Disentangling Hate Across Target Identities
Paper and Code
Oct 14, 2024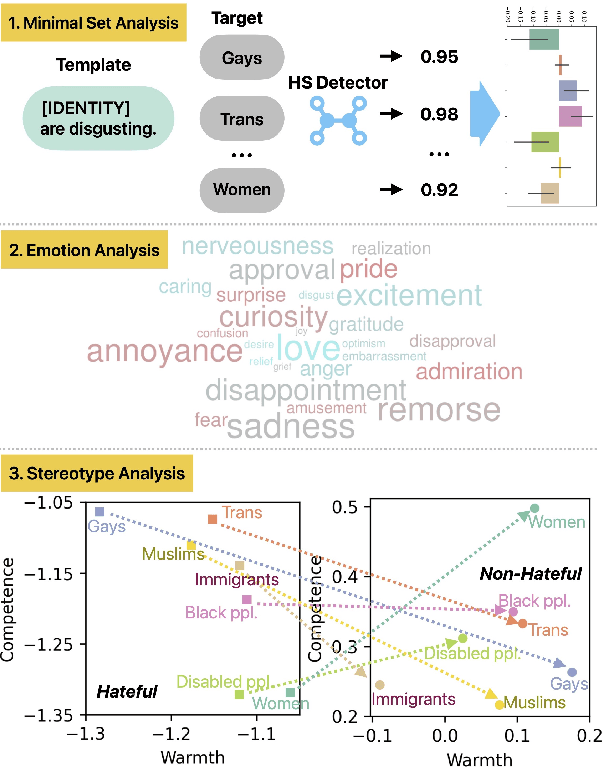
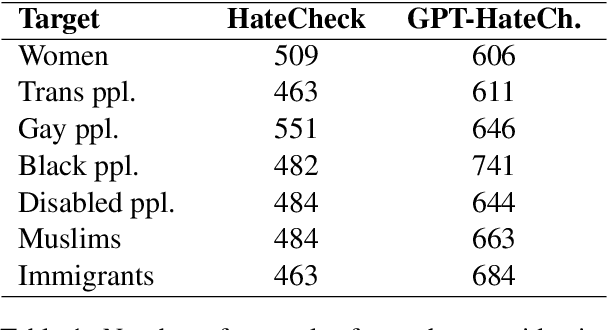
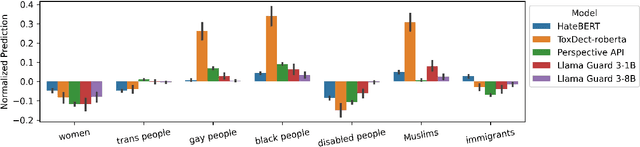
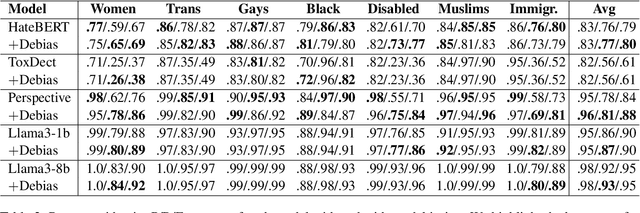
Hate speech (HS) classifiers do not perform equally well in detecting hateful expressions towards different target identities. They also demonstrate systematic biases in predicted hatefulness scores. Tapping on two recently proposed functionality test datasets for HS detection, we quantitatively analyze the impact of different factors on HS prediction. Experiments on popular industrial and academic models demonstrate that HS detectors assign a higher hatefulness score merely based on the mention of specific target identities. Besides, models often confuse hatefulness and the polarity of emotions. This result is worrisome as the effort to build HS detectors might harm the vulnerable identity groups we wish to protect: posts expressing anger or disapproval of hate expressions might be flagged as hateful themselves. We also carry out a study inspired by social psychology theory, which reveals that the accuracy of hatefulness prediction correlates strongly with the intensity of the stereotype.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge