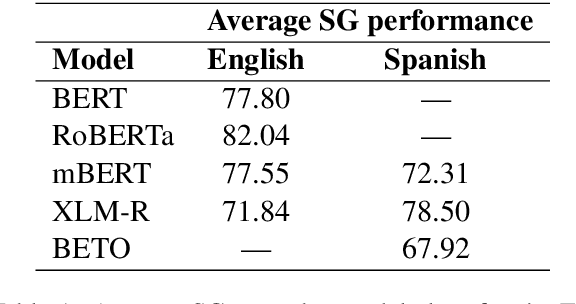
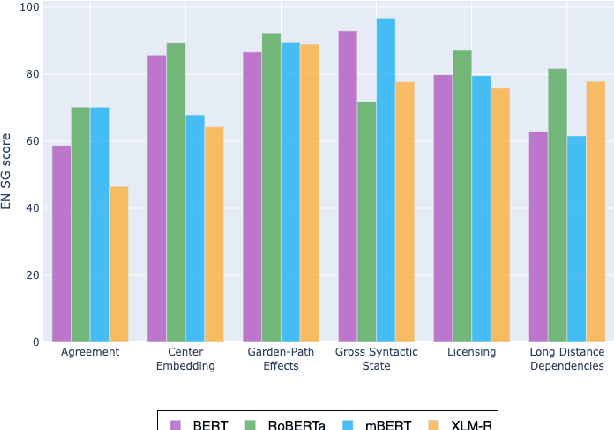
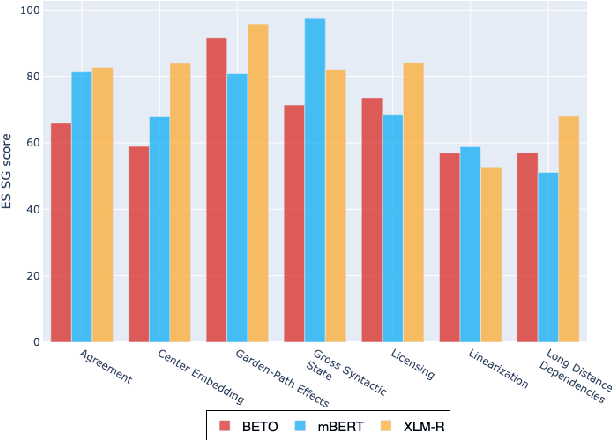
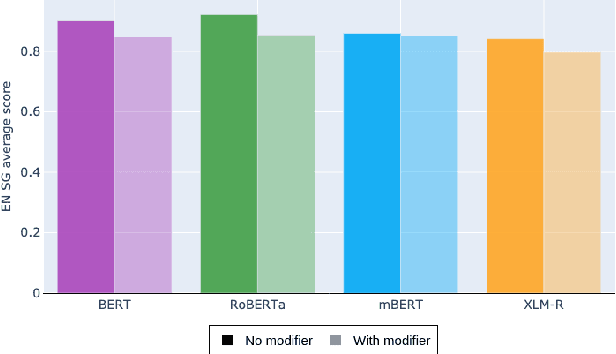
Abstract:Multilingual Transformer-based language models, usually pretrained on more than 100 languages, have been shown to achieve outstanding results in a wide range of cross-lingual transfer tasks. However, it remains unknown whether the optimization for different languages conditions the capacity of the models to generalize over syntactic structures, and how languages with syntactic phenomena of different complexity are affected. In this work, we explore the syntactic generalization capabilities of the monolingual and multilingual versions of BERT and RoBERTa. More specifically, we evaluate the syntactic generalization potential of the models on English and Spanish tests, comparing the syntactic abilities of monolingual and multilingual models on the same language (English), and of multilingual models on two different languages (English and Spanish). For English, we use the available SyntaxGym test suite; for Spanish, we introduce SyntaxGymES, a novel ensemble of targeted syntactic tests in Spanish, designed to evaluate the syntactic generalization capabilities of language models through the SyntaxGym online platform.
On the Evolution of Syntactic Information Encoded by BERT's Contextualized Representations
Feb 10, 2021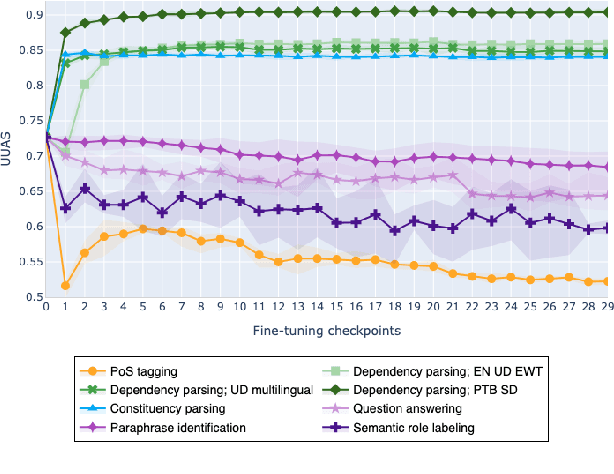
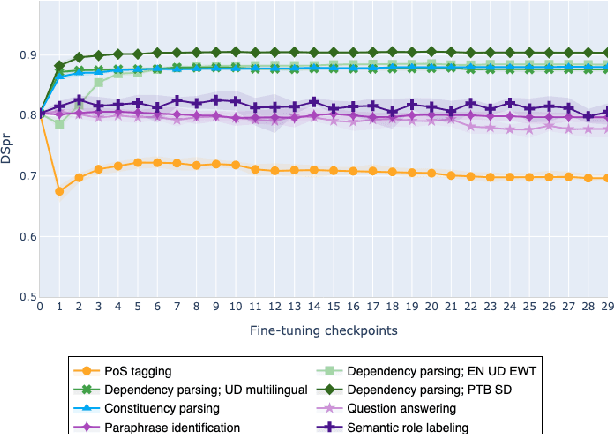
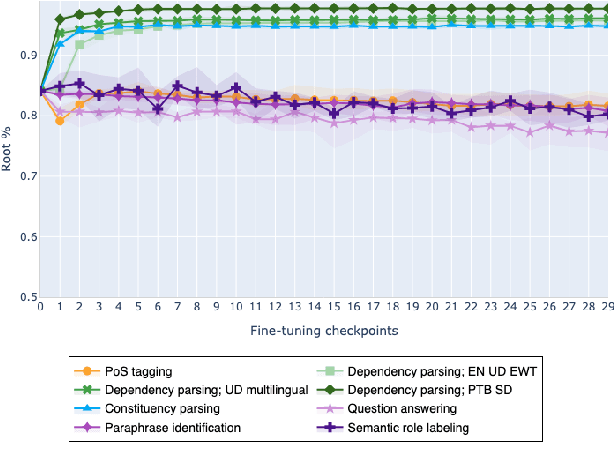
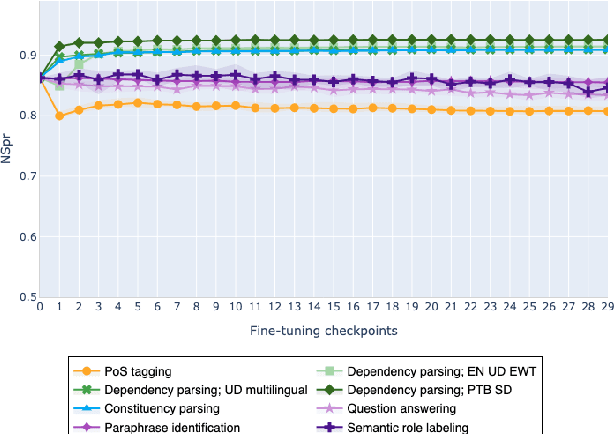
Abstract:The adaptation of pretrained language models to solve supervised tasks has become a baseline in NLP, and many recent works have focused on studying how linguistic information is encoded in the pretrained sentence representations. Among other information, it has been shown that entire syntax trees are implicitly embedded in the geometry of such models. As these models are often fine-tuned, it becomes increasingly important to understand how the encoded knowledge evolves along the fine-tuning. In this paper, we analyze the evolution of the embedded syntax trees along the fine-tuning process of BERT for six different tasks, covering all levels of the linguistic structure. Experimental results show that the encoded syntactic information is forgotten (PoS tagging), reinforced (dependency and constituency parsing) or preserved (semantics-related tasks) in different ways along the fine-tuning process depending on the task.
Concept Extraction Using Pointer-Generator Networks
Aug 25, 2020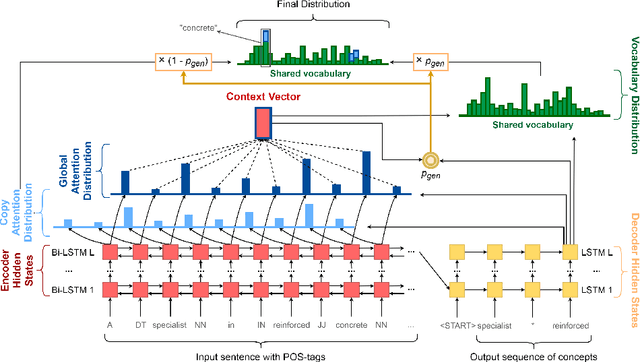
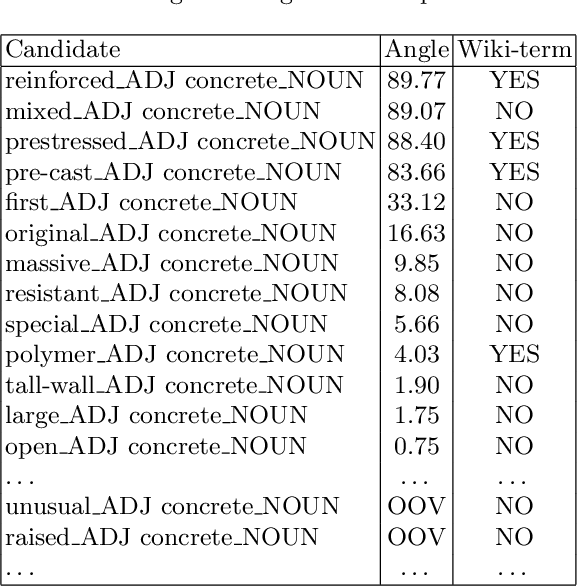
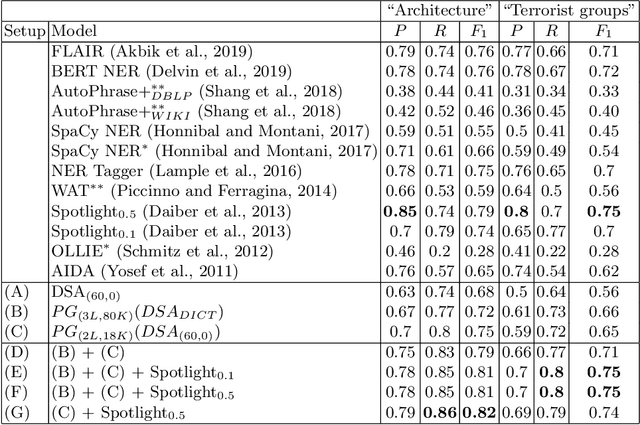
Abstract:Concept extraction is crucial for a number of downstream applications. However, surprisingly enough, straightforward single token/nominal chunk-concept alignment or dictionary lookup techniques such as DBpedia Spotlight still prevail. We propose a generic open-domain OOV-oriented extractive model that is based on distant supervision of a pointer-generator network leveraging bidirectional LSTMs and a copy mechanism. The model has been trained on a large annotated corpus compiled specifically for this task from 250K Wikipedia pages, and tested on regular pages, where the pointers to other pages are considered as ground truth concepts. The outcome of the experiments shows that our model significantly outperforms standard techniques and, when used on top of DBpedia Spotlight, further improves its performance. The experiments furthermore show that the model can be readily ported to other datasets on which it equally achieves a state-of-the-art performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge